Understanding Drive Designations on Your Computer
In operating systems like Windows, storage devices are assigned letters for easy identification and access. This system allows the operating system and users to differentiate between various storage locations. The drive letter assignment often follows the order in which drives are installed in the computer. However, the user can sometimes configure the assignment during the operating system setup. This means the sequence can be influenced by the user’s choices during the initial system configuration.
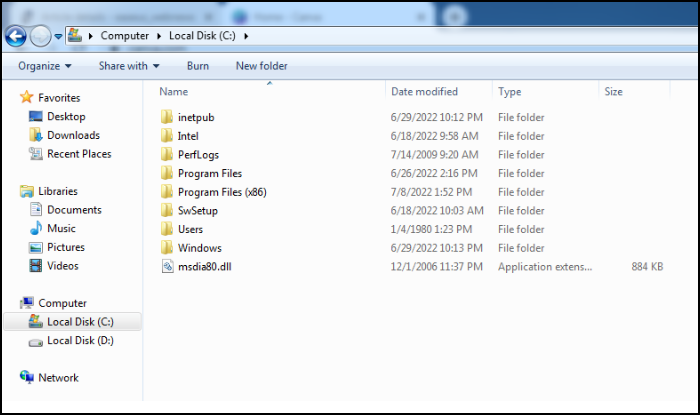
The “C” drive is typically reserved for the primary hard drive, which houses the operating system, system files, and applications necessary for the computer to function. Other drive letters, such as “D,” “E,” and so on, are then assigned to additional storage devices. What is D drive in computer usually represents? Other hard drive partitions, optical drives (like CD or DVD drives), or even external storage devices connected via USB. Understanding this system of drive designations is fundamental to managing files and storage effectively. The system allows users to navigate and organize their data.
The specific purpose and content of drives beyond the “C” drive can vary significantly from one computer to another, based on user preference and system configuration. A “D” drive might be a partition of the primary hard drive. It can also be a completely separate physical drive. Sometimes it’s even a removable drive. The drive’s function is determined by how the user sets up their system and what they choose to store on each drive. Considering what is d drive in computer, its utilization depends on the user’s specific needs and how they choose to manage their digital content. This flexibility allows for customized storage solutions, where users can dedicate specific drives to particular types of data or applications.
Demystifying the Functionality of the D Drive
The D drive’s purpose on a computer system is varied and depends significantly on how the user has configured their machine. Understanding “what is d drive in computer” requires acknowledging its role as a secondary storage location. Typically, the D drive represents a separate partition on the primary hard drive or a physically distinct storage device. It could be a second hard disk drive, a solid-state drive (SSD), an optical drive used for CDs and DVDs, or even an external USB drive. The operating system recognizes each of these storage mediums as a separate drive, assigning it a unique letter.
In many standard configurations, the C drive is reserved for the operating system and core program files. This leaves the D drive available for various other purposes. One common use is to store applications and program files separate from the operating system. This separation offers organizational benefits and can potentially streamline system performance. By keeping the operating system on a dedicated drive, you reduce the risk of fragmentation and improve overall responsiveness. Furthermore, users frequently utilize the D drive for storing data files such as documents, images, videos, and music. Creating this distinction between system files and personal data adds an extra layer of organization and simplifies backup procedures.
Another vital function of the D drive is to serve as a location for system backups or disk images. Creating a backup on a separate drive ensures data security in case of a system failure or drive corruption affecting the C drive. Moreover, game installations are often directed to the D drive, freeing up space on the primary drive and potentially improving game loading times, particularly if the D drive is an SSD. Therefore, answering “what is d drive in computer” boils down to recognizing its flexibility. It’s a versatile storage space adaptable to the user’s needs, allowing for better file organization, enhanced system performance, and robust data protection strategies. The “what is d drive in computer” definition, thus, is strongly linked to user customization and storage management practices.
How to Locate and Access the D Drive on Your System
Accessing the D drive on a Windows system is a straightforward process. This section details how to locate and access the D drive, allowing users to manage their files and understand their computer’s storage configuration. Understanding “what is d drive in computer” helps users navigate their system effectively.
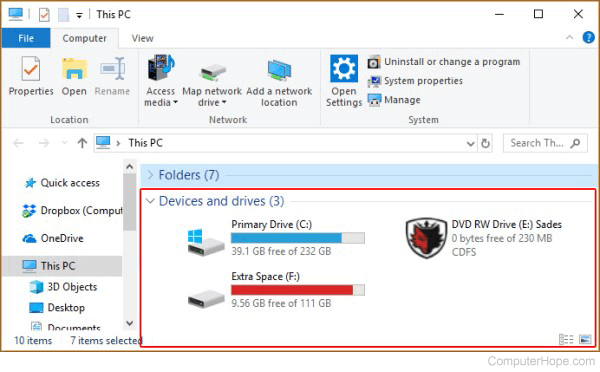
To find the D drive, begin by opening File Explorer. This can be done by clicking the File Explorer icon on the taskbar or by searching for “File Explorer” in the Windows search bar. Once File Explorer is open, look for “This PC” or “My Computer” in the left-hand navigation pane. Clicking on “This PC” will display all the drives connected to your computer, including the C drive (typically the main system drive) and any other drives, such as the D drive. The D drive will be listed with its corresponding label, if one has been assigned. If the D drive is a CD/DVD drive, it will appear when a disc is inserted. If the D drive does not show up, it may not be properly connected or recognized by the system. Further troubleshooting steps will be needed in that case. “What is d drive in computer” becomes a critical question when the drive is not readily visible.
Once the D drive is located, accessing its contents is as simple as double-clicking its icon in File Explorer. This will open the D drive, displaying all the folders and files stored within. From there, users can browse, copy, move, delete, and manage their data as needed. Right-clicking the D drive icon provides additional options such as formatting the drive (exercise caution when using this option), creating a shortcut, or viewing its properties, which include information such as used and free space. While the process is primarily focused on Windows, other operating systems have similar methods for accessing secondary drives. Knowing “what is d drive in computer” and how to access it allows for efficient file management and optimal system performance.
Common Uses for the D Drive on a PC
The D drive in a computer serves a multitude of purposes, enhancing both organization and system performance. Understanding “what is d drive in computer” is crucial for effective storage management. Often, it acts as a repository for applications, keeping them separate from the operating system on the C drive.
Data files, including documents, photos, and videos, frequently find a home on the D drive. Storing these files separately offers several advantages. Firstly, it simplifies backups. A user can back up the D drive without including system files, saving time and space. Secondly, it aids in organization. Keeping personal files separate from system files creates a cleaner, more manageable file structure. Thirdly, in the event of an operating system failure, data on the D drive remains safe, reducing the risk of data loss. Many users choose the D drive as the primary location for their backups, providing an extra layer of security against unforeseen circumstances. When considering “what is d drive in computer”, think of it as a versatile space for storing everything beyond essential system files.
Another common use for the D drive is for game installations. Modern games often consume significant storage space, and installing them on a separate drive can prevent the C drive from becoming cluttered. This can also potentially improve game loading times, especially if the D drive is a solid-state drive (SSD). Furthermore, using the D drive for applications and data isolates these files from the operating system. This separation can improve system stability and responsiveness, as the operating system has more dedicated resources. Essentially, “what is d drive in computer” often translates to a dedicated space for enhancing both the user experience and the overall performance of the computer.
Troubleshooting: What to Do If Your D Drive Is Missing
Encountering a missing D drive can be a frustrating experience. Several reasons can cause the D drive to disappear from your Windows Explorer view. Understanding these potential causes is the first step toward resolving the issue. This section addresses the common reasons why your D drive might be missing and provides troubleshooting steps to restore its visibility and functionality. For users wondering “what is d drive in computer” when it’s not visible, it is essential to determine the root cause.
One of the most common reasons for a missing D drive is a loose or disconnected drive. This is particularly relevant for external hard drives or if you’ve recently made hardware changes inside your computer. Check the physical connections of the drive to ensure they are securely plugged into both the computer and the drive itself. Another possibility is that the drive is not properly partitioned or formatted. In this case, the drive might be recognized by the system but not assigned a drive letter. This often happens with new drives that haven’t been initialized. Driver issues can also lead to the D drive not being recognized. Outdated, corrupted, or incompatible drivers can prevent the operating system from communicating with the drive. Finally, a less common but still possible cause is a drive letter conflict. If another device is using the letter D, the system might not display the D drive correctly. Determining “what is d drive in computer” is linked to its proper recognition by the system. It can also mean the disk is failing and needs replacing soon.
Several solutions can help restore a missing D drive. First, check all physical connections, ensuring the drive is securely connected. Next, access Disk Management (search for “Disk Management” in the Windows search bar). Look for the drive in the list of disks. If it’s listed but without a drive letter, right-click on it and select “Change Drive Letter and Paths” to assign the letter D. If the drive appears as unallocated space, you’ll need to create a new partition and format it. Be extremely cautious when doing this, as it will erase any existing data on the drive (if any). If you suspect a driver issue, update or reinstall the drivers for the drive. You can usually find the latest drivers on the manufacturer’s website. If there’s a drive letter conflict, use Disk Management to change the drive letter of the conflicting device or the D drive itself (if possible). Important Disclaimer: Before attempting any of these fixes, back up any important data on the drive if possible. Data loss can occur during troubleshooting, especially when dealing with partitions and formatting. Seeking assistance from a qualified technician is always a good option if you’re uncomfortable performing these steps yourself. Taking precautionary actions is key to ensuring “what is d drive in computer” remains accessible and protected.
Customizing Your Storage: Changing a Drive Letter
The ability to change a drive letter offers a degree of customization for your computer’s storage. While the operating system automatically assigns drive letters, users can reassign them. This re-designation is particularly useful in scenarios where a preference for a specific letter exists. It can also help resolve conflicts, or simply for organizational purposes. Understanding what is d drive in computer helps to better organize your data. For example, a user might prefer to have their external hard drive consistently assigned to a specific letter like “E” or “F,” regardless of the order in which devices are connected.
Changing drive letters is accomplished through the Disk Management tool in Windows. This tool provides a graphical interface for managing drives and partitions. To change a drive letter, you must first access Disk Management. You can access it by searching for “Disk Management” in the Windows search bar. Right-clicking on the desired drive within Disk Management will bring up a context menu. Select the “Change Drive Letter and Paths” option. From there, you can assign a new letter to the selected drive. What is d drive in computer if not a common letter, is still important. The process may slightly differ on other operating systems, but the core principle remains the same: utilizing a system utility to reassign the desired letter.
While changing drive letters can be helpful, it’s crucial to exercise caution. Incorrectly reassigning drive letters can lead to applications failing to locate their associated files. This could result in program malfunctions. Before making any changes, ensure you understand the potential consequences. It’s also wise to back up important data. In general, only change drive letters if necessary to avoid potential problems. Consider the implications of changing the “D” drive assignment, especially if programs or shortcuts are configured to access resources on what is d drive in computer. A callout box displaying: “Caution: Changing drive letters can cause applications to fail. Proceed with caution and only if necessary,” would be highly recommended to alert users of the potential risks involved.
SSD vs. HDD: Understanding the Impact on Your D Drive Performance
The type of drive used for the D drive significantly impacts its performance. Understanding the differences between Solid State Drives (SSDs) and Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) is crucial when considering “what is d drive in computer” and how it functions within your system. SSDs and HDDs differ vastly in how they store and retrieve data, which directly affects speed and overall system responsiveness.
SSDs utilize flash memory to store data, offering significantly faster read and write speeds compared to HDDs. This translates to quicker application loading times, faster file transfers, and an overall more responsive computing experience when the D drive, “what is d drive in computer”, houses applications or frequently accessed data. An SSD-based D drive excels in scenarios demanding speed and responsiveness. The inherent technology allows data to be accessed almost instantaneously. HDDs, on the other hand, store data on spinning magnetic platters. Retrieving data requires the drive to physically move the read/write head to the correct location on the platter, a process that is considerably slower than the electronic data access of an SSD. The difference in speed is noticeable, especially when launching large applications or accessing numerous files. While using the D drive, “what is d drive in computer”, on an HDD is a viable option, it doesn’t offer the same performance benefits.
While SSDs offer superior performance, HDDs typically provide more storage capacity at a lower cost per gigabyte. Price, availability, and storage requirements are important factors. Consumers decide for one or the other based on those needs. A large HDD as a D drive, “what is d drive in computer”, is suitable for storing large media libraries or backups where speed is not the primary concern. SSDs are frequently more expensive for the same storage capacity. This makes them a premium option for users who prioritize performance above all else. Considering budget constraints and specific usage scenarios ensures choosing the optimal type of drive for your D drive. This decision impacts overall system performance and user experience, regarding “what is d drive in computer” means for individual needs.
Optimizing Your D Drive for Maximum Efficiency
Maintaining the health and performance of your D drive is crucial for a smooth computing experience. Several strategies can be implemented to ensure the drive operates efficiently over time. Understanding “what is d drive in computer” and how it functions is the first step toward optimization. The following tips are designed to help users maximize the potential of their D drive, whether it’s a traditional HDD or a faster SSD.
For traditional Hard Disk Drives (HDDs), defragmentation is a key maintenance task. Over time, files become fragmented, meaning parts of a single file are stored in different locations on the drive. This fragmentation slows down read and write speeds. Defragmenting the drive rearranges these file fragments, placing them closer together for faster access. Windows includes a built-in defragmentation tool that can be scheduled to run automatically. Solid State Drives (SSDs), however, should not be defragmented. Defragmenting an SSD can reduce its lifespan due to the way SSDs store data. Instead, ensure that TRIM is enabled, which automatically optimizes SSD performance. Another important aspect of D drive optimization is removing unnecessary files. Regularly clearing the Recycle Bin, deleting temporary files, and uninstalling unused programs can free up valuable space and improve performance. Windows’ Disk Cleanup tool can help automate this process, identifying and removing various types of unnecessary files.
Effective file management also plays a significant role in D drive optimization. Organizing files into folders and using descriptive names makes it easier to find what you need and reduces the time the system spends searching for files. Regularly backing up important data from the D drive to another location is also recommended. This protects against data loss in case of drive failure or other unforeseen events. Consider using cloud storage or an external hard drive for backups. Regularly scanning the D drive for malware is important. Malware can consume system resources and slow down performance. Using a reputable antivirus program and keeping it up-to-date can help protect against these threats. By following these optimization tips, users can ensure that their D drive operates at its best, providing reliable storage and contributing to a faster and more responsive computing experience. Knowing “what is d drive in computer” and its optimal performance parameters allows for better system management. Optimizing “what is d drive in computer” contributes to a better understanding of overall computer health.