The Significance of Strong Leg Muscles
Building leg muscles is an essential aspect of any comprehensive fitness regimen. Strong leg muscles contribute to improved stability, balance, and athletic performance. By focusing on leg muscle development, individuals can enhance their overall fitness and reduce the risk of injuries during various activities, both in and out of the gym.
Leg muscles play a crucial role in everyday movements, such as walking, running, jumping, and lifting. A well-developed lower body can help distribute weight evenly, reducing the strain on joints and promoting proper posture. Furthermore, strong leg muscles can improve power and explosiveness in sports and other physical pursuits, making them an essential component of any training program.
Moreover, building leg muscles goes beyond the immediate benefits of increased strength and improved functionality. A balanced lower body workout routine can contribute to a leaner, more defined physique, as leg muscles are some of the largest and most metabolically active in the human body. As a result, focusing on leg muscle development can lead to increased caloric expenditure, even at rest, supporting weight loss and overall health goals.
In summary, the significance of strong leg muscles cannot be overstated. By incorporating a leg-focused workout routine into a comprehensive fitness plan, individuals can enjoy numerous benefits, including improved stability, balance, athletic performance, and overall fitness. In the following sections, we will explore the anatomy of leg muscles, effective exercises, and various strategies to support leg muscle growth and development.
Understanding the Anatomy of Leg Muscles
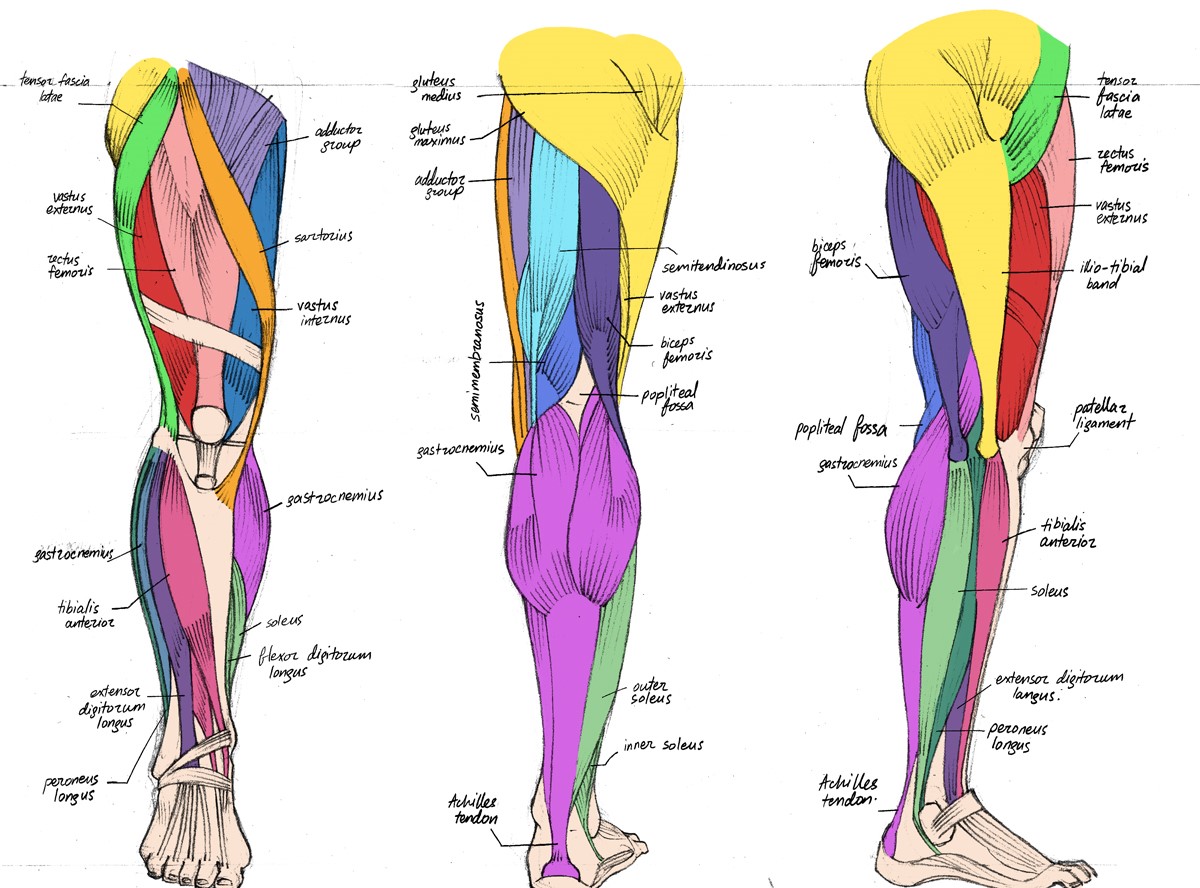
To effectively build up leg muscles, it is crucial to understand the major muscle groups in the lower body and their functions. The primary muscle groups in the legs include the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and calves. These muscle groups work together during lower body exercises, contributing to overall leg strength and stability.
Quadriceps
The quadriceps, located at the front of the thigh, are a group of four muscles responsible for extending the knee and stabilizing the leg during movements such as squats and lunges. The four muscles that make up the quadriceps are the rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, and vastus intermedius.
Hamstrings
The hamstrings, located at the back of the thigh, are a group of three muscles primarily responsible for flexing the knee and extending the hip. The three muscles that make up the hamstrings are the biceps femoris, semitendinosus, and semimembranosus.
Glutes
The glutes, located at the buttocks, are a group of three muscles primarily responsible for hip extension, external rotation, and abduction. The three muscles that make up the glutes are the gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, and gluteus minimus.
Calves
The calves, located at the back of the lower leg, are a group of two muscles primarily responsible for plantar flexion, or pointing the foot downward. The two muscles that make up the calves are the gastrocnemius and the soleus.
Understanding the anatomy of leg muscles is essential for designing an effective leg-focused workout routine. By targeting each muscle group with specific exercises, individuals can ensure balanced muscle development and maximize their potential for leg muscle growth and strength.
Designing a Leg-Focused Workout Routine
A well-structured leg-focused workout routine is essential for building up leg muscles effectively. Key elements to consider when designing a leg workout include exercise selection, volume, frequency, and intensity. Additionally, incorporating progressive overload and periodization can help maximize muscle growth and strength gains over time.
Exercise Selection
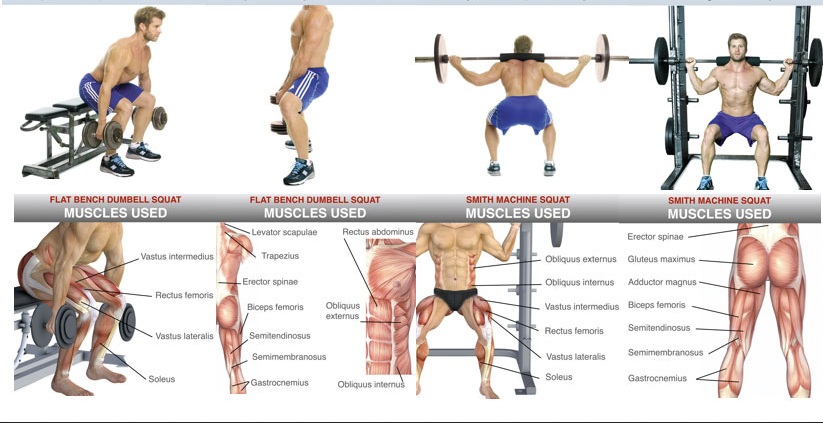
Choose exercises that target each of the major muscle groups in the legs, including the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and calves. Some effective exercises for building leg muscles include squats, lunges, deadlifts, leg presses, and calf raises. For a comprehensive workout, include both compound and isolation exercises to ensure balanced muscle development.
Volume
Volume refers to the total amount of work performed during a workout, often measured by the number of sets and repetitions for each exercise. Aim for 3-5 sets of 8-12 repetitions for each exercise, focusing on proper form and technique. Adjust the volume as needed to challenge the muscles and promote growth without causing excessive fatigue or increasing the risk of injury.
Frequency
Frequency refers to the number of times a muscle group is trained per week. For leg muscle development, aim to train the legs 2-3 times per week, allowing adequate recovery time between workouts. This can be achieved by incorporating leg exercises into a full-body workout routine or dedicating separate days to leg-focused training sessions.
Intensity
Intensity refers to the amount of weight or resistance used during exercises. To build leg muscles, gradually increase the intensity by adding weight or resistance as strength improves. This can help promote muscle growth, enhance strength gains, and challenge the body to adapt and grow.
Progressive Overload and Periodization
Progressive overload involves gradually increasing the volume, frequency, or intensity of a workout over time. This can help ensure continued muscle growth and strength gains, as the body is constantly challenged to adapt and grow. Periodization, or the strategic planning of workout phases, can also support long-term leg muscle development by varying the training intensity, volume, and exercise selection throughout different stages of a training program.
Effective Exercises for Building Leg Muscles
A well-rounded leg workout routine should include a variety of exercises that target each of the major muscle groups in the legs. By incorporating both compound and isolation exercises, individuals can ensure balanced muscle development and maximize their potential for leg muscle growth and strength.
Squats
Squats are a compound exercise that primarily targets the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes. To perform a squat, stand with feet hip-width apart, and hold a barbell or dumbbells at shoulder level. Slowly lower the body as if sitting back into a chair, keeping the knees behind the toes and the back straight. Pause at the bottom of the movement, then push through the heels to return to the starting position.
Lunges
Lunges are a versatile exercise that targets the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes. To perform a lunge, stand with feet hip-width apart and take a large step forward with one foot. Lower the body until the front thigh is parallel with the floor and the back knee is nearly touching the ground. Push through the front heel to return to the starting position, then repeat with the opposite leg.
Nutritional Strategies for Leg Muscle Growth
Nutrition plays a vital role in muscle growth and recovery, particularly when focusing on building up leg muscles. By following a well-balanced diet and incorporating specific nutritional strategies, individuals can optimize their muscle growth and support their leg muscle development goals.
Protein Intake
Protein is an essential macronutrient for muscle growth and repair. Aim to consume 1.2-1.6 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight daily to support muscle recovery and growth. Include a variety of protein sources in your diet, such as lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy, legumes, and nuts.
Caloric Surplus
To build leg muscles, it is essential to consume more calories than you burn, creating a caloric surplus. This excess energy can be used to support muscle growth and recovery. Aim for a surplus of 250-500 calories per day, adjusting as needed based on progress and body composition changes.
Hydration
Proper hydration is crucial for overall health, exercise performance, and muscle recovery. Aim to drink at least 8-10 cups of water per day, increasing your intake as needed based on activity level, climate, and individual needs. Consuming water before, during, and after workouts can also help maintain hydration and support muscle function.
Supplements
While a well-balanced diet should provide all the necessary nutrients for muscle growth and recovery, some supplements may support leg muscle development. Creatine, a naturally occurring compound found in small amounts in some foods, can help increase muscle strength and size. Beta-alanine, an amino acid, may also help improve exercise performance and reduce muscle fatigue.
Meal Timing
While meal timing is not as critical as overall diet and caloric intake, consuming protein and carbohydrates after a workout may help promote muscle recovery and growth. Aim to consume a meal or protein shake containing 20-30 grams of protein and 30-50 grams of carbohydrates within 30-60 minutes of completing your leg workout.
Incorporating Cardiovascular Training for Leg Endurance
Cardiovascular training can provide numerous benefits for leg endurance and overall fitness when building up leg muscles. By incorporating various forms of cardio into your leg-focused workout routine, you can improve your leg muscle endurance, cardiovascular health, and overall athletic performance.
Benefits of Cardiovascular Training
Cardiovascular training offers several benefits for leg muscle development, including improved leg endurance, increased caloric expenditure, enhanced cardiovascular health, and reduced risk of injury. By incorporating cardio into your workout routine, you can challenge your leg muscles in new ways, promoting muscle growth and supporting overall fitness goals.
Forms of Cardio
Various forms of cardio can be incorporated into a leg-focused workout routine, including running, cycling, swimming, and stair climbing. Choose activities that you enjoy and that target the leg muscles, ensuring a challenging and engaging workout experience.
Incorporating Cardio into Your Workout Routine
To effectively incorporate cardio into your leg-focused workout routine, consider the following strategies:
- Perform cardio on separate days from strength training: Allowing adequate recovery time between strength training and cardio sessions can help prevent fatigue and ensure optimal muscle growth and performance.
- Incorporate cardio after strength training: Performing cardio after a leg workout can help improve leg muscle endurance and promote overall fitness gains.
- Alternate between high-intensity interval training (HIIT) and steady-state cardio: HIIT workouts involve short bursts of high-intensity exercise followed by periods of rest, while steady-state cardio involves maintaining a consistent pace for an extended period. Alternating between these two forms of cardio can help challenge the leg muscles in different ways and promote overall fitness gains.
By incorporating cardiovascular training into your leg-focused workout routine, you can improve leg endurance, support overall fitness goals, and enhance your athletic performance. Remember to listen to your body, prioritize recovery, and adjust your cardio routine as needed based on progress and individual needs.
Tracking Progress and Setting Realistic Goals
Tracking progress and setting realistic goals are essential components of a successful leg muscle development plan. By monitoring your strength gains, muscle growth, and performance improvements, you can stay motivated, identify areas for improvement, and adjust your workout routine as needed to achieve your desired results.
Monitoring Strength Gains
Tracking strength gains is an effective way to measure progress and determine the effectiveness of your leg-focused workout routine. Consider keeping a workout log or journal, where you can record the exercises, sets, repetitions, and weights used during each workout. Regularly reviewing this information can help you identify trends, set new goals, and make adjustments to your workout routine as needed.
Measuring Muscle Growth
Monitoring muscle growth can be more challenging than tracking strength gains, as it requires regular measurements of muscle size and definition. Consider using a tape measure to track changes in the circumference of your legs, or take progress photos to visually assess muscle development over time. Remember that muscle growth is a gradual process, and it may take several weeks or months to notice significant changes.
Assessing Performance Improvements
Assessing performance improvements involves evaluating your overall fitness level, athletic ability, and endurance. Consider tracking your running or cycling times, the number of repetitions completed during leg exercises, or your ability to perform new or more challenging exercises. Regularly assessing performance improvements can help you identify areas for improvement and adjust your workout routine accordingly.
Setting Realistic Goals
Setting realistic goals is crucial for maintaining motivation and achieving success in leg muscle development. Consider setting short-term and long-term goals, such as increasing the weight used during leg exercises, adding new exercises to your workout routine, or achieving a specific level of muscle definition. Remember to be patient, as building leg muscles takes time, dedication, and consistency.
Staying Motivated and Overcoming Plateaus
Staying motivated and overcoming plateaus are essential for long-term success in leg muscle development. Consider incorporating variety into your workout routine, seeking guidance from fitness professionals, and prioritizing rest and recovery to help maintain motivation and prevent plateaus. Remember that progress may be slow at times, but with persistence and dedication, you can achieve your leg muscle development goals.
Maintaining Motivation and Overcoming Plateaus
Maintaining motivation and overcoming plateaus are essential aspects of building leg muscles. By incorporating variety into your workout routine, prioritizing rest and recovery, and seeking guidance from fitness professionals, you can stay motivated and continue making progress towards your leg muscle development goals.
Incorporating Variety into Your Workout Routine
Incorporating variety into your workout routine can help maintain motivation and prevent plateaus in leg muscle development. Consider changing the exercises, sets, repetitions, or weights used during each workout, or alternating between different workout routines on a regular basis. This can help challenge your leg muscles in new ways, promote muscle growth, and prevent boredom or stagnation.
Prioritizing Rest and Recovery
Rest and recovery are essential components of a successful leg muscle development plan. Ensure that you are getting adequate sleep, taking rest days between workouts, and allowing your leg muscles time to recover and rebuild after each workout. This can help prevent injury, reduce muscle soreness, and promote optimal muscle growth and performance.
Seeking Guidance from Fitness Professionals
Seeking guidance from fitness professionals, such as personal trainers or coaches, can help maintain motivation and overcome plateaus in leg muscle development. Fitness professionals can provide personalized advice, feedback, and support, helping you to refine your workout routine, improve your form and technique, and achieve your leg muscle development goals.
Staying Motivated
Staying motivated is essential for long-term success in leg muscle development. Consider setting short-term and long-term goals, tracking your progress, and celebrating your achievements along the way. Remember that building leg muscles takes time, dedication, and consistency, and that setbacks and plateaus are a natural part of the process.
Overcoming Plateaus
Overcoming plateaus in leg muscle development can be challenging, but it is possible with persistence and dedication. Consider reassessing your workout routine, adjusting your nutrition or supplement plan, or seeking guidance from fitness professionals to help break through plateaus and continue making progress towards your leg muscle development goals.