Introduction: The Need for eBike Classifications
Understanding eBike classifications is crucial for riders, regulators, and manufacturers alike, as the popularity of eBikes continues to soar. Clear guidelines are essential to ensure safety, promote fair access to cycling infrastructure, and foster a thriving eBike industry. With the rapid growth of eBike technology and usage, it is increasingly important to distinguish between different eBike classifications to make informed decisions and comply with local regulations.

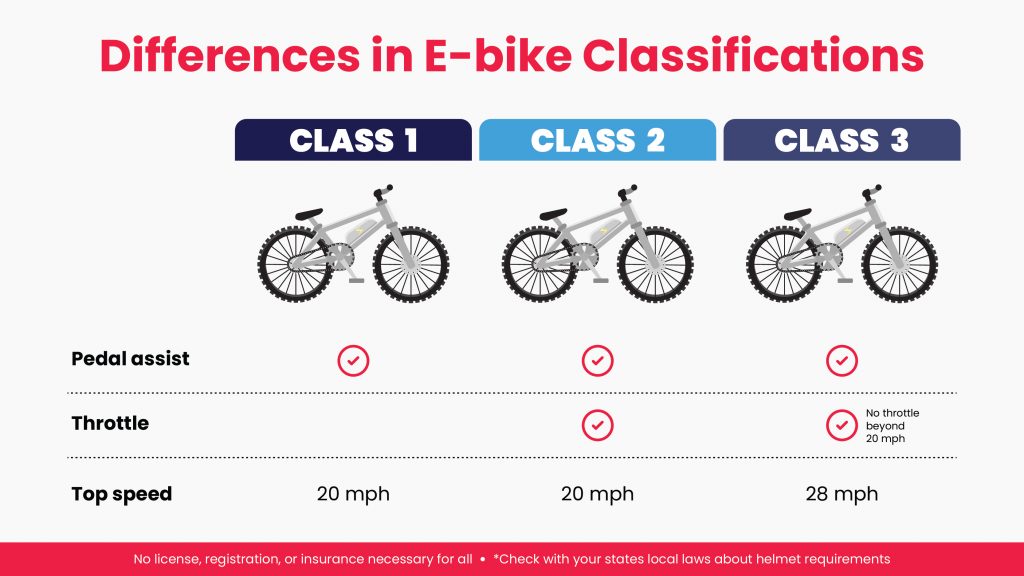
Class 1 eBikes: Pedal-Assist with a Throttle Limit
Class 1 eBikes, also known as pedal-assist bikes, offer riders an electric motor that provides assistance only when the rider is pedaling. This classification has a throttle limit of up to 20 mph, ensuring that the motor will not propel the bike beyond this speed without pedal input. Class 1 eBikes are popular among commuters, recreational riders, and fitness enthusiasts who seek a low-impact workout or an alternative mode of transportation.
These eBikes are designed for various terrains, from paved roads and bike paths to light off-road trails. They cater to a wide range of riders, including those with physical limitations who may need motor assistance to maintain their cycling hobby. Class 1 eBikes can be found in specialty bike shops, online retailers, and some department stores, making them accessible to a broad audience.
Class 2 eBikes: Throttle-Assist with a Speed Limit
Class 2 eBikes are characterized by their throttle-assist feature, which propels the bike forward without the need for pedaling. The motor assistance in this classification is limited to a top speed of 20 mph, ensuring that the bike does not exceed this speed when using the throttle. This class is popular among commuters and urban riders who seek a convenient and effortless mode of transportation.
Class 2 eBikes cater to a wide range of users, including those with physical limitations or those who prefer a more leisurely riding experience. They are suitable for various terrains, including paved roads, bike paths, and some light off-road trails. These eBikes can be found in specialty bike shops, online retailers, and department stores, making them easily accessible to potential buyers.

Class 3 eBikes: Speed Pedelecs with a Throttle Limit
Class 3 eBikes, also known as speed pedelecs, offer a unique blend of power and speed. These bikes are equipped with a pedal-assist motor that can reach a maximum speed of 28 mph, making them an appealing option for commuters and fitness enthusiasts seeking a faster and more efficient mode of transportation. Like Class 2 eBikes, Class 3 models can also have a throttle-assist feature, but it is limited to speeds of 20 mph.
Class 3 eBikes cater to experienced riders who are comfortable with higher speeds and have a solid understanding of traffic rules and safety regulations. Due to their increased speed capabilities, these eBikes are typically not allowed on bike paths or trails that have a speed limit of 20 mph or lower. Instead, they are designed for use on roads and other areas where higher-speed traffic is common.
How to Choose the Right eBike Classification for You
Selecting the appropriate eBike classification is crucial for ensuring a safe and enjoyable riding experience. To make an informed decision, consider the following factors:
- Riding style: Determine how you plan to use your eBike. If you prefer a more leisurely ride, a Class 1 or Class 2 eBike may be suitable. For a faster and more intense workout, consider a Class 3 eBike. If you’re interested in off-road adventures, look into eBikes designed for trails and rough terrains.
- Experience: Assess your cycling experience and comfort level with various types of eBikes. Novice riders may want to start with a Class 1 or Class 2 eBike, while more experienced cyclists might prefer the speed and power of a Class 3 eBike.
- Local regulations: Familiarize yourself with eBike laws and regulations in your area. Some regions have restrictions on where certain classes of eBikes can be ridden, so it’s essential to choose a classification that complies with local rules.
Once you’ve determined the right eBike classification for your needs, explore your options by visiting local bike shops, searching online retailers, and participating in eBike community forums. By engaging with fellow riders and industry experts, you can gain valuable insights and make a well-informed decision.

eBike Classification Laws and Regulations: A Global Perspective
As the eBike market continues to expand, understanding local laws and regulations is essential for riders, regulators, and manufacturers alike. eBike classification laws vary significantly from one country to another, with some regions adopting more stringent rules than others. Here, we explore eBike classification laws and regulations in several countries, highlighting similarities and differences.
- United States: The U.S. has three primary eBike classifications, as described in previous sections. Federal law categorizes eBikes as two- or three-wheeled vehicles with fully operable pedals and a motor of no more than 750 watts. State and local regulations may impose additional restrictions, so it’s crucial to research local laws before purchasing and riding an eBike.
- Canada: Canada follows a similar three-class system, with maximum assisted speeds of 32 km/h (20 mph) for Class 1 and Class 2 eBikes and 45 km/h (28 mph) for Class 3 eBikes. Helmets are mandatory for all riders, and eBikes are subject to the same rules as traditional bicycles in most provinces. However, some provinces have age restrictions and require a driver’s license and registration for Class 3 eBikes.
- European Union: The European Union has established a harmonized eBike classification system, categorizing eBikes as those with pedal assistance up to 25 km/h (15.5 mph) and a motor power output of no more than 250 watts. Throttle-assist eBikes are not permitted under this system. EU member states may impose additional requirements, such as helmet use, age restrictions, and insurance.
- Australia: Australia’s eBike classification system is complex, with various state-specific regulations. Generally, eBikes are classified as either “power-assisted pedal cycles” (PAPCs) or motorcycles. PAPCs must have a maximum motor power output of 200 watts, and pedal assistance must cease at 25 km/h (15.5 mph). Some states allow throttle-assist eBikes, while others do not. Helmet use and age restrictions vary by state.
Understanding local eBike laws and regulations is crucial for ensuring a safe and enjoyable riding experience. Before purchasing an eBike, research your region’s specific rules and regulations to ensure compliance and avoid potential legal issues. By staying informed and adhering to local guidelines, riders can contribute to the safe and responsible growth of the eBike community.

The Future of eBike Classifications: Trends and Predictions
As the eBike market continues to evolve, understanding emerging trends and future predictions for eBike classifications is essential for riders and the industry alike. Advances in technology and potential regulatory changes may significantly impact eBike classifications, leading to new opportunities and challenges.
- Smart eBike Technology: The integration of smart technology in eBikes is becoming increasingly popular. Features such as GPS tracking, mobile app integration, and advanced battery management systems can enhance the user experience and potentially influence future eBike classification regulations. As smart eBikes become more prevalent, regulators may need to adapt classification criteria to accommodate these advancements.
- Adaptive eBikes: Adaptive eBikes, designed for riders with disabilities or mobility challenges, are gaining traction in the market. These eBikes often feature specialized components and assistance systems, which may not fit neatly into existing classification categories. As adaptive eBikes become more common, regulators may need to reevaluate classification criteria to ensure inclusivity and accessibility.
- Regulatory Changes: As eBikes gain popularity, some regions are considering updates to their classification systems. For instance, the European Union is exploring the possibility of increasing the maximum assisted speed for eBikes from 25 km/h (15.5 mph) to 32 km/h (20 mph). Such changes could lead to more diverse eBike offerings and create new opportunities for riders and manufacturers.
By staying informed about these trends and predictions, riders and manufacturers can make proactive decisions and contribute to the growth and development of the eBike market. As technology advances and regulatory landscapes shift, understanding eBike classifications remains crucial for ensuring safety, compliance, and an enjoyable riding experience.
Conclusion: Making Informed Decisions in the eBike Market
Understanding eBike classifications is crucial for riders, regulators, and manufacturers alike, as the popularity of eBikes continues to grow. Clear guidelines help ensure safety, compliance with local regulations, and an enjoyable riding experience for all users. By familiarizing themselves with the different eBike classifications, riders can make informed decisions based on their riding style, experience, and local rules.
Class 1, 2, and 3 eBikes each cater to distinct user needs and preferences. Class 1 eBikes, with their pedal-assist and throttle limit up to 20 mph, are ideal for casual riders and commuters seeking a low-impact, accessible mode of transportation. Class 2 eBikes, with their throttle-assist and speed limit up to 20 mph, offer convenience and ease of use for those who may not want to pedal consistently. Class 3 eBikes, or speed pedelecs, provide a more intense riding experience with their throttle limit up to 28 mph, appealing to experienced cyclists and thrill-seekers.
As the eBike market evolves, staying informed about emerging trends and predictions is essential. Advances in technology, such as smart eBike features and adaptive designs, may influence future eBike classification regulations. Additionally, regulatory changes in various countries can create new opportunities and challenges for riders and manufacturers. By understanding these developments, the eBike community can contribute to the growth and development of the industry while ensuring safety and compliance.
In conclusion, understanding eBike classifications is vital for making informed decisions in the eBike market. By prioritizing safety, compliance, and an enjoyable riding experience, riders and manufacturers can help shape the future of eBike classifications and contribute to the continued success of this dynamic and innovative industry.

