What is VO2 Max and Why Does it Matter?
VO2 max, or maximal oxygen uptake, is a measure of an individual’s aerobic fitness, representing the maximum amount of oxygen the body can utilize during intense exercise. It is a crucial indicator of cardiovascular health, athletic performance, and overall physical fitness. A higher VO2 max value is associated with better cardiovascular health, increased endurance, and enhanced athletic performance. In contrast, a lower VO2 max value may indicate a higher risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease and diabetes. Understanding VO2 max is essential for individuals of all ages, as it provides valuable insights into their aerobic fitness and guides the development of effective exercise programs. As we explore the relationship between VO2 max and age, it becomes clear that this metric plays a vital role in maintaining optimal health and fitness across the lifespan, particularly when considering VO2 max by age.
How to Improve Your VO2 Max at Any Age
Regular exercise and a healthy lifestyle are essential for improving VO2 max, regardless of age. Engaging in aerobic exercises, such as running, cycling, or swimming, can increase cardiovascular fitness and boost VO2 max. Additionally, incorporating high-intensity interval training (HIIT) and strength training can also enhance VO2 max. A well-balanced diet, rich in nutrients and antioxidants, can also support aerobic fitness. Furthermore, managing stress levels, getting adequate sleep, and avoiding smoking can all contribute to improved VO2 max. While age-specific factors can influence VO2 max, understanding the importance of regular exercise and a healthy lifestyle can help individuals of all ages optimize their aerobic fitness and improve their overall health. As we explore the relationship between VO2 max and age, it’s clear that a healthy lifestyle is crucial for maintaining optimal VO2 max by age.
The Age Factor: How VO2 Max Changes Across the Lifespan
As individuals age, their VO2 max naturally declines, leading to decreased aerobic fitness and increased risk of chronic diseases. This decline is a result of various physiological changes, including reduced cardiac output, decreased mitochondrial density, and impaired oxygen delivery to the muscles. However, regular exercise and a healthy lifestyle can slow down or even reverse this decline, allowing individuals to maintain optimal VO2 max by age. In fact, studies have shown that older adults who engage in regular aerobic exercise can increase their VO2 max by up to 20%, significantly improving their overall health and fitness. Understanding the age-related changes in VO2 max is crucial for developing effective exercise programs and lifestyle strategies that cater to the unique needs of different age groups. By acknowledging the impact of age on VO2 max, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain their aerobic fitness and promote healthy aging.
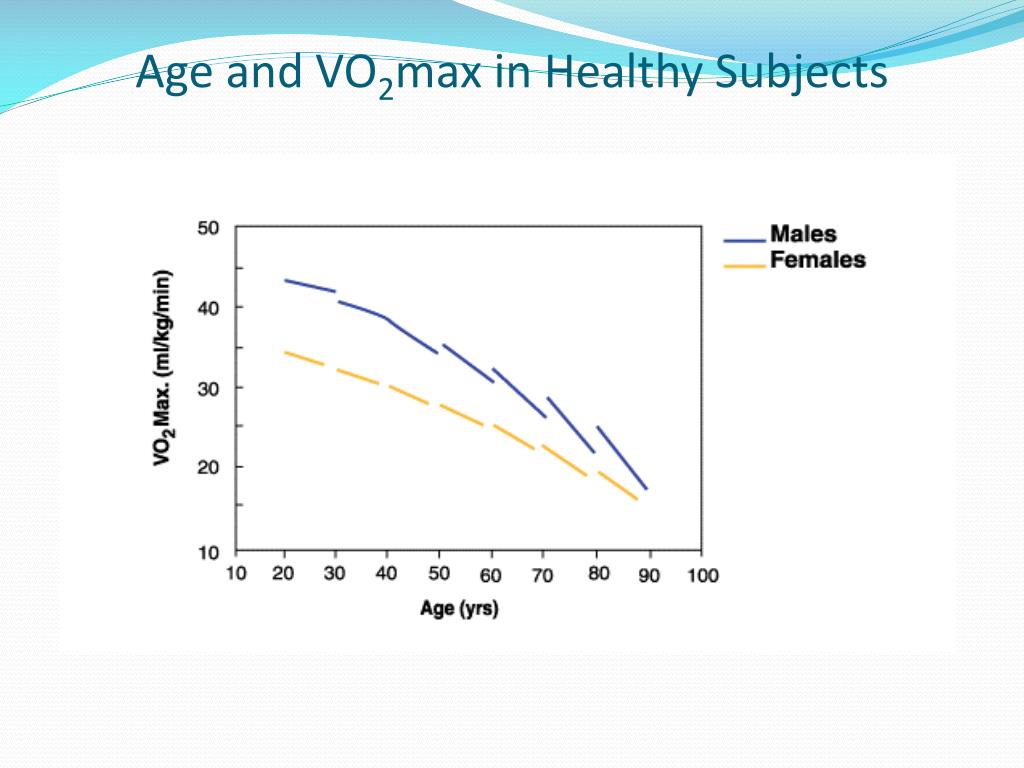
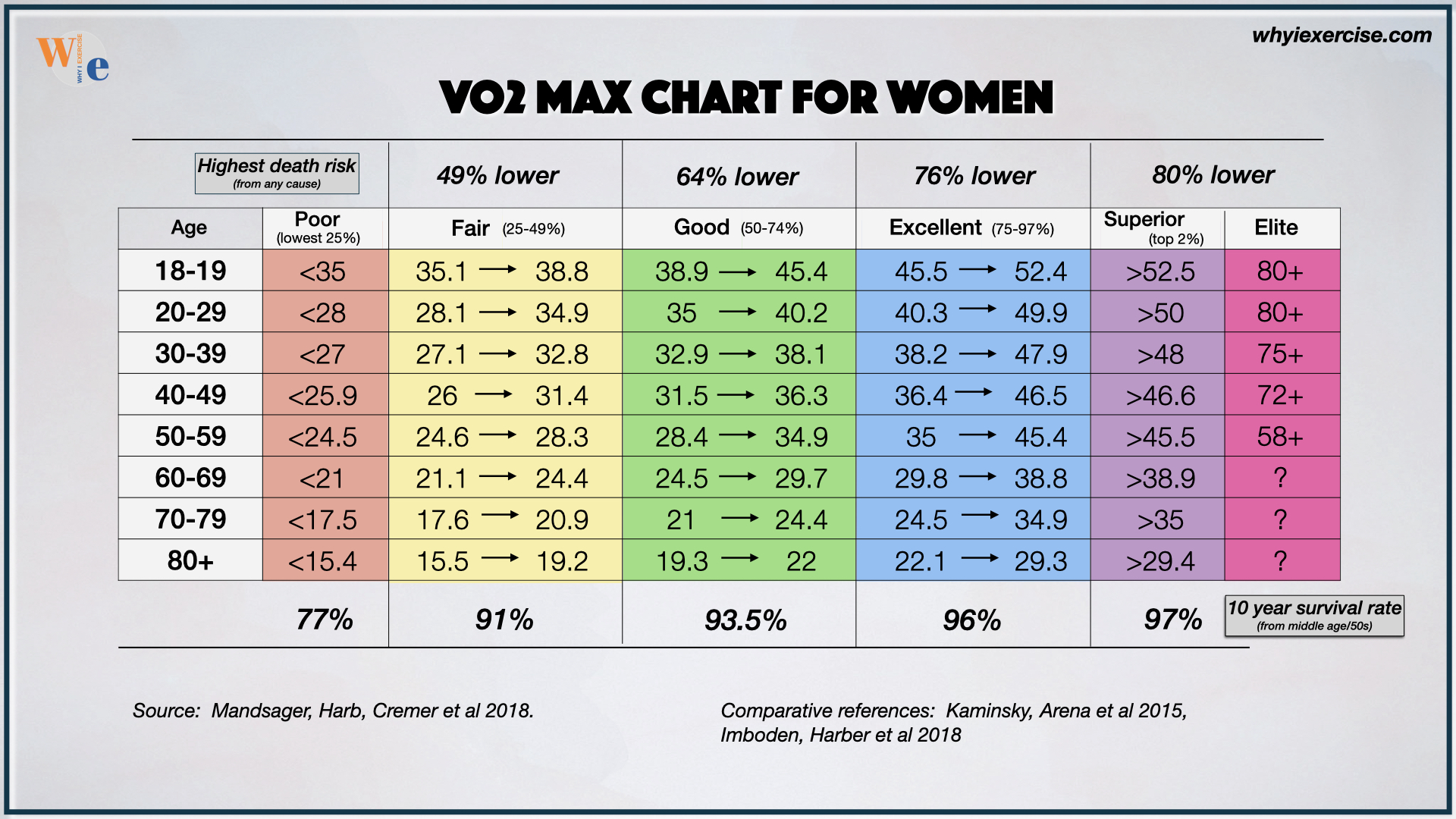
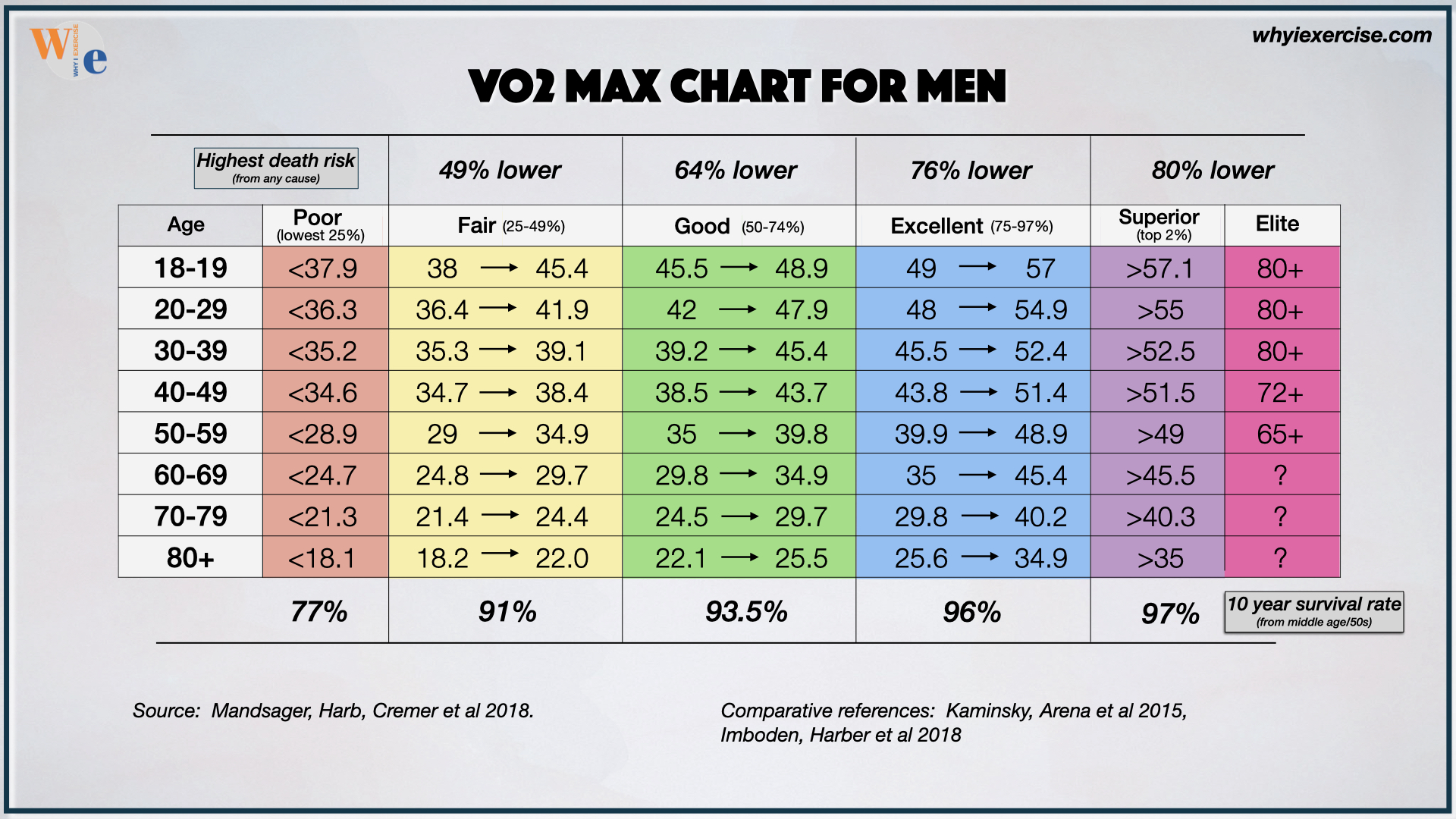
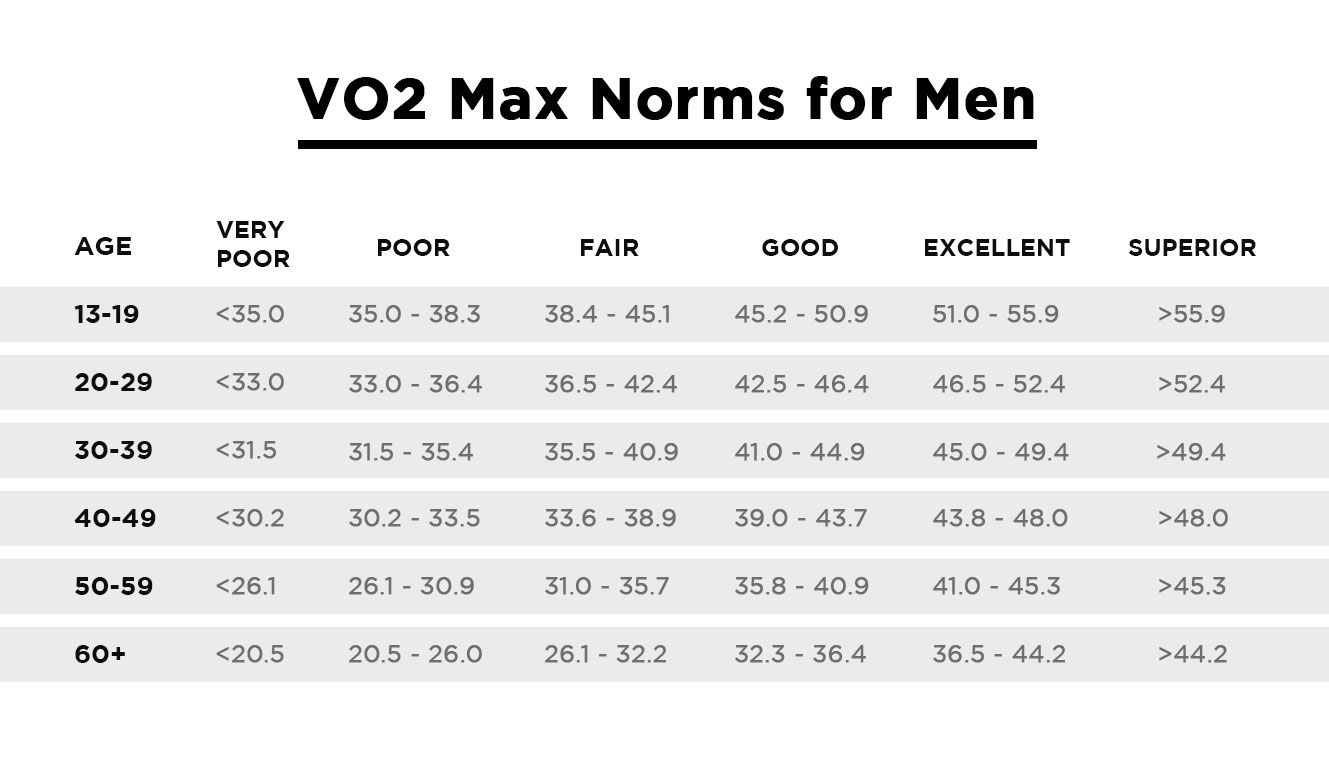
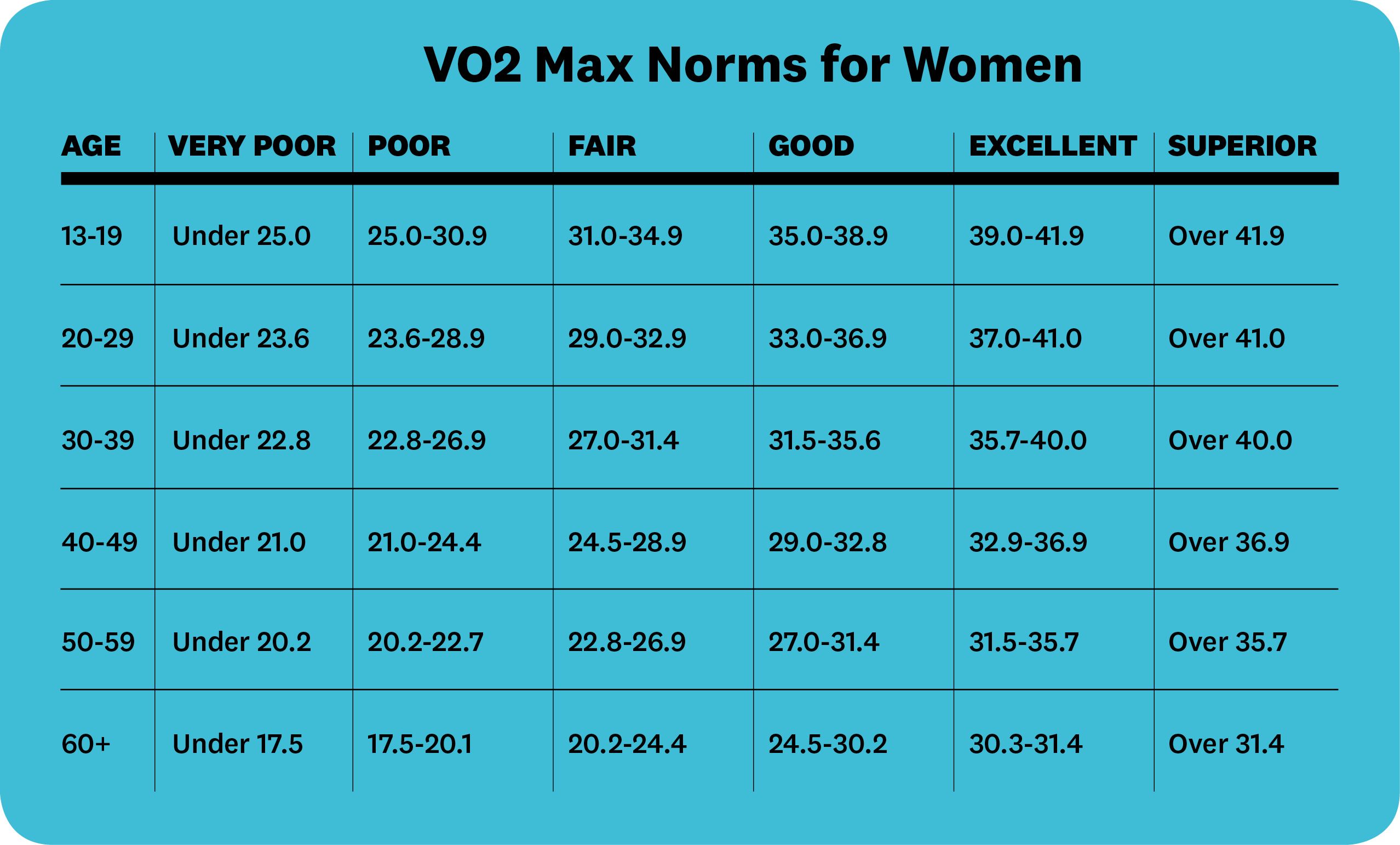
VO2 Max by Age: A Breakdown of Average Values
The following table provides a breakdown of average VO2 max values for different age groups, highlighting the natural decline of VO2 max by age:
| Age Group | Average VO2 Max (ml/kg/min) |
|---|---|
| 20-29 | 42-45 |
| 30-39 | 38-42 |
| 40-49 | 34-38 |
| 50-59 | 30-34 |
| 60-69 | 26-30 |
| 70+ | 22-26 |
These values represent the average VO2 max for each age group, with higher values indicating better aerobic fitness. As shown, VO2 max by age declines steadily, with a significant drop-off after the age of 40. Understanding these average values can help individuals set realistic fitness goals and track their progress over time. By incorporating regular exercise and a healthy lifestyle, individuals can slow down or even reverse this decline, maintaining optimal VO2 max by age and promoting overall health and well-being.
Factors Affecting VO2 Max in Young Adults (20-39)
In young adults, VO2 max is influenced by a combination of genetic and lifestyle factors. Genetics play a significant role, with heritability estimates suggesting that 30-50% of the variation in VO2 max is attributed to genetic differences. However, regular exercise and a healthy lifestyle can also have a profound impact on VO2 max in this age group. For example, research has shown that young adults who engage in regular aerobic exercise can increase their VO2 max by up to 15%. Additionally, lifestyle choices such as a balanced diet, adequate sleep, and stress management can also support optimal VO2 max. Furthermore, young adults who are physically active tend to have higher VO2 max values than their sedentary counterparts, highlighting the importance of regular exercise in maintaining aerobic fitness. By understanding these factors, young adults can take proactive steps to optimize their VO2 max and set themselves up for a lifetime of good health and fitness.
VO2 Max in Middle Age (40-59): The Impact of Aging and Lifestyle
In middle age, VO2 max by age begins to decline more rapidly, with average values decreasing by 1-2% per year. This decline is attributed to a combination of natural aging processes and lifestyle factors. As people enter middle age, they may experience a decrease in physical activity, an increase in body fat, and a decline in muscle mass, all of which can negatively impact VO2 max. Additionally, middle-aged individuals may experience increased stress levels, poor sleep quality, and a decline in overall health, further contributing to the decline in VO2 max. However, it’s not all doom and gloom. By incorporating regular exercise, such as aerobic exercise and strength training, middle-aged individuals can slow down or even reverse this decline. A healthy diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can also support optimal VO2 max. Furthermore, stress management techniques, such as meditation and yoga, can help mitigate the negative impact of stress on VO2 max. By understanding the factors that affect VO2 max in middle age, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain or improve their aerobic fitness, setting themselves up for a healthy and active older age.
Optimizing VO2 Max in Older Adults (60+): Strategies for Healthy Aging
In older adults, optimizing VO2 max is crucial for maintaining independence, mobility, and overall health. While VO2 max naturally declines with age, regular exercise and a healthy lifestyle can help slow down or even reverse this decline. One effective strategy is to incorporate aerobic exercise, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, into daily routine. Resistance training, such as weightlifting or bodyweight exercises, can also help improve VO2 max by increasing muscle mass and strength. Additionally, older adults can benefit from high-intensity interval training (HIIT), which has been shown to improve VO2 max in this age group. A well-balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein can also support optimal VO2 max. Furthermore, stress management techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or tai chi, can help mitigate the negative impact of stress on VO2 max. By incorporating these strategies into daily life, older adults can maintain or improve their VO2 max, reducing the risk of chronic diseases and improving overall health and well-being. By understanding the importance of VO2 max by age, older adults can take proactive steps to optimize their aerobic fitness and enjoy a healthy and active older age.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Aerobic Fitness at Any Age
In conclusion, understanding VO2 max by age is crucial for optimizing aerobic fitness and overall health across the lifespan. By recognizing the natural decline of VO2 max with age, individuals can take proactive steps to slow down or even reverse this decline through regular exercise and a healthy lifestyle. Whether you’re a young adult, middle-aged, or older adult, incorporating aerobic exercise, strength training, and stress management into your daily routine can help improve or maintain your VO2 max. By making informed lifestyle choices and staying committed to a healthy routine, individuals can take control of their aerobic fitness and enjoy a healthier, more active life at any age. Remember, VO2 max by age is not a fixed trait, and with the right strategies and mindset, anyone can optimize their aerobic fitness and unlock their full potential.