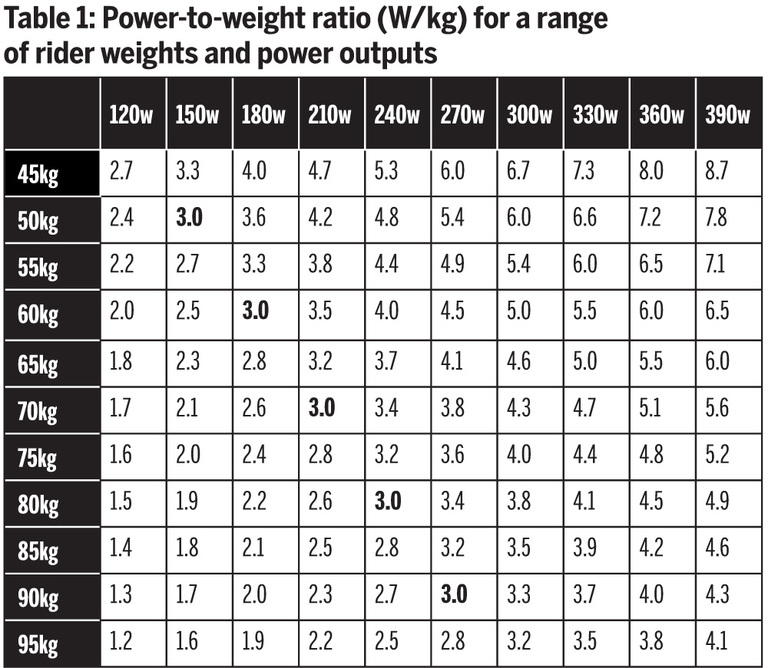
Why Power-to-Weight Ratio Matters in Cycling
In the pursuit of cycling excellence, one metric stands out as a key determinant of success: the power-to-weight ratio. This critical measure of a rider’s ability to generate power relative to their body weight is a decisive factor in achieving peak performance. A high power-to-weight ratio enables cyclists to accelerate faster, climb more efficiently, and maintain a high pace over long distances, giving them a significant competitive edge.
The importance of power-to-weight ratio lies in its impact on a rider’s overall efficiency. When a cyclist can produce a high amount of power while maintaining a lean, efficient physique, they are able to conserve energy and reduce the risk of fatigue. This, in turn, allows them to push themselves harder and longer, ultimately leading to improved performance and results.
In the world of professional cycling, the power-to-weight ratio is a closely guarded secret, with top riders and teams constantly seeking to optimize this metric to gain a competitive advantage. By understanding the significance of power-to-weight ratio and how to improve it, cyclists of all levels can unlock their full potential and take their performance to new heights.
Understanding Your Current Power Output and Weight
To optimize your cycling power-to-weight ratio, it’s essential to have a clear understanding of your current power output and weight. This involves measuring your power output using tools like watt meters or cycling computers, and tracking your weight and body composition.
Measuring power output is a crucial step in understanding your cycling performance. Watt meters and cycling computers provide accurate data on your power output, allowing you to track your progress and identify areas for improvement. When choosing a power meter, consider factors such as accuracy, reliability, and ease of use. Additionally, ensure that your power meter is calibrated regularly to ensure accurate readings.
Accurately tracking your weight and body composition is also vital in optimizing your power-to-weight ratio. This involves regularly monitoring your weight, body fat percentage, and lean muscle mass. Use a reliable scale and body fat caliper to track your progress, and consider working with a sports dietitian or nutritionist to develop a personalized nutrition plan.
By understanding your current power output and weight, you can set realistic goals and develop a targeted training plan to improve your cycling performance. This data-driven approach will help you optimize your power-to-weight ratio, leading to improved efficiency, speed, and overall performance.
How to Boost Your Power Output on the Bike
Increasing power output is a critical component of optimizing your cycling power-to-weight ratio. By incorporating targeted training strategies into your routine, you can significantly improve your performance and efficiency on the bike.
High-intensity interval training (HIIT) is a highly effective way to boost power output. This involves short, intense bursts of effort followed by active recovery periods. For example, try incorporating 30-second all-out sprints into your ride, followed by 30 seconds of easy spinning. Repeat for 20-30 minutes, 2-3 times a week.
Strength training is another key component of increasing power output. Focus on exercises that target your legs, core, and glutes, such as squats, lunges, and deadlifts. Aim to do 2-3 strength training sessions per week, with a focus on low-to-moderate weights and high reps.
Cadence drills are also an effective way to improve power output. Try incorporating high-cadence drills into your ride, such as spinning at 100-120 RPM for 10-15 minutes. This will help improve your pedaling efficiency and increase your power output.
In addition to these training strategies, it’s essential to incorporate rest and recovery into your routine. Adequate rest and recovery allow your body to adapt to the demands of training, leading to increased power output and improved performance. Aim to take 1-2 rest days per week, and prioritize sleep, nutrition, and stretching to aid in recovery.
By incorporating these training strategies into your routine, you can significantly improve your power output and optimize your cycling power-to-weight ratio. Remember to always listen to your body and adjust your training plan as needed, and don’t be afraid to seek guidance from a coach or trainer if you need additional support.
Optimizing Your Bike and Gear for Maximum Efficiency
When it comes to optimizing your cycling power-to-weight ratio, having the right bike and gear can make all the difference. A well-fitting bike, aerodynamic components, and carefully selected gear can help you maximize power output and reduce energy waste.
Proper bike fit is essential for efficient pedaling and optimal power output. A bike that fits correctly will allow you to maintain a comfortable riding position, reducing energy waste and improving pedaling efficiency. Consider working with a professional bike fitter to ensure your bike is tailored to your unique needs and riding style.
Aerodynamics also play a critical role in maximizing power output. Aerodynamic components such as wheels, frames, and handlebars can help reduce air resistance, allowing you to maintain speed and efficiency with less effort. Consider investing in aerodynamic components, and pay attention to your riding position to minimize air resistance.
Gear selection is another key factor in optimizing your cycling power-to-weight ratio. The right gear selection can help you maintain an optimal cadence, reducing energy waste and improving power output. Consider experimenting with different gear ratios and cassette sizes to find the optimal setup for your riding style and terrain.
In addition to these factors, regular bike maintenance is also crucial for maximizing power output and reducing energy waste. Regularly clean and lubricate your chain, check your tire pressure, and perform routine maintenance tasks to ensure your bike is running smoothly and efficiently.
By optimizing your bike and gear, you can significantly improve your cycling power-to-weight ratio, leading to improved performance and efficiency on the bike. Remember to always prioritize comfort, safety, and efficiency when selecting and setting up your bike and gear.
The Role of Nutrition and Recovery in Power-to-Weight Optimization
Nutrition and recovery play a critical role in optimizing a cyclist’s power-to-weight ratio. A well-planned nutrition strategy can help support power output, while a recovery plan can aid in weight management and overall performance.
When it comes to fueling, cyclists should focus on consuming a balanced diet that includes complex carbohydrates, lean protein, and healthy fats. Aim to eat a meal or snack that includes a mix of these macronutrients 1-3 hours before a ride, and prioritize hydration by drinking plenty of water or a sports drink.
During a ride, cyclists can use energy gels, bars, or chews to maintain energy levels and support power output. Look for products that contain a mix of simple and complex carbohydrates, as well as electrolytes to aid in hydration.
After a ride, recovery nutrition is critical for aiding in weight management and supporting muscle repair. Consume a meal or snack that includes a mix of carbohydrates and protein within 30-60 minutes of finishing a ride, and prioritize hydration by drinking plenty of water or a sports drink.
In addition to nutrition, recovery strategies such as stretching, foam rolling, and massage can aid in weight management and overall performance. These strategies can help reduce muscle soreness and inflammation, allowing cyclists to recover faster and train more frequently.
Rest and recovery are also critical components of optimizing a cyclist’s power-to-weight ratio. Aim to get 7-9 hours of sleep per night, and prioritize rest days or easy spins to allow your body to recover from intense training.
By prioritizing nutrition and recovery, cyclists can optimize their power-to-weight ratio, leading to improved performance and efficiency on the bike. Remember to always listen to your body and adjust your nutrition and recovery plan as needed to support your training goals.
Real-World Examples: How Pro Cyclists Achieve an Ideal Power-to-Weight Ratio
Professional cyclists are a great source of inspiration for those looking to optimize their cycling power-to-weight ratio. By examining the training strategies and nutrition plans of successful pro cyclists, riders can gain valuable insights into how to improve their own performance.
Take, for example, Chris Froome, a four-time Tour de France winner. Froome’s success can be attributed to his meticulous attention to detail when it comes to his power-to-weight ratio. He works closely with his coaches and nutritionists to ensure that his training and nutrition plans are tailored to his specific needs and goals.
Froome’s training strategy focuses on high-intensity interval training, strength training, and cadence drills to boost his power output. He also prioritizes nutrition and recovery, fueling his body with a balanced diet that includes complex carbohydrates, lean protein, and healthy fats. By optimizing his power-to-weight ratio, Froome is able to maintain a high level of performance over long distances.
Another example is Anna van der Breggen, a Dutch professional cyclist who has won numerous titles including the Olympic road race and the Giro Rosa. Van der Breggen’s success can be attributed to her focus on building her power output through strength training and high-intensity interval training. She also prioritizes nutrition and recovery, fueling her body with a balanced diet and getting adequate rest and recovery time.
By examining the training strategies and nutrition plans of successful pro cyclists like Froome and van der Breggen, riders can gain valuable insights into how to improve their own cycling power-to-weight ratio. Remember, optimizing your power-to-weight ratio takes time, patience, and dedication, but with the right training and nutrition plan, you can achieve your goals and take your cycling performance to the next level.
Creating a Personalized Training Plan to Improve Your Power-to-Weight Ratio
Creating a personalized training plan is crucial to improving your cycling power-to-weight ratio. A well-structured plan takes into account your current fitness level, goals, and available training time. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you create a customized training plan:
Step 1: Set Specific and Achievable Goals
Define your goals, whether it’s to increase your power output, reduce your weight, or improve your overall cycling efficiency. Make sure your goals are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). For example, “I want to increase my power output by 20 watts in 12 weeks.”
Step 2: Assess Your Current Fitness Level
Evaluate your current power output, weight, and body composition. Use tools like watt meters or cycling computers to measure your power output, and track your weight and body composition regularly.
Step 3: Choose Your Training Strategies
Select training strategies that align with your goals and fitness level. For example, if you want to increase your power output, you may focus on high-intensity interval training, strength training, and cadence drills.
Step 4: Create a Periodized Training Plan
Divide your training plan into periods or phases, each with specific goals and training strategies. For example, you may have a base training phase, a build phase, and a peak phase. Each phase should last several weeks to allow for progressive overload and adaptation.
Step 5: Track Your Progress and Adjust Your Plan
Regularly track your progress, including your power output, weight, and body composition. Use this data to adjust your training plan, making sure you’re on track to achieve your goals.
By following these steps, you can create a personalized training plan that helps you improve your cycling power-to-weight ratio and achieve your goals. Remember to stay consistent, patient, and dedicated, and you’ll be on your way to unlocking your full cycling potential.
Overcoming Common Obstacles to Achieving an Ideal Power-to-Weight Ratio
Optimizing your cycling power-to-weight ratio can be a challenging and complex process. Cyclists often face common obstacles that can hinder their progress and prevent them from achieving their goals. Here are some common challenges and solutions to help you overcome them:
Plateaus: When Progress Stalls
It’s common to experience a plateau in your training, where you feel like you’re not making progress despite consistent effort. To overcome a plateau, try changing your training strategy, incorporating new exercises or drills, or seeking guidance from a coach or experienced cyclist.
Injuries: Managing Setbacks and Staying on Track
Injuries are an unfortunate reality for many cyclists. To minimize the impact of an injury, focus on active recovery, including stretching, foam rolling, and light cardio exercises. Also, prioritize nutrition and rest to aid in the recovery process.
Mental Blocks: Building Confidence and Motivation
Mental blocks can be a significant obstacle to achieving an ideal power-to-weight ratio. To overcome mental blocks, focus on building confidence through small victories, setting realistic goals, and celebrating progress. Additionally, surround yourself with a supportive community of cyclists who can provide motivation and encouragement.
Lack of Time: Fitting Training into a Busy Schedule
Many cyclists struggle to find time to train, especially those with busy schedules. To overcome this obstacle, prioritize your training, focus on high-intensity interval training, and incorporate strength training and cadence drills into your routine.
By understanding and addressing these common obstacles, cyclists can overcome the challenges that stand in the way of achieving an ideal cycling power-to-weight ratio. Remember, optimizing your power-to-weight ratio takes time, patience, and dedication, but with the right mindset and strategies, you can overcome any obstacle and achieve your goals.