Unlocking the Power of Heart Rate Zones in Cycling
Heart rate zone training is a powerful tool for cyclists seeking to optimize their performance, increase endurance, and enhance overall fitness. By understanding and utilizing cycling heart rate zones, riders can tailor their workouts to specific goals and objectives, such as improving cardiovascular fitness, increasing speed, or enhancing fat burning. Cycling heart rate zones provide a precise and effective way to measure and manage physical exertion, allowing riders to push themselves to new heights while minimizing the risk of injury or burnout. Whether you’re a seasoned pro or a beginner looking to take your cycling to the next level, incorporating heart rate zone training into your routine can have a transformative impact on your performance and overall fitness.
Understanding Your Maximum Heart Rate: The Foundation of Zone Training
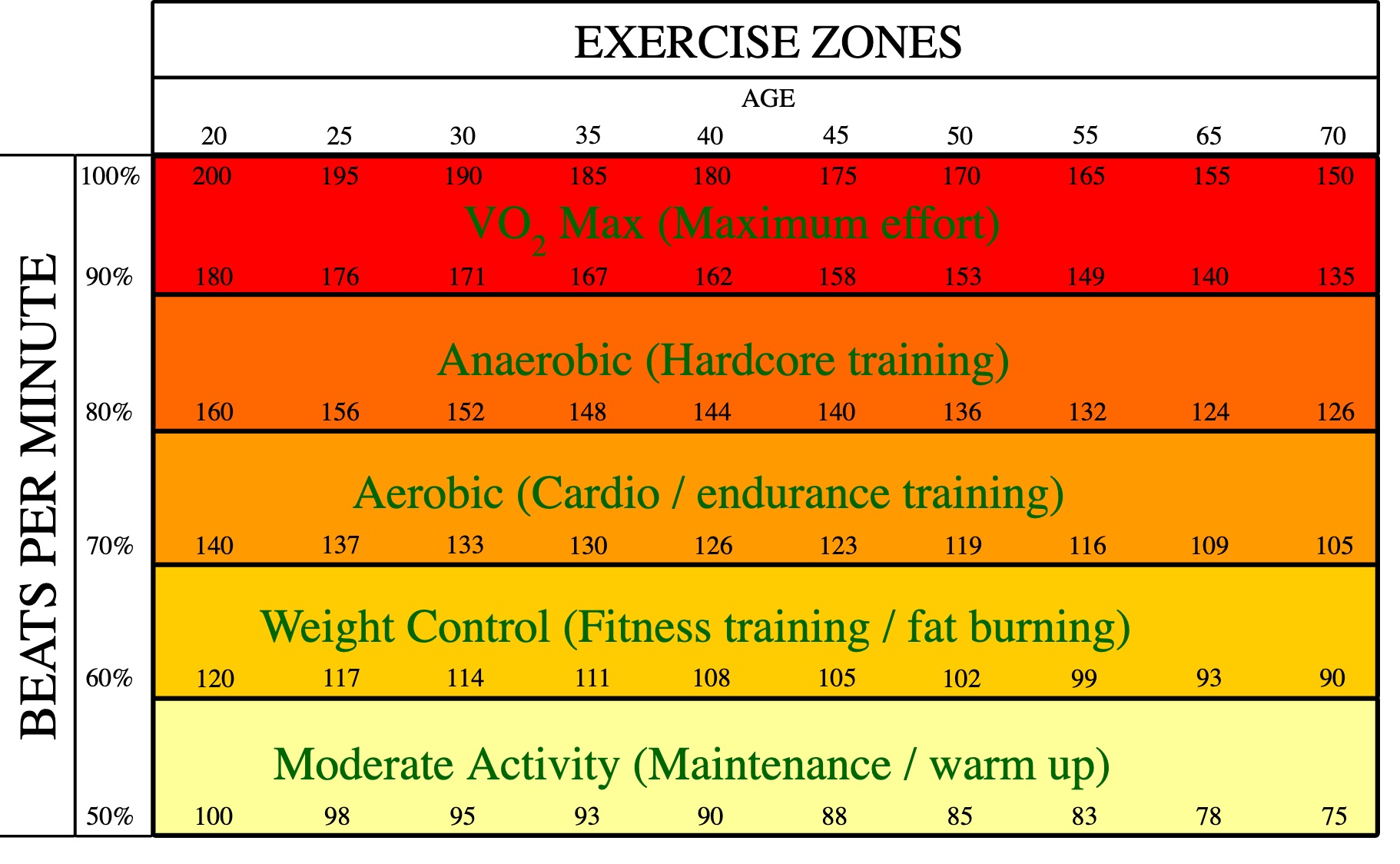
Before diving into the world of cycling heart rate zones, it’s essential to understand the foundation of zone training: maximum heart rate (MHR). MHR is the highest number of beats per minute your heart can achieve during intense exercise. Knowing your MHR is crucial, as it serves as the basis for calculating your individual heart rate zones. There are two common methods for determining MHR: the formula method and field tests. The formula method involves subtracting your age from 220, while field tests involve performing a maximum intensity exercise and measuring your heart rate. For example, a 30-year-old cyclist would have an estimated MHR of 190 beats per minute using the formula method. Accurately determining your MHR is vital, as it will impact the accuracy of your heart rate zone calculations and ultimately, the effectiveness of your training.
How to Determine Your Cycling Heart Rate Zones
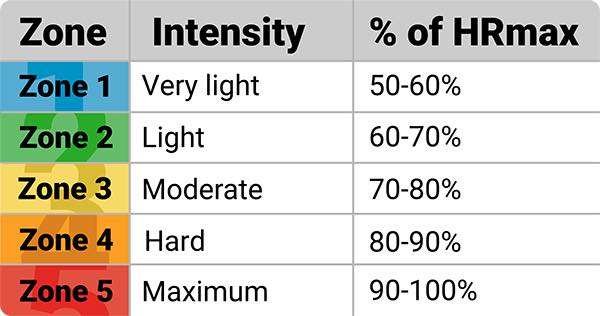
Once you’ve determined your maximum heart rate (MHR), you can calculate your individual cycling heart rate zones. There are typically five heart rate zones, each corresponding to a specific intensity level. Zone 1, also known as the recovery zone, is 50-60% of MHR, while Zone 5, the maximum intensity zone, is 90-100% of MHR. To calculate your heart rate zones, follow these steps: 1) determine your MHR, 2) calculate your lactate threshold heart rate (LTHR) by subtracting 10-15 beats from your MHR, and 3) use the following percentages to calculate each zone: Zone 1 (50-60% of MHR), Zone 2 (60-70% of MHR), Zone 3 (70-80% of MHR), Zone 4 (80-90% of MHR), and Zone 5 (90-100% of MHR). For example, if your MHR is 190 beats per minute, your Zone 2 would be 114-133 beats per minute. Understanding your individual heart rate zones is crucial for creating an effective cycling heart rate zones training plan.
The Benefits of Training in Different Heart Rate Zones
Training in different cycling heart rate zones offers a range of benefits that can improve overall cycling performance and fitness. Zone 1, the recovery zone, allows for active recovery and improved cardiovascular fitness. Zone 2, the endurance zone, increases stamina and endurance, making it ideal for long rides or century training. Zone 3, the tempo zone, enhances lactate threshold and increases speed, making it suitable for hill repeats and interval training. Zone 4, the lactate threshold zone, improves anaerobic endurance and increases power output, making it ideal for high-intensity interval training. Finally, Zone 5, the maximum intensity zone, boosts maximum power output and speed, making it suitable for short, all-out efforts like sprints. By incorporating training in different heart rate zones, cyclists can experience improved cardiovascular fitness, increased endurance, and enhanced fat burning, ultimately leading to improved overall performance.
Creating a Heart Rate Zone-Based Cycling Workout Plan
To get the most out of cycling heart rate zones, it’s essential to create a structured workout plan that incorporates different zones to achieve specific goals. A well-designed plan should include a mix of endurance, tempo, and high-intensity interval training to improve overall fitness and performance. Here’s a step-by-step guide to creating a heart rate zone-based cycling workout plan:
1. Identify your goals: Determine what you want to achieve through your cycling training, whether it’s improving endurance, increasing speed, or enhancing overall fitness.
2. Assess your current fitness level: Evaluate your current fitness level by tracking your heart rate data during different types of rides.
3. Create a periodized training plan: Divide your training into specific periods or phases, each with a focus on a different heart rate zone.
4. Incorporate zone-specific workouts: Design workouts that target specific heart rate zones, such as Zone 2 endurance rides or Zone 4 high-intensity interval training.
5. Include rest and recovery days: Make sure to include rest and recovery days in your plan to allow your body to adapt to the demands of training.
Example Workout Plan:
Monday: Zone 2 endurance ride (60-70% MHR)
Tuesday: Zone 4 high-intensity interval training (80-90% MHR)
Wednesday: Rest day
Thursday: Zone 3 tempo ride (70-80% MHR)
Friday: Zone 1 active recovery ride (50-60% MHR)
By incorporating cycling heart rate zones into your workout plan, you can create a structured and effective training program that helps you achieve your goals and improve overall performance.
Monitoring Your Progress: The Role of Heart Rate Data in Cycling
Tracking heart rate data is a crucial aspect of training with cycling heart rate zones. By monitoring your heart rate data, you can gain valuable insights into your body’s response to different types of training, allowing you to adjust your workouts, prevent overtraining or undertraining, and optimize your performance.
Heart rate data can be used to:
– Monitor progress: Track changes in your heart rate data over time to see how your body is adapting to training.
– Adjust workouts: Use heart rate data to adjust the intensity and duration of your workouts based on your current fitness level.
– Prevent overtraining: Identify signs of overtraining, such as elevated resting heart rate or decreased heart rate variability, and adjust your training accordingly.
– Optimize performance: Use heart rate data to identify areas for improvement and optimize your training to achieve specific goals.
There are several ways to track heart rate data, including:
– Wearable heart rate monitors: Devices such as chest straps or smartwatches that track heart rate data in real-time.
– Cycling computers: Devices that track heart rate data, as well as other metrics such as speed, distance, and cadence.
– Mobile apps: Apps that track heart rate data and provide insights into training and progress.
By incorporating heart rate data into your training, you can take your cycling performance to the next level and achieve your goals more efficiently.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Training with Heart Rate Zones
When incorporating cycling heart rate zones into a training program, it’s essential to avoid common mistakes that can hinder progress and lead to ineffective training. By being aware of these mistakes, cyclists can optimize their training and achieve their goals more efficiently.
One common mistake is incorrect zone calculation. This can occur when cyclists miscalculate their maximum heart rate or fail to adjust their zones based on changes in fitness level. To avoid this mistake, it’s crucial to regularly reassess maximum heart rate and adjust zones accordingly.
Another mistake is inadequate warm-up and cool-down. Failing to properly warm up before a workout can lead to poor performance and increased risk of injury, while inadequate cool-down can impede recovery. Cyclists should ensure they include a thorough warm-up and cool-down in their workouts to optimize performance and recovery.
Insufficient recovery time is another common mistake. Cyclists often underestimate the importance of recovery time, leading to inadequate rest and recovery. This can result in overtraining, decreased performance, and increased risk of injury. It’s essential to include adequate recovery time in a training program to allow the body to adapt and recover.
Failing to incorporate variety in a training program is another mistake. Cycling heart rate zones should be used in conjunction with other training methods, such as interval training and hill repeats, to provide a well-rounded and effective training program. By incorporating variety, cyclists can avoid plateaus and continue to make progress towards their goals.
By being aware of these common mistakes, cyclists can optimize their training with cycling heart rate zones and achieve their goals more efficiently. By incorporating heart rate zone training into a cycling routine, cyclists can improve performance, increase motivation, and enhance overall fitness.
Taking Your Cycling to the Next Level with Heart Rate Zone Training
Incorporating cycling heart rate zones into a training program can have a transformative impact on cycling performance. By understanding the importance of maximum heart rate, determining individual heart rate zones, and creating a structured workout plan, cyclists can optimize their training and achieve their goals more efficiently.
Training with cycling heart rate zones offers a range of benefits, including improved cardiovascular fitness, increased endurance, and enhanced fat burning. By incorporating heart rate zone training into a cycling routine, cyclists can experience improved performance, increased motivation, and enhanced overall fitness.
Moreover, heart rate zone training provides a structured approach to training, allowing cyclists to tailor their workouts to specific goals and objectives. Whether aiming to improve overall fitness, increase endurance, or enhance performance, cycling heart rate zones provide a proven and effective method for achieving success.
By avoiding common mistakes, such as incorrect zone calculation and inadequate warm-up and cool-down, cyclists can ensure they are getting the most out of their training. With a well-structured workout plan and a commitment to tracking progress, cyclists can take their performance to the next level and achieve their goals.
In conclusion, cycling heart rate zones offer a powerful tool for optimizing cycling performance. By incorporating heart rate zone training into a cycling routine, cyclists can experience improved performance, increased motivation, and enhanced overall fitness. With a structured approach to training and a commitment to tracking progress, cyclists can achieve their goals and take their performance to new heights.