Knee Pain Symptoms: Identifying the Source of Discomfort
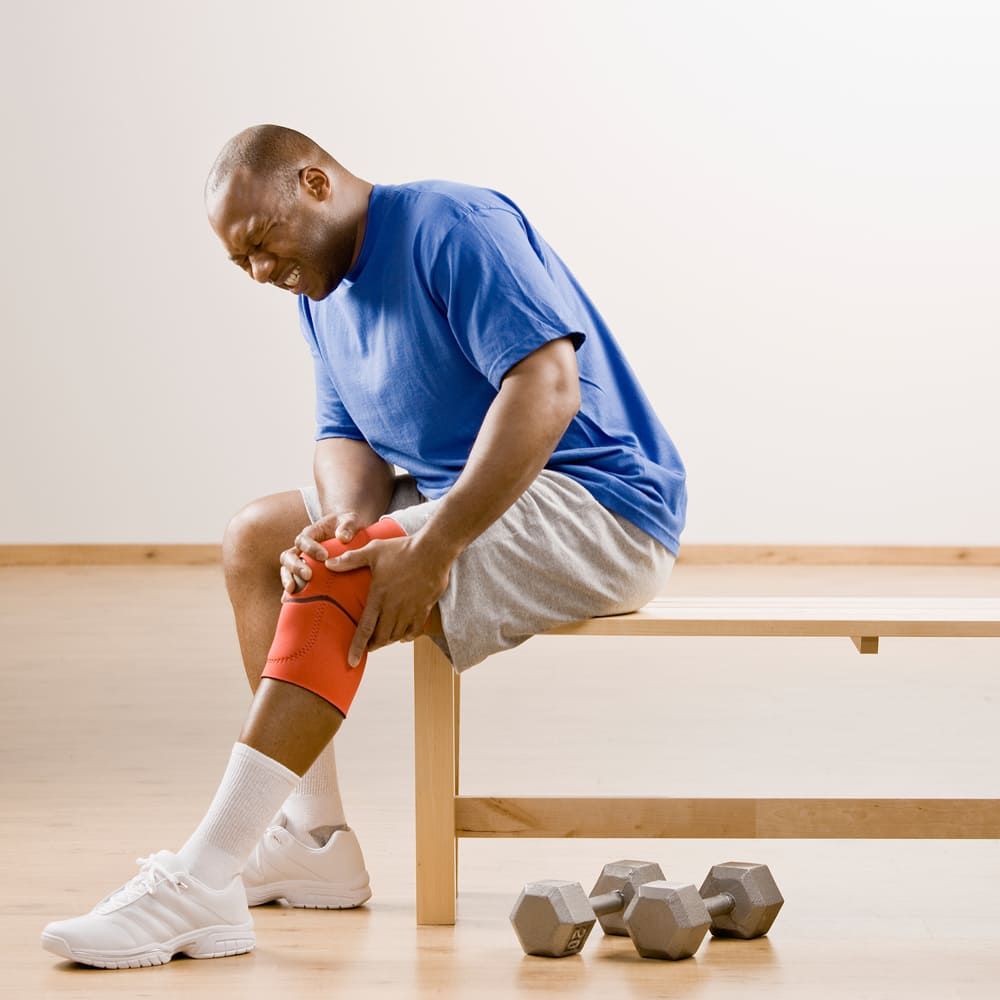
Knee-related leg pain can manifest in various ways, making it essential to recognize the common symptoms and identify the underlying cause of the discomfort. Sharp pain, dull aches, swelling, and limited mobility are all potential indicators of pain in the leg right above the knee. These symptoms can be triggered by a range of factors, from overuse injuries to underlying medical conditions.
Identifying the source of pain in the leg right above the knee is crucial for effective treatment and management. Failing to address the underlying cause can lead to prolonged recovery times, increased risk of further injury, and decreased quality of life. By recognizing the symptoms and understanding their causes, individuals can take the first step towards alleviating their pain and regaining optimal knee function.
The Anatomy of the Knee: How It Affects Leg Pain
The knee is a complex joint that consists of bones, ligaments, and tendons. The bones involved in the knee joint include the femur (thigh bone), tibia (shin bone), and patella (kneecap). The ligaments, such as the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), connect the bones and provide stability to the joint. The tendons, including the quadriceps and hamstring tendons, connect the muscles to the bones and facilitate movement.
Injuries or conditions affecting these structures can lead to pain in the leg above the knee. For instance, a torn ACL or PCL can cause instability and pain in the knee, which can radiate to the leg above the knee. Similarly, tendinitis or bursitis in the quadriceps or hamstring tendons can cause pain and inflammation in the leg above the knee. Understanding the anatomy of the knee is essential for identifying the underlying cause of pain in the leg right above the knee and developing an effective treatment plan.
How to Diagnose the Cause of Your Knee-Related Leg Pain
Diagnosing the cause of knee-related leg pain requires a combination of self-assessment, medical evaluation, and diagnostic tests. The first step is to identify the symptoms and characteristics of the pain, including its location, severity, and duration. Individuals can ask themselves questions such as: Is the pain sharp or dull? Is it constant or intermittent? Does it worsen with activity or improve with rest?
A medical evaluation by a healthcare professional is also essential for diagnosing the cause of knee-related leg pain. The doctor will perform a physical examination, take a medical history, and may order diagnostic tests such as X-rays, MRIs, or ultrasound to rule out underlying conditions. The doctor may also perform specific tests, such as the Lachman test or the McMurray test, to assess the stability and function of the knee joint.
In some cases, diagnostic tests may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis. X-rays can help identify bone fractures or degenerative joint disease, while MRIs can detect soft tissue injuries, such as torn ligaments or tendons. Ultrasound can also be used to evaluate the tendons and ligaments surrounding the knee joint.
By combining self-assessment, medical evaluation, and diagnostic tests, individuals can identify the underlying cause of their knee-related leg pain and develop an effective treatment plan to alleviate their symptoms and restore optimal knee function. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for addressing pain in the leg right above the knee and preventing further injury or complications.
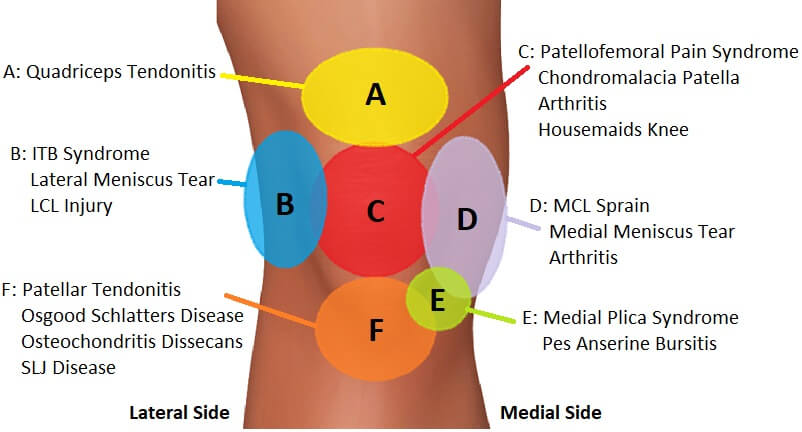
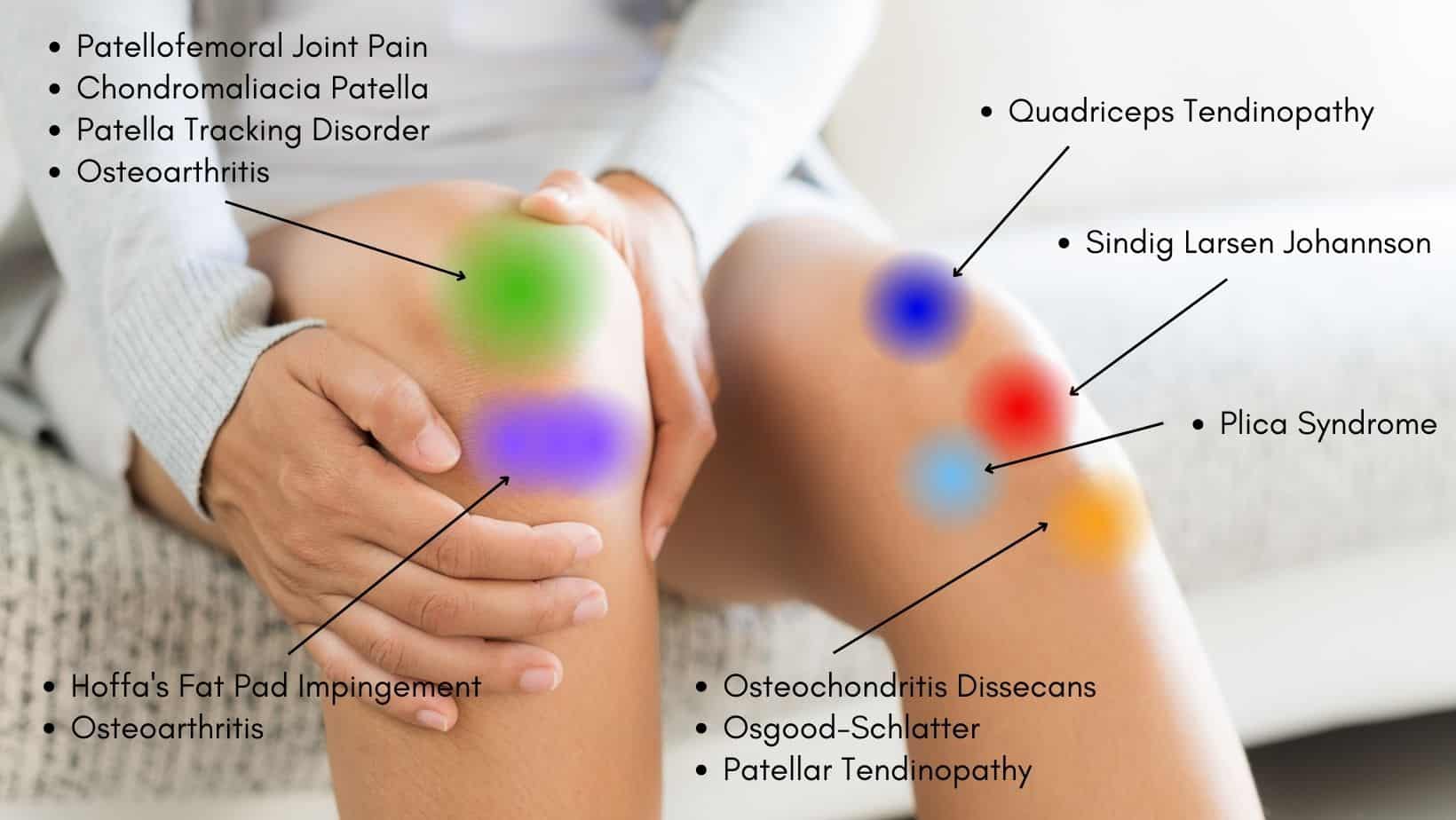
Common Causes of Pain in the Leg Right Above the Knee
Pain in the leg right above the knee can be caused by a variety of factors. Some of the most common causes include runner’s knee, IT band syndrome, patellofemoral pain syndrome, and bursitis. Understanding the underlying cause of the pain is essential for developing an effective treatment plan.
Runner’s knee, also known as patellofemoral pain syndrome, is a common condition that affects the knee joint. It is characterized by pain in the front of the knee, usually around the kneecap, and is often caused by overuse, poor tracking of the kneecap, or weak quadriceps muscles.
IT band syndrome is another common cause of pain in the leg right above the knee. The IT band is a ligament that runs down the outside of the thigh, from the hip to the knee. Friction between the IT band and the lateral condyle of the femur can cause pain and inflammation, especially in runners and cyclists.
Bursitis is a condition that affects the fluid-filled sacs, or bursae, that cushion the joints and reduce friction. Inflammation of the bursae in the knee joint can cause pain, swelling, and limited mobility, especially in the leg right above the knee.
Other causes of pain in the leg right above the knee include tendonitis, osteoarthritis, and meniscal tears. Tendonitis is inflammation of the tendons, which connect the muscles to the bones. Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that can cause pain and stiffness in the knee joint. Meniscal tears are tears in the cartilage that cushions the knee joint, and can cause pain, swelling, and limited mobility.
Accurate diagnosis of the underlying cause of pain in the leg right above the knee is essential for developing an effective treatment plan. By understanding the common causes of this type of pain, individuals can take the first step towards alleviating their symptoms and restoring optimal knee function.
Treatment Options for Knee-Related Leg Pain
Treatment for pain in the leg right above the knee typically involves a combination of conservative and invasive approaches. The goal of treatment is to alleviate symptoms, restore optimal knee function, and prevent future episodes of pain.
Conservative treatment options for knee-related leg pain include rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). This approach is often effective in reducing pain and inflammation, especially in the early stages of injury or condition. Physical therapy can also be beneficial in strengthening the surrounding muscles, improving flexibility, and enhancing knee function.
Bracing can also be used to provide additional support and stability to the knee joint. This can be particularly helpful for individuals with ligamentous injuries or conditions such as patellofemoral pain syndrome. In some cases, orthotics or shoe inserts may be recommended to correct biomechanical abnormalities and reduce stress on the knee joint.
Surgical intervention may be necessary in cases where conservative treatment has been unsuccessful or if the underlying condition is severe. Surgical options may include arthroscopy, ligament reconstruction, or joint replacement. It is essential to discuss the benefits and drawbacks of each approach with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate course of treatment.
In addition to these treatment options, lifestyle modifications can also play a crucial role in alleviating pain in the leg right above the knee. This may include avoiding activities that exacerbate the condition, incorporating low-impact exercises into daily routines, and maintaining a healthy weight to reduce stress on the knee joint.
Ultimately, the most effective treatment plan for knee-related leg pain will depend on the underlying cause of the condition, as well as the individual’s overall health and lifestyle. By working with a healthcare professional and exploring the various treatment options available, individuals can develop a personalized plan to alleviate their symptoms and restore optimal knee function.
Exercises and Stretches to Relieve Knee-Related Leg Pain
Engaging in regular exercises and stretches can help alleviate pain in the leg right above the knee by strengthening the surrounding muscles, improving flexibility, and enhancing knee function. Here are some exercises and stretches that can be beneficial:
Quadriceps Strengthening Exercises: Weak quadriceps muscles can contribute to pain in the leg right above the knee. Strengthening these muscles through exercises such as leg extensions, leg presses, and squats can help alleviate symptoms.
Hamstring Stretches: Tight hamstring muscles can put additional stress on the knee joint, leading to pain. Stretching the hamstrings through exercises such as standing hamstring stretches and seated hamstring stretches can help reduce tension and alleviate pain.
IT Band Stretches: The IT band is a ligament that runs down the outside of the thigh, from the hip to the knee. Stretching the IT band through exercises such as standing IT band stretches and side-lying IT band stretches can help reduce friction and alleviate pain.
Patellar Mobilization Exercises: The patella, or kneecap, can become misaligned, leading to pain in the leg right above the knee. Mobilizing the patella through exercises such as patellar mobilization exercises can help restore proper tracking and alleviate symptoms.
It is essential to note that before starting any exercise or stretch program, individuals should consult with a healthcare professional to ensure that the exercises are appropriate for their specific condition and needs. Additionally, it is crucial to start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and frequency of exercises to avoid exacerbating the condition.
By incorporating these exercises and stretches into daily routines, individuals can help alleviate pain in the leg right above the knee, improve knee function, and reduce the risk of future episodes of pain.
Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Future Knee-Related Leg Pain
Making lifestyle changes can play a crucial role in preventing future episodes of pain in the leg right above the knee. By incorporating simple modifications into daily routines, individuals can reduce the risk of knee-related leg pain and maintain optimal knee function.
Proper Footwear: Wearing shoes that fit properly and provide adequate support can help reduce stress on the knee joint. Avoiding high heels, flat shoes, or shoes with inadequate arch support can help prevent pain in the leg right above the knee.
Orthotics: Custom orthotics or shoe inserts can help correct biomechanical abnormalities and reduce stress on the knee joint. These devices can be particularly beneficial for individuals with conditions such as overpronation or flat feet.
Modifications to Daily Activities: Avoiding activities that exacerbate pain in the leg right above the knee can help prevent future episodes of pain. This may include avoiding repetitive bending, twisting, or heavy lifting, and taking regular breaks to rest and stretch.
Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce stress on the knee joint and prevent pain in the leg right above the knee. Even small amounts of weight loss can make a significant difference in reducing the risk of knee-related leg pain.
Proper Running and Exercise Techniques: For individuals who engage in regular exercise or running, proper techniques can help reduce the risk of knee-related leg pain. This may include avoiding overstriding, wearing proper footwear, and incorporating strengthening exercises into training routines.
By incorporating these lifestyle changes into daily routines, individuals can reduce the risk of pain in the leg right above the knee and maintain optimal knee function. It is essential to remember that prevention is key, and making small changes now can have a significant impact on knee health in the long run.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Knee-Related Leg Pain
While knee-related leg pain can often be managed with self-care techniques and lifestyle changes, there are certain scenarios in which it is essential to seek medical attention. Failing to do so can lead to further injury, prolonged recovery, and increased risk of chronic pain.
Severe Pain: If pain in the leg right above the knee is severe, sudden, or accompanied by a popping or snapping sound, medical attention should be sought immediately. This could be indicative of a serious injury, such as a torn ligament or broken bone.
Swelling: Significant swelling in the knee or leg can be a sign of a more serious underlying condition, such as a fracture, infection, or inflammatory disorder. Medical attention should be sought if swelling is severe, rapid, or accompanied by pain, redness, or warmth.
Limited Mobility: If pain in the leg right above the knee is accompanied by limited mobility, stiffness, or difficulty walking, medical attention should be sought. This could be indicative of a more serious underlying condition, such as a meniscal tear or ligament sprain.
Fever: If pain in the leg right above the knee is accompanied by a fever, medical attention should be sought. This could be indicative of an infection, such as septic arthritis or cellulitis.
Redness or Warmth: If the knee or leg is red, warm, or tender to the touch, medical attention should be sought. This could be indicative of an infection or inflammatory disorder.
By seeking medical attention in these scenarios, individuals can receive prompt diagnosis and treatment, reducing the risk of further injury and promoting optimal recovery from pain in the leg right above the knee.