Understanding Bike Crank Sizes: An Overview
Bike crank sizes play a crucial role in cycling, significantly impacting pedaling efficiency, power transfer, and rider comfort. The crank length, a key component of the bike’s drivetrain, connects the pedals to the bike and varies in length between models and riders. A bike crank size chart serves as an essential reference for cyclists, helping them make informed decisions about their equipment and optimizing their performance on the road or trail.
Relevance of Body Measurements: Factors to Consider
A cyclist’s body measurements, such as height, inseam length, and riding style, significantly influence the choice of bike crank size. For instance, taller riders typically require longer crank arms to achieve optimal pedaling efficiency and power transfer, while shorter riders benefit from shorter crank arms. Inseam length, a measurement of the distance from the groin to the ankle, also plays a critical role in determining the ideal crank length. Riders with longer inseams generally require longer crank arms, and vice versa. Additionally, different cycling disciplines, such as road, mountain, or track cycling, may necessitate specific crank size adjustments to accommodate varying riding styles and terrains.
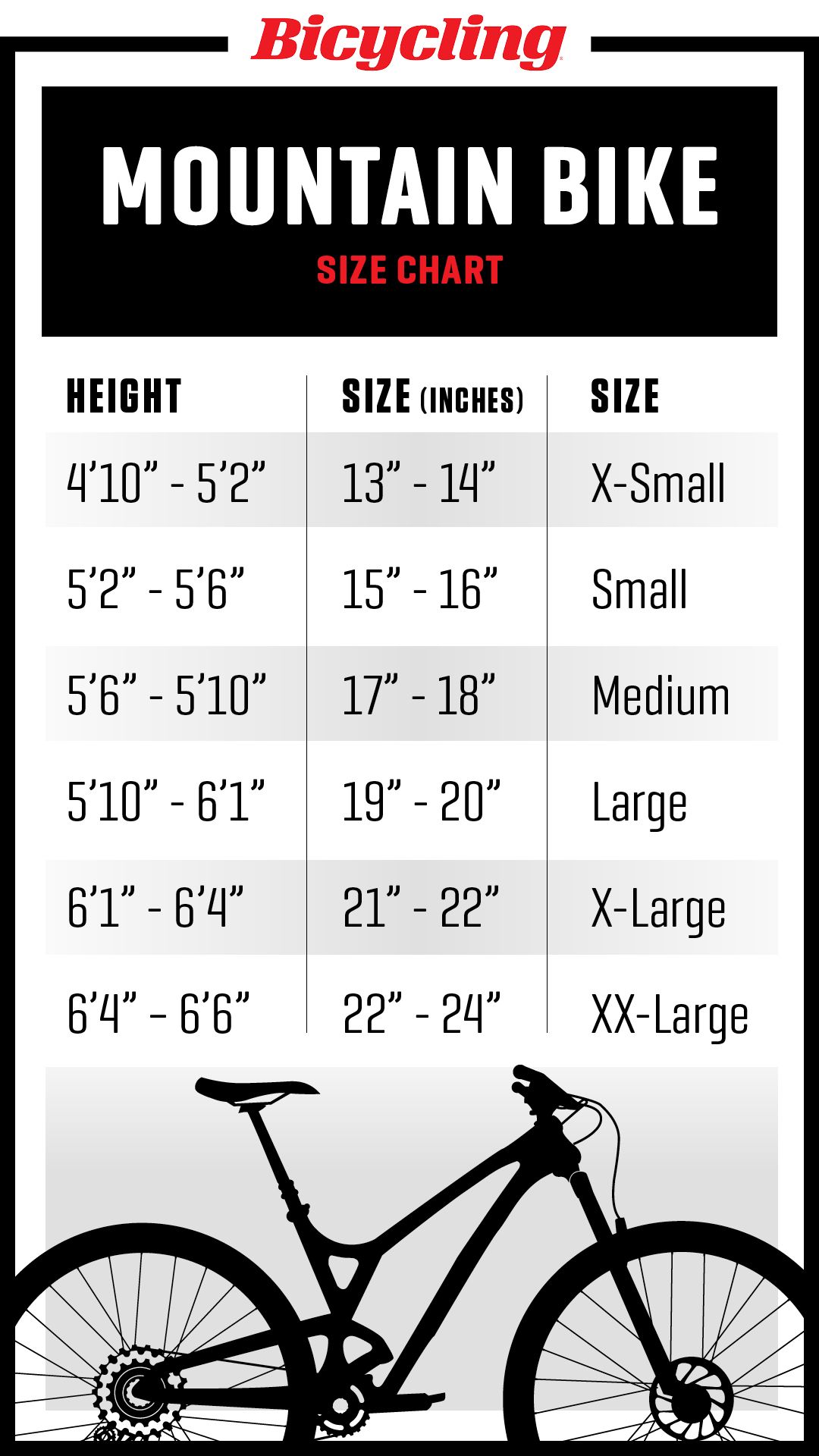
Standard Bike Crank Sizes: A General Overview
Bike crank sizes typically range from 165 to 180 millimeters, with the most common lengths being 170, 172.5, and 175 millimeters. Shorter crank arms, such as 165 or 170 millimeters, are often recommended for smaller riders, cyclocross, and mountain biking, as they allow for better maneuverability and quicker pedal strokes. Longer crank arms, like 175 or 180 millimeters, are more suitable for taller riders and road cycling, as they provide increased leverage and power output.
The following chart outlines standard bike crank sizes and their corresponding applications:
| Crank Length (mm) | Recommended For |
|---|---|
| 165 | Small riders, cyclocross, and mountain biking |
| 170 | Average-sized riders, all-around use |
| 172.5 | Taller-than-average riders, road cycling |
| 175 | Very tall riders, road cycling and track cycling |
| 180 | Exceptionally tall riders, track cycling |
Popular brands and models offering a variety of bike crank sizes include Shimano, SRAM, and Campagnolo, among others. These manufacturers cater to a wide range of cycling disciplines and rider preferences, ensuring that cyclists can find the perfect bike crank size for their needs.
Selecting the Ideal Bike Crank Size: A Step-by-Step Guide
Choosing the right bike crank size is crucial for optimizing pedaling efficiency, power transfer, and comfort. To determine the ideal bike crank size, follow these steps:
-
Assess your body measurements: Measure your height, inseam length, and riding style to establish a baseline for selecting the appropriate crank length. Taller riders and those with longer inseams typically require longer crank arms, while shorter riders and those with shorter inseams benefit from shorter crank arms.
-
Consider your cycling discipline: Different cycling disciplines have specific crank length recommendations. For example, cyclocross and mountain biking often utilize shorter crank arms for better maneuverability and quicker pedal strokes, while road cycling and track cycling typically employ longer crank arms for increased leverage and power output.
-
Research popular brands and models: Brands such as Shimano, SRAM, and Campagnolo offer a range of bike crank sizes catering to various cycling disciplines and rider preferences. Familiarize yourself with these options to find the perfect bike crank size for your needs.
-
Test and adjust: Once you have selected a bike crank size, test it on the road or trail to assess its performance. If necessary, make adjustments to ensure optimal pedaling efficiency, power transfer, and comfort. Remember that personal preferences and specific use cases may warrant deviations from standard bike crank size recommendations.
By following this step-by-step guide, cyclists can make informed decisions about bike crank size selection, ultimately enhancing their cycling experience and performance.
Pros and Cons of Adjusting Bike Crank Size: Balancing Benefits and Drawbacks
Adjusting bike crank size can offer various advantages, such as improved pedaling efficiency, power transfer, and comfort. However, it is essential to weigh these benefits against potential drawbacks, including compatibility issues, cost, and performance trade-offs.
Advantages of Adjusting Bike Crank Size
- Improved pedaling efficiency: A properly sized bike crank can optimize the pedaling stroke, reducing dead spots and increasing overall efficiency.
- Enhanced power transfer: Larger bike crank sizes can provide increased leverage, leading to improved power output and acceleration.
- Greater comfort: Selecting a bike crank size that suits your body measurements and riding style can reduce strain and discomfort, particularly in the knees and hips.
Disadvantages of Adjusting Bike Crank Size
- Compatibility issues: Changing bike crank sizes may require modifications to other components, such as the bottom bracket, chainrings, or pedals, which can lead to additional costs and potential compatibility problems.
- Cost: Upgrading to a new bike crank size or model can be expensive, especially if additional components must be replaced or modified.
- Performance trade-offs: Altering bike crank size may have unintended consequences on bike handling, maneuverability, and overall performance. Cyclists should carefully consider these factors before making any changes.
By understanding the advantages and disadvantages of adjusting bike crank size, cyclists can make informed decisions about their equipment and optimize their performance on the road or trail.
Maintaining and Upgrading Bike Crank Sizes: Best Practices
Maintaining and upgrading bike crank sizes is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. By following best practices, cyclists can keep their bike cranks in pristine condition and adapt to changing needs or preferences.
Cleaning and Lubrication
- Cleaning: Regularly clean your bike crank with a soft brush and mild detergent to remove dirt, debris, and grime. Be sure to rinse thoroughly and dry completely to prevent corrosion.
- Lubrication: Apply a high-quality bicycle lubricant to the bike crank’s moving parts, such as the pedal threads, chainring bolts, and spindle, to ensure smooth operation and reduce wear.
Inspection and Maintenance
- Inspection: Periodically inspect your bike crank for signs of wear, damage, or looseness. Check for any play in the bottom bracket, crank arms, or pedals, and tighten or replace components as necessary.
- Maintenance: Adhere to the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule for your specific bike crank model. This may include periodic overhauls, rebuilds, or component replacements to maintain optimal performance and longevity.
Compatible Components and Accessories
- Chainrings: Ensure that your chainrings are compatible with your bike crank size and model. Consider factors such as bolt-circle diameter (BCD), chainline, and tooth profile when selecting chainrings.
- Bottom Brackets: Choose a bottom bracket that is compatible with your bike crank size, frame, and pedal type. Consider factors such as shell width, spindle length, and bearing type when selecting a bottom bracket.
- Pedals: Ensure that your pedals are compatible with your bike crank size and model. Consider factors such as thread type, spindle diameter, and pedal body style when selecting pedals.
By following these best practices, cyclists can maintain and upgrade their bike crank sizes effectively, ensuring optimal performance and longevity for their cycling needs.
Expert Opinions and Real-World Experiences: Learning from the Pros
Expert opinions and real-world experiences can provide valuable insights into the nuances of bike crank size selection and its impact on cycling performance. By learning from the pros, cyclists can make informed decisions about their equipment and optimize their performance on the road or trail.
Expert Opinions
- Industry professionals: Industry professionals, such as bike fit specialists, engineers, and product managers, often have unique perspectives on bike crank size selection based on their expertise and experience. These insights can help cyclists understand the complex interplay between bike crank size, pedaling efficiency, power transfer, and comfort.
- Research and development: Companies specializing in bike components and accessories often invest heavily in research and development to optimize bike crank size and design. By staying informed about the latest findings and innovations, cyclists can benefit from the collective knowledge and expertise of these organizations.
Real-World Experiences
- Professional cyclists: Professional cyclists, both past and present, offer a wealth of knowledge and experience regarding bike crank size selection and its impact on performance. By studying their equipment choices, adjustments, and preferences, cyclists can gain valuable insights into the role of bike crank size in competitive cycling.
- Amateur cyclists: Amateur cyclists, too, can provide valuable real-world experiences and perspectives on bike crank size selection. Online forums, social media groups, and local cycling communities offer opportunities for cyclists to share their experiences, successes, and challenges related to bike crank size and cycling performance.
By staying informed about expert opinions and real-world experiences, cyclists can make educated decisions about bike crank size selection, ultimately enhancing their cycling experience and performance.
Staying Informed: Keeping Up with the Latest Trends and Developments
The world of bike crank technology is constantly evolving, with new trends and developments emerging regularly. By staying informed about these advancements, cyclists can ensure they are using the most efficient and comfortable equipment for their needs. Here are some tips for keeping up with the latest trends and developments in bike crank technology:
Follow Industry News and Publications
- Bike magazines: Subscribe to reputable bike magazines, either in print or digital format, to stay informed about the latest bike crank technology and trends.
- Online forums and blogs: Participate in online forums and blogs dedicated to cycling, where industry professionals, cycling enthusiasts, and experts share their insights, experiences, and knowledge about bike crank technology and trends.
- Manufacturer websites and newsletters: Regularly visit the websites of popular bike crank manufacturers, such as Shimano, SRAM, and Campagnolo, to learn about their latest products, innovations, and developments.
Attend Cycling Events and Trade Shows
- Bike expos: Attend bike expos and trade shows to see the latest bike crank technology and trends up close, as well as to network with industry professionals and fellow cycling enthusiasts.
- Cycling events: Participate in cycling events, such as races, tours, and group rides, to learn about the latest bike crank technology and trends from other cyclists and industry professionals.
Engage with the Cycling Community
- Local bike shops: Visit local bike shops to discuss bike crank technology and trends with knowledgeable staff and fellow cyclists.
- Cycling clubs and organizations: Join cycling clubs and organizations to connect with other cyclists, attend educational events, and learn about the latest bike crank technology and trends.
By staying informed about the latest trends and developments in bike crank technology, cyclists can make educated decisions about their equipment, optimize their performance, and adapt to changing needs and preferences. Continuous learning and adaptation are essential components of a successful and enjoyable cycling experience.