The Significance of Calculating Calories Burned on a Bike
Understanding the number of calories burned on a bike is crucial for tracking fitness progress, creating a balanced diet, and setting realistic exercise goals. By monitoring caloric expenditure, cyclists can ensure they are maintaining a healthy weight, building endurance, and improving overall fitness. Moreover, knowing the caloric burn can help cyclists adjust their diet and exercise routines to optimize performance and achieve their desired outcomes.
How Does Cycling Contribute to Caloric Expenditure?
Cycling is an effective way to burn calories due to its cardiovascular nature and the ability to perform it at varying intensities. Several factors influence the number of calories burned on a bike, including body weight, intensity, and duration of the ride. Additionally, the type of cycling—road, mountain, or indoor—can impact caloric expenditure.
Heavier individuals tend to burn more calories during a bike ride due to the increased energy required to move their bodies. Intensity plays a significant role, as well; high-intensity interval training (HIIT) or riding uphill can significantly increase the number of calories burned compared to a leisurely, flat ride. The duration of the ride also impacts caloric expenditure, with longer rides leading to more calories burned.
Road cycling, mountain biking, and indoor cycling all have different caloric expenditure profiles. Road cycling often involves longer distances at moderate intensities, while mountain biking includes more varied terrain and intensities. Indoor cycling, such as spinning classes, typically features high-intensity intervals and resistance training, resulting in a higher caloric burn per hour.
Estimating Calories Burned During a Bike Ride
Estimating the number of calories burned on a bike ride can be accomplished through various methods, each with its advantages and limitations. Utilizing online calculators, fitness trackers, and heart rate monitors are common techniques for approximating caloric expenditure.
Online Calculators
Online calculators typically require users to input their weight, duration, and intensity of the ride to estimate caloric burn. These calculators are easily accessible and often free to use, making them a convenient option for cyclists. However, they may not account for individual variations in metabolism or fitness levels, potentially leading to inaccurate estimations.
Fitness Trackers
Fitness trackers, such as wristbands or smartwatches, can monitor heart rate, movement, and other physiological parameters to estimate caloric expenditure during a bike ride. These devices offer real-time data and can be more accurate than online calculators, as they account for individual variations in metabolism and fitness levels. However, they may still have limitations in accurately measuring caloric burn during cycling, especially if not properly calibrated.
Heart Rate Monitors
Heart rate monitors, either worn as a chest strap or integrated into a fitness tracker, can provide a more accurate estimation of caloric burn during a bike ride. By measuring heart rate and applying specific formulas, these monitors can account for individual variations in metabolism and fitness levels. However, they may not be as convenient as online calculators and can be more expensive than other options.
It is essential to consider the advantages and limitations of each method when estimating calories burned on a bike ride. Utilizing multiple methods, such as combining an online calculator with a fitness tracker, can help improve the accuracy of caloric expenditure estimations.
Comparing Caloric Expenditure Across Different Activities
Cycling is an effective way to burn calories, but it is essential to compare its caloric expenditure to other popular physical activities to understand its unique benefits and drawbacks. Running, swimming, and weightlifting are common exercises that can also contribute significantly to caloric burn.
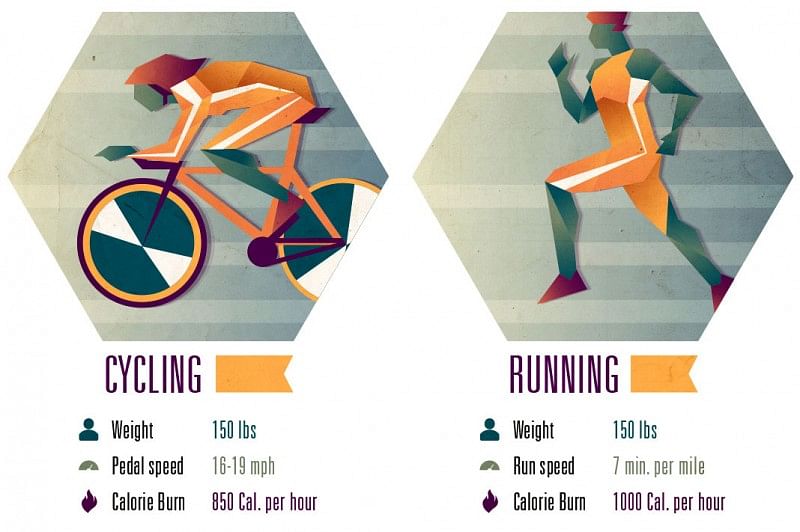
Cycling vs. Running
Running typically burns more calories per hour than cycling due to the higher impact nature of the activity. However, cycling can be a more sustainable exercise option for individuals with joint issues or those seeking a lower-impact workout. Additionally, cycling can be performed at higher intensities for longer durations than running, potentially leading to similar overall caloric burns.
Cycling vs. Swimming
Swimming is another low-impact exercise that can burn a significant number of calories, depending on the stroke and intensity. While swimming may burn more calories than cycling in certain scenarios, cycling can be more accessible and convenient for many individuals, as it does not require a pool or specialized equipment.
Cycling vs. Weightlifting
Weightlifting is a strength-training exercise that primarily targets muscle development rather than caloric burn. However, incorporating weightlifting into a comprehensive fitness plan can increase overall caloric expenditure by building lean muscle mass, which in turn increases resting metabolic rate. Cycling can complement weightlifting by providing cardiovascular exercise and promoting active recovery.
Comparing caloric expenditure across different activities highlights the unique benefits and drawbacks of cycling as a calorie-burning exercise. While other activities may burn more calories in specific scenarios, cycling offers a sustainable, low-impact, and accessible option for many individuals seeking to improve their fitness and burn calories.
Maximizing Caloric Expenditure During Cycling Sessions
To maximize the number of calories burned during bike rides, incorporating interval training, adjusting resistance, and maintaining proper posture can significantly impact caloric expenditure. These practical tips and techniques can help cyclists increase their overall caloric burn and improve their fitness levels.
Incorporating Interval Training
Interval training involves alternating between high-intensity and low-intensity periods during a workout. This approach can help cyclists burn more calories in less time by increasing their heart rate and metabolic rate. Incorporating interval training into cycling sessions can be as simple as alternating between high-cadence sprints and recovery periods or tackling challenging hills followed by rest intervals.
Adjusting Resistance
Adjusting resistance on a bike can help cyclists build strength and endurance, ultimately leading to a higher caloric burn. Incorporating resistance training into cycling sessions can be done by increasing the resistance on a stationary bike or tackling uphill climbs during outdoor rides. By challenging the muscles, cyclists can improve their overall fitness and caloric expenditure.
Maintaining Proper Posture
Maintaining proper posture during a bike ride can help cyclists engage the correct muscles and optimize their pedaling efficiency. A proper cycling position involves keeping the back straight, engaging the core, and ensuring a comfortable grip on the handlebars. By maintaining proper posture, cyclists can reduce strain on their bodies and maximize their caloric burn during rides.
Maximizing caloric expenditure during cycling sessions can be achieved through incorporating interval training, adjusting resistance, and maintaining proper posture. These practical tips and techniques can help cyclists increase their overall caloric burn, improve their fitness levels, and achieve their exercise goals.
Incorporating Cycling into a Comprehensive Fitness Plan
Cycling can be an integral part of a well-rounded fitness plan when combined with cross-training, rest days, and proper nutrition. By considering these factors, cyclists can optimize their overall fitness, reduce the risk of injury, and achieve their exercise goals.
Cross-Training
Cross-training involves incorporating various exercises and activities into a fitness routine to improve overall fitness and reduce the risk of injury. For cyclists, cross-training can include activities such as weightlifting, swimming, or yoga. By engaging different muscle groups and energy systems, cross-training can help cyclists improve their strength, flexibility, and endurance, ultimately leading to increased caloric burn during bike rides.
Rest Days
Rest days are crucial for allowing the body to recover and rebuild after intense exercise sessions. By incorporating rest days into a fitness plan, cyclists can prevent overtraining, reduce the risk of injury, and improve their overall performance. During rest days, the body can repair damaged muscle tissue, replenish energy stores, and adapt to the demands of cycling, ultimately leading to increased caloric burn during subsequent rides.
Nutrition
Proper nutrition plays a significant role in optimizing caloric burn during cycling sessions. Consuming a balanced diet rich in carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats can help cyclists fuel their workouts, recover more efficiently, and improve their overall fitness. Additionally, staying hydrated before, during, and after bike rides can help maintain energy levels, regulate body temperature, and support overall performance.
Incorporating cycling into a comprehensive fitness plan involves considering factors such as cross-training, rest days, and nutrition. By balancing cardiovascular exercise with strength training and flexibility workouts, cyclists can optimize their overall fitness, reduce the risk of injury, and achieve their exercise goals.
Real-World Examples: Caloric Expenditure in Popular Bike Rides
Understanding the number of calories burned during real-world bike rides can help cyclists set realistic exercise goals and track their fitness progress. Here are a few examples of caloric expenditure in popular bike rides, such as Tour de France stages, famous cycling events, and local bike trails.
Tour de France Stages
Tour de France stages vary in length and terrain, resulting in different caloric burns for riders. For instance, a 100-mile (160.9 km) mountain stage with an average speed of 20 mph (32.1 km/h) and an elevation gain of 10,000 feet (3,048 m) can burn approximately 5,000 to 6,000 calories for a professional cyclist. However, for an amateur cyclist, the caloric burn may be closer to 3,000 to 4,000 calories, depending on their weight, intensity, and fitness level.
Famous Cycling Events
Other famous cycling events, such as the Paris-Roubaix or the Giro d’Italia, can also result in significant caloric burns. For example, a 100-mile (160.9 km) Paris-Roubaix race with an average speed of 25 mph (40.2 km/h) and numerous cobblestone sections can burn approximately 4,000 to 5,000 calories for an amateur cyclist. Similarly, a 100-mile (160.9 km) Giro d’Italia stage with an average speed of 22 mph (35.4 km/h) and challenging mountain climbs can burn around 3,500 to 4,500 calories for an amateur cyclist.
Local Bike Trails
Local bike trails offer opportunities for recreational cyclists to enjoy scenic rides while tracking their caloric burn. For instance, a 20-mile (32.2 km) trail ride with an average speed of 15 mph (24.1 km/h) and moderate hills can burn approximately 800 to 1,200 calories for an amateur cyclist, depending on their weight and fitness level.
Real-world examples of caloric expenditure in popular bike rides, such as Tour de France stages, famous cycling events, and local bike trails, can help cyclists set realistic exercise goals and track their fitness progress. By understanding the factors contributing to caloric burn, cyclists can optimize their workouts and achieve their exercise objectives.
Maintaining Motivation and Tracking Progress
Staying motivated and tracking progress in caloric expenditure and overall fitness is crucial for long-term success in cycling. By setting personal goals, joining cycling groups, and celebrating achievements, cyclists can maintain their motivation and continue to improve their fitness levels.
Setting Personal Goals
Setting specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals can help cyclists maintain their motivation and track their progress. For example, a cyclist might aim to complete a 50-mile (80.5 km) ride within three months, gradually increasing their weekly mileage to prepare. By breaking down larger goals into smaller, manageable steps, cyclists can stay motivated and monitor their progress over time.
Joining Cycling Groups
Joining cycling groups can provide cyclists with a sense of community, support, and accountability. By participating in group rides, cyclists can challenge themselves, learn from more experienced riders, and build lasting friendships. Additionally, group rides can help cyclists maintain their motivation by providing a regular schedule of rides and social interactions.
Celebrating Achievements
Celebrating achievements, no matter how small, can help cyclists stay motivated and recognize their progress. By acknowledging their accomplishments, cyclists can boost their confidence, self-esteem, and motivation to continue improving. Celebrating achievements can include treating oneself to a new piece of cycling gear, enjoying a favorite meal, or sharing successes with friends and family.
Maintaining motivation and tracking progress in caloric expenditure and overall fitness is essential for long-term success in cycling. By setting personal goals, joining cycling groups, and celebrating achievements, cyclists can stay motivated, monitor their progress, and continue to improve their fitness levels.