What Are Caliper Brakes and How Do They Differ from Other Brake Systems?
Caliper brakes are a type of brake system commonly found in various vehicles and bicycles. Their primary function is to slow down or stop the vehicle or bicycle by applying pressure on the wheels, thereby converting the kinetic energy into heat. This pressure is generated through the interaction between the brake pads and the rotors or rims of the wheels.
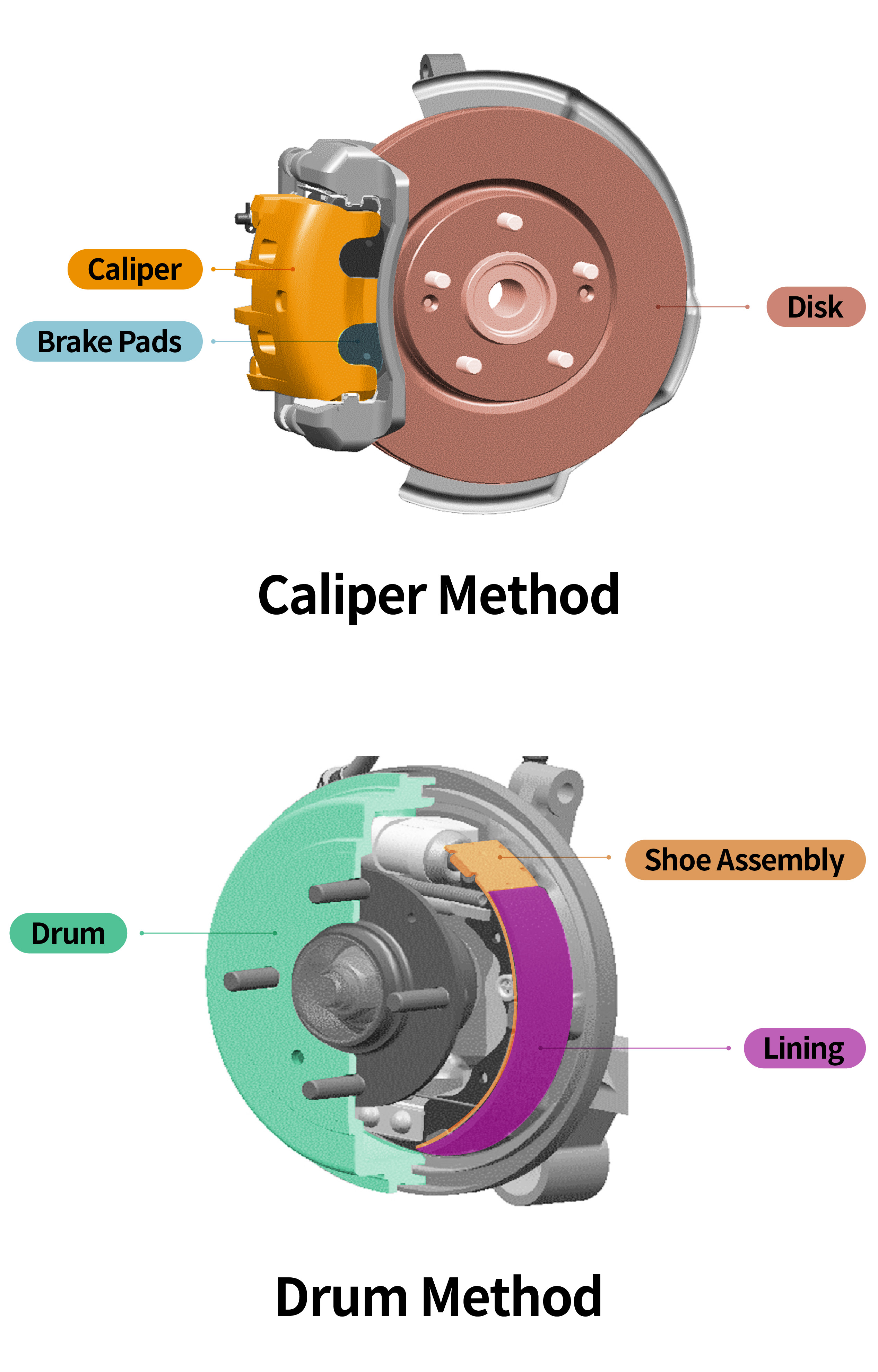
In contrast to drum brakes, which are enclosed and less exposed to external elements, caliper brakes are open and more susceptible to contaminants such as dirt, water, and grime. Caliper brakes also differ from disc brakes, which use a rotor that is typically larger and more robust than the rotors found in caliper brakes. Caliper brakes are generally lighter and more cost-effective than disc brakes, making them a popular choice for many bicycles and smaller vehicles.
Anatomy of Caliper Brakes: Key Components and Their Functions
Caliper brakes consist of several essential components that work together to slow down or stop the vehicle or bicycle. These components include brake pads, brake shoes, brake levers, and caliper bodies.
Brake pads are the consumable parts of the brake system that come into contact with the rotors or rims to generate friction and convert kinetic energy into heat. They are typically made of materials such as metallic, organic, or ceramic compounds, each with its unique properties and trade-offs in terms of braking power, durability, and noise.
Brake shoes are curved pieces of metal that house the brake pads and guide them into position when the brakes are applied. They are usually made of steel or other durable materials and are designed to withstand the heat and wear generated during the braking process.
Brake levers are the components that the rider or driver actuates to apply the brakes. They convert the mechanical force applied by the user into hydraulic or cable pressure, which in turn activates the caliper bodies.
Caliper bodies are the part of the brake system that houses the brake pads and shoes and applies pressure to the rotors or rims when the brakes are engaged. They are typically made of lightweight materials such as aluminum or magnesium and are designed to be both strong and corrosion-resistant.
Together, these components form a cohesive system that enables the rider or driver to control the speed and movement of their vehicle or bicycle safely and efficiently. Understanding the anatomy of caliper brakes is essential for anyone looking to maintain, upgrade, or replace their braking system.
How Caliper Brakes Generate Stopping Power: The Role of Friction
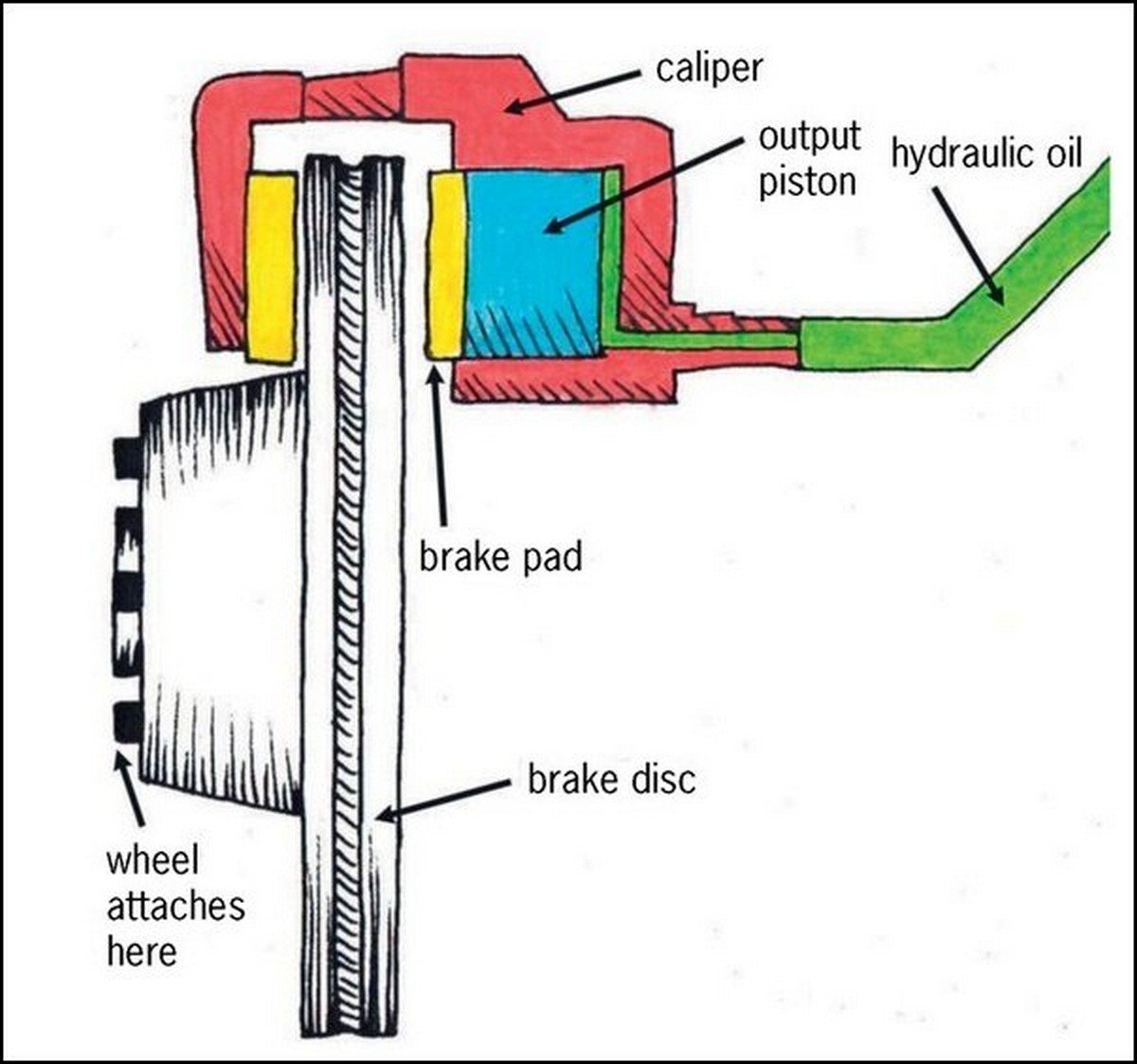
Friction plays a critical role in the operation of caliper brakes. When the brake lever is actuated, it triggers a mechanical or hydraulic mechanism that pushes the brake pads against the rotors or rims of the wheels. This contact generates friction, which in turn converts the kinetic energy of the vehicle or bicycle into heat. The heat dissipates into the surrounding air, causing the rotors or rims to cool down and the vehicle or bicycle to slow down or stop.
The amount of friction generated during the braking process depends on several factors, including the type and quality of the brake pads, the speed and weight of the vehicle or bicycle, and the condition of the rotors or rims. High-quality brake pads made of materials such as ceramic or metallic compounds can provide superior braking power and durability compared to lower-quality organic or semi-metallic pads. Similarly, well-maintained rotors or rims with smooth and even surfaces can improve the overall braking performance and reduce the risk of squeaking or other common issues.
It is important to note that excessive heat generated during the braking process can have adverse effects on the performance and longevity of the brake system. Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can cause the brake pads to wear down more quickly, the rotors or rims to warp or crack, and the hydraulic or cable systems to fail. Regular inspections, adjustments, and cleanings can help mitigate these risks and ensure optimal performance and safety.
Hydraulic vs Mechanical Caliper Brakes: A Comparative Analysis
When it comes to caliper brakes, there are two main types: hydraulic and mechanical. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between them often depends on the specific needs and preferences of the user.
Hydraulic Caliper Brakes
Hydraulic caliper brakes use a sealed fluid system to transmit force from the brake lever to the caliper bodies. This design allows for greater modulation and braking power, as well as reduced maintenance requirements compared to mechanical caliper brakes. Hydraulic caliper brakes are commonly used in high-performance bicycles and motorcycles, as well as in some automotive applications.
Mechanical Caliper Brakes
Mechanical caliper brakes, on the other hand, use a cable system to transmit force from the brake lever to the caliper bodies. While they may not offer the same level of modulation and braking power as hydraulic caliper brakes, they are generally easier to install, adjust, and maintain. Mechanical caliper brakes are commonly used in entry-level and mid-range bicycles, as well as in some automotive and industrial applications.
Choosing the Right Type of Caliper Brakes
When choosing between hydraulic and mechanical caliper brakes, there are several factors to consider. These include budget, performance expectations, maintenance requirements, and compatibility with the vehicle or bicycle. In general, hydraulic caliper brakes are better suited for high-performance applications where modulation and braking power are critical, while mechanical caliper brakes are a more cost-effective and user-friendly option for everyday use.
Some popular aftermarket brands and models of caliper brakes include Shimano, SRAM, Avid, Campagnolo, and TRP. These brands are known for their quality, reliability, and performance, and offer a range of options to suit different needs and preferences.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Caliper Brakes: Weighing the Pros and Cons
Caliper brakes are a popular choice for many vehicles and bicycles due to their lightweight, easy-to-maintain design and simple operation. However, like any brake system, they have their own set of advantages and disadvantages that users should be aware of before making a purchasing decision.
Advantages of Caliper Brakes
One of the main advantages of caliper brakes is their lightweight design. Compared to other brake systems, such as drum or disc brakes, caliper brakes have fewer moving parts and require less material to manufacture. This makes them a popular choice for weight-conscious cyclists and drivers who want to maximize performance without sacrificing safety.
Another advantage of caliper brakes is their ease of maintenance. With fewer moving parts than other brake systems, caliper brakes are relatively simple to service and adjust. This can save users time and money in the long run, as they can perform routine maintenance tasks themselves without needing to rely on a professional mechanic.
Disadvantages of Caliper Brakes
One of the main disadvantages of caliper brakes is their susceptibility to warping or fading in wet or muddy conditions. When exposed to moisture or debris, the brake pads and rotors or rims can become contaminated, reducing their ability to generate friction and convert kinetic energy into heat. This can result in reduced braking power and increased stopping distances, which can be dangerous in certain situations.
Another disadvantage of caliper brakes is their limited braking power compared to other brake systems. While they are sufficient for most everyday driving and cycling scenarios, they may not provide the same level of stopping power as drum or disc brakes in high-performance or emergency situations. This is especially true for heavier vehicles or bicycles, where the additional weight can put extra strain on the brake system.
Overall, caliper brakes are a reliable and cost-effective brake system for many vehicles and bicycles. While they have their own set of advantages and disadvantages, they remain a popular choice for users who value lightweight design, ease of maintenance, and simple operation.
Troubleshooting Common Caliper Brake Issues: A Practical Guide
Caliper brakes are generally reliable and low-maintenance, but like any mechanical system, they can experience issues that affect their performance. Here are some common problems that users may encounter, along with practical advice on how to troubleshoot and repair them.
Squeaking Brakes
Squeaking or squealing brakes are a common issue that can be caused by a variety of factors, including contamination of the brake pads, glazing of the brake pad material, or uneven wear. To troubleshoot squeaking brakes, start by inspecting the brake pads for signs of wear or damage. If the pads are worn unevenly or have become glazed, they may need to be replaced. Clean the brake pads and rotors or rims with a suitable cleaning solution, and avoid using household cleaners or solvents, which can damage the brake components.
Reduced Braking Power
Reduced braking power can be caused by a variety of factors, including contamination of the brake pads, worn or damaged brake pads, or air in the brake lines. To troubleshoot reduced braking power, start by inspecting the brake pads for signs of wear or damage. If the pads are worn unevenly or have become glazed, they may need to be replaced. Bleed the brake lines to remove any air, and check for leaks or damage to the brake lines or hoses. If the issue persists, consult a professional mechanic for further assistance.
Uneven Brake Pad Wear
Uneven brake pad wear can be caused by a variety of factors, including misalignment of the brake pads, contamination of the brake pads, or uneven application of the brakes. To troubleshoot uneven brake pad wear, start by inspecting the brake pads for signs of wear or damage. If the pads are worn unevenly, adjust the brake caliper to ensure that the pads are properly aligned. Clean the brake pads and rotors or rims with a suitable cleaning solution, and avoid using household cleaners or solvents, which can damage the brake components.
Safety Precautions
When troubleshooting or repairing caliper brakes, it is important to take safety precautions to prevent injury or damage to the brake system. Always wear protective gear, such as gloves and safety glasses, and work in a well-ventilated area. Use only tools and supplies that are designed for use with brake systems, and avoid using household cleaners or solvents, which can damage the brake components. If you are unsure about how to perform a repair, consult a professional mechanic for further assistance.
Upgrading or Replacing Caliper Brakes: Factors to Consider
If you’re considering upgrading or replacing your caliper brakes, there are several factors to keep in mind. Here are some tips to help you make an informed decision.
Budget
The cost of caliper brakes can vary widely depending on the brand, model, and features. Before you start shopping, determine your budget and look for brakes that offer the best value for your money. Keep in mind that higher-priced brakes may offer better performance and durability, but they may not be necessary for your needs.
Performance Expectations
Consider your performance expectations when choosing caliper brakes. If you’re a casual rider or driver who only uses their brakes occasionally, you may not need the same level of performance as a competitive cyclist or race car driver. Look for brakes that offer the level of performance you need without overspending.
Compatibility
Make sure the caliper brakes you choose are compatible with your vehicle or bicycle. Check the manufacturer’s specifications to ensure that the brakes will fit properly and work with your existing brake system. If you’re unsure, consult a professional mechanic for assistance.
Popular Aftermarket Brands and Models
Some popular aftermarket brands and models of caliper brakes known for their quality and reliability include Shimano, SRAM, Campagnolo, and TRP. These brands offer a range of options to suit different needs and budgets, from entry-level to high-performance models.
Installation
Installing caliper brakes can be a complex process, especially if you’re replacing an existing brake system. If you’re not comfortable doing it yourself, consider hiring a professional mechanic to install the brakes for you. This can help ensure that the brakes are installed correctly and function properly.
Maintaining Caliper Brakes for Optimal Performance: Tips and Best Practices
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the optimal performance of your caliper brakes. Here are some tips and best practices to help you maintain your brakes and keep them in good working order.
Inspections
Regularly inspect your caliper brakes for signs of wear or damage. Look for worn or damaged brake pads, contaminated or corroded brake components, and leaks or damage to the brake lines or hoses. If you notice any issues, address them promptly to prevent further damage or safety hazards.
Adjustments
Adjust your caliper brakes as needed to ensure proper alignment and function. This may include adjusting the brake pads to ensure even wear, adjusting the brake cable tension to ensure proper modulation, or adjusting the brake caliper position to ensure proper alignment with the rotor or rim.
Cleanings
Clean your caliper brakes regularly to remove dirt, grime, and other contaminants that can affect their performance. Use a suitable cleaning solution and avoid using household cleaners or solvents, which can damage the brake components. Dry the brake components thoroughly after cleaning to prevent corrosion.
Lubrication
Lubricate your caliper brakes as needed to ensure smooth operation and prevent wear or damage. Use a suitable lubricant, such as a brake grease or oil, and avoid using household oils or lubricants, which can damage the brake components. Apply lubricant sparingly and wipe away any excess to prevent contamination.
Brake Pads
Select the right brake pads for your caliper brakes to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Consider factors such as the type of riding or driving you do, the conditions you ride or drive in, and the recommendations of the brake pad manufacturer. Look for high-quality brake pads that are designed for use with caliper brakes and offer good stopping power, durability, and resistance to wear or fade.
Safety Precautions
When maintaining your caliper brakes, always take safety precautions to prevent injury or damage to the brake system. Wear protective gear, such as gloves and safety glasses, and work in a well-ventilated area. Use only tools and supplies that are designed for use with brake systems, and avoid using household cleaners or solvents, which can damage the brake components. If you’re unsure about how to perform a maintenance task, consult a professional mechanic for further assistance.