Understanding Autism and Bicycle Selection
Cycling can offer numerous benefits for children with autism, including improved physical fitness, increased independence, and enhanced social interaction. However, selecting the right bike is crucial to ensure a positive and safe riding experience. Autistic children often have unique needs and abilities that must be taken into account when choosing a bike. Factors such as bike type, size, weight, and special features can significantly impact a child’s ability to ride and enjoy the activity.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing Bikes for Autistic Kids
Selecting the right bike for an autistic child involves considering several key factors. First and foremost, bike type is crucial. Autistic children may benefit from bikes with adaptive features, such as those with adjustable seats, handlebars, or pedals. Specialized bikes, such as tricycles or balance bikes, may also be suitable for certain children. Bike size is another important consideration, as a bike that is too large or too small can be difficult for a child to maneuver and control.
Bike weight is also a critical factor, as heavier bikes can be challenging for autistic children to handle and may lead to frustration or disinterest. Special features, such as training wheels, coaster brakes, or hand brakes, can also impact a child’s ability to ride and enjoy the activity. When selecting a bike for an autistic child, it is essential to consider their unique needs and abilities and choose a bike that is safe, comfortable, and enjoyable to ride.
Top Bike Picks for Autistic Children
When it comes to selecting the right bike for an autistic child, there are several top-rated options available. Here are a few of our top picks:
- Strider 12 Sport Balance Bike: This balance bike is designed for children as young as 18 months and features a lightweight frame, adjustable seat and handlebars, and puncture-proof tires. The Strider 12 Sport Balance Bike is an excellent option for autistic children who are just starting to learn how to ride a bike, as it helps to build balance and coordination.
- Woom 3 Pedal Bike: The Woom 3 Pedal Bike is a lightweight and durable option that is suitable for children aged 3 to 5 years old. It features adjustable handlebars, a low standover height, and easy-to-use hand brakes. The Woom 3 Pedal Bike is an excellent choice for autistic children who are ready to transition from a balance bike to a pedal bike.
- Burley Piccolo Trailer Cycle: The Burley Piccolo Trailer Cycle is a unique option that attaches to the back of an adult bike, allowing autistic children to experience the joys of biking while still feeling secure and supported. It features a comfortable seat, adjustable handlebars, and a sturdy frame. The Burley Piccolo Trailer Cycle is an excellent option for autistic children who may need additional support or assistance while riding.
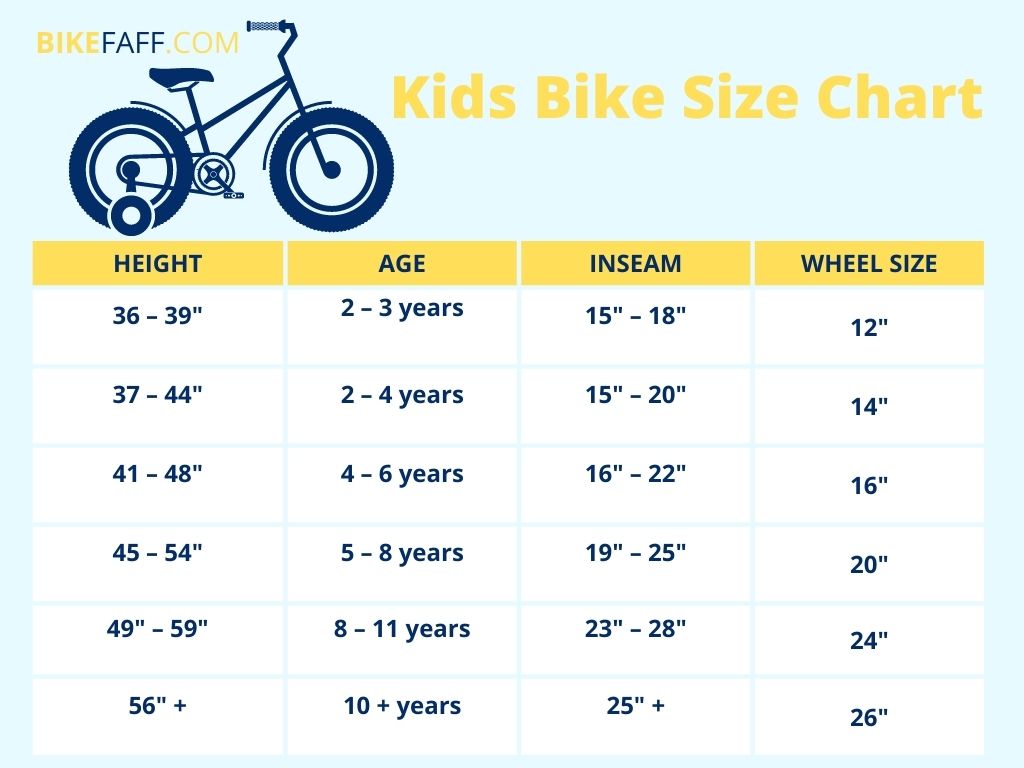
How to Measure Your Child’s Bike Size
Measuring your child’s bike size is crucial to ensure a proper fit and safe riding experience. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to measure your child’s bike size:
- Measure your child’s inseam: Have your child stand with their back against a wall, and measure from the ground to their crotch. This measurement will help you determine the appropriate bike frame size.
- Check the standover height: The standover height is the distance between the ground and the top tube of the bike frame. Your child should be able to stand over the bike with both feet flat on the ground, with a small gap between their crotch and the top tube.
- Measure the wheel size: The wheel size will determine the overall size of the bike. Smaller wheels are typically used for younger children, while larger wheels are used for older children. Common wheel sizes for children’s bikes include 12″, 16″, 20″, and 24″.
- Consider the bike’s weight: A lighter bike is generally easier for a child to handle and maneuver. Look for bikes made from lightweight materials, such as aluminum or carbon fiber.
- Ensure the bike is adjustable: Many children’s bikes come with adjustable seats and handlebars, allowing you to customize the fit as your child grows.
When selecting a bike for an autistic child, it is essential to ensure a proper fit to enhance their riding experience. A bike that is too large or too small can be challenging to handle and may lead to frustration or disinterest. By following these steps, you can help ensure a safe and enjoyable riding experience for your child.
Teaching Autistic Children to Ride Bikes: Tips and Strategies
Teaching an autistic child to ride a bike can be a rewarding experience, but it may require some additional patience and creativity. Here are some tips and strategies for teaching autistic children to ride bikes:
- Start with a balance bike: Balance bikes, also known as running bikes, are designed to help children learn how to balance and steer before introducing pedals. Balance bikes can be an excellent option for autistic children who may struggle with coordination or balance.
- Choose a quiet and familiar location: Autistic children may become overwhelmed or distracted by loud noises or unfamiliar environments. Choose a quiet and familiar location, such as a park or empty parking lot, to help your child feel more comfortable and focused.
- Break the process down into smaller steps: Teaching an autistic child to ride a bike can be a complex and overwhelming process. Break the process down into smaller steps, such as learning to balance, steer, pedal, and brake, to help your child build confidence and skills gradually.
- Use visual aids and prompts: Visual aids and prompts, such as pictures or videos, can be helpful for autistic children who may struggle with verbal instructions. Consider using visual aids to demonstrate each step of the process and provide clear and consistent feedback.
- Incorporate sensory breaks: Autistic children may become overwhelmed or overstimulated by physical activity. Incorporate sensory breaks, such as deep breathing exercises or stretching, to help your child regulate their sensory input and prevent meltdowns or shutdowns.
- Celebrate successes and progress: Celebrating successes and progress, no matter how small, can help build your child’s confidence and motivation. Be sure to acknowledge and praise your child’s efforts and accomplishments throughout the learning process.
Teaching an autistic child to ride a bike requires patience, creativity, and flexibility. By breaking the process down into smaller steps, using visual aids and prompts, and incorporating sensory breaks, you can help your child build confidence and skills gradually. Remember to celebrate successes and progress, and provide a safe and supportive learning environment for your child.
Accessories to Enhance the Biking Experience for Autistic Children
Accessories can help make biking a safer and more enjoyable experience for autistic children. Here are some accessories to consider:
- Helmets: Helmets are essential for protecting your child’s head in case of a fall or accident. Look for helmets that are comfortable, adjustable, and meet safety standards. Consider helmets with bright colors or reflective materials to increase visibility.
- Lights and reflectors: Lights and reflectors can help improve your child’s visibility, especially when riding in low-light conditions. Consider attaching lights to the front and back of the bike, as well as reflectors to the wheels and pedals.
- Bells and horns: Bells and horns can help your child signal their presence to others and alert pedestrians or other cyclists of their approach.
- Training wheels: Training wheels can help your child learn to balance and build confidence on a bike. Look for training wheels that are adjustable and easy to install.
- Bike mirrors: Bike mirrors can help your child see what’s behind them without having to turn their head. Look for mirrors that are easy to install and adjust.
- Water bottles and cages: Staying hydrated is important for any physical activity, including biking. Consider attaching a water bottle and cage to your child’s bike to make it easy for them to stay hydrated during their ride.
By considering these accessories, you can help enhance your child’s biking experience and ensure a safe and enjoyable ride. Remember to always prioritize safety and comfort when selecting accessories for your child’s bike.
Maintaining and Servicing Your Child’s Bike: A Basic Guide
Regular maintenance and servicing can help ensure your child’s bike is safe, reliable, and enjoyable to ride. Here are some tips for maintaining and servicing your child’s bike:
- Clean and lubricate the chain: A dirty or rusty chain can make pedaling difficult and cause unnecessary wear and tear on the bike’s components. Clean and lubricate the chain regularly to keep it in good condition.
- Check the brakes: Make sure the brakes are working properly and adjust them if necessary. Check the brake pads for wear and replace them if they are worn down.
- Inflate the tires: Properly inflated tires can help improve your child’s ride and prevent flats. Check the tire pressure regularly and inflate them to the recommended level.
- Tighten loose bolts and screws: Over time, bolts and screws can become loose, which can affect the bike’s performance and safety. Tighten any loose bolts or screws to keep the bike in good condition.
- Check for wear and tear: Regularly inspect the bike for signs of wear and tear, such as bent or broken parts. Replace any damaged parts as needed.
- Consider professional servicing: If you’re not comfortable performing maintenance or servicing tasks yourself, consider taking the bike to a professional for servicing. A professional bike mechanic can help ensure the bike is in good condition and safe to ride.
By following these maintenance and servicing tips, you can help ensure your child’s bike is safe, reliable, and enjoyable to ride. Regular maintenance can also help extend the life of the bike and prevent costly repairs down the line.
Frequently Asked Questions About Bikes for Autistic Children
Here are some common questions and answers about bikes for autistic children:
What age is appropriate for a child with autism to start riding a bike?
The appropriate age for a child with autism to start riding a bike depends on their individual abilities and development. Some children with autism may be ready to start riding a bike as early as 3 or 4 years old, while others may not be ready until they are older. It’s important to consider your child’s physical and cognitive abilities, as well as their interest in biking, when determining the appropriate age to start.
How can I encourage my child with autism to ride a bike?
Here are some tips to encourage your child with autism to ride a bike:
- Start with a balance bike or a tricycle to help your child get used to the idea of biking.
- Make it fun by adding decorations, streamers, or a bell to the bike.
- Find a safe and quiet place to practice riding, such as a park or a quiet neighborhood street.
- Break the process down into small steps and celebrate each success.
- Provide positive reinforcement and encouragement throughout the process.
What are some common challenges when teaching autistic children to ride bikes?
Some common challenges when teaching autistic children to ride bikes include:
- Difficulty with balance and coordination.
- Sensory sensitivities to the movement or sound of the bike.
- Anxiety or fear of falling or getting hurt.
- Difficulty with sequencing or following instructions.
- Short attention span or difficulty focusing.
It’s important to be patient and understanding of these challenges, and to provide extra support and encouragement as needed.
What are some benefits of biking for autistic children?
Biking can provide numerous benefits for autistic children, including:
- Improved physical fitness and gross motor skills.
- Increased independence and self-confidence.
- Opportunities for social interaction and communication.
- Reduced anxiety and stress.
- Improved sensory integration and processing.
By selecting the right bike and providing a supportive and encouraging environment, you can help your autistic child experience the many benefits of biking.