Why Power-to-Weight Ratio Matters in Fitness and Sports
In the pursuit of peak performance, athletes and fitness enthusiasts often focus on improving their strength, speed, and endurance. However, there’s a crucial factor that can make all the difference: power-to-weight ratio. This ratio is a measure of an individual’s ability to generate power relative to their body weight, and it plays a significant role in various sports and fitness activities, such as cycling, running, and weightlifting.
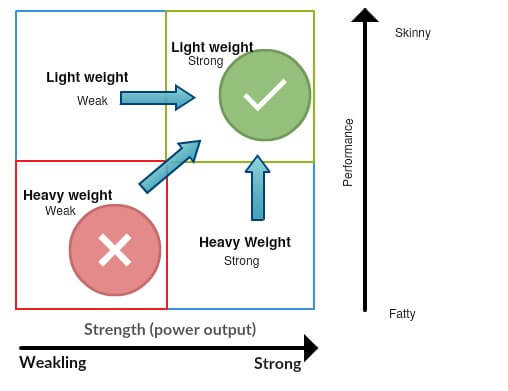
A good power-to-weight ratio can significantly impact overall performance and efficiency. For instance, a cyclist with a high power-to-weight ratio can maintain a faster pace over a longer distance, while a weightlifter with a high power-to-weight ratio can lift heavier weights with ease. In essence, a good power-to-weight ratio enables athletes to perform at their best, reducing the risk of injury and improving their overall fitness. So, what is a good power to weight ratio? The answer lies in understanding the intricacies of this ratio and how it affects athletic performance.
Understanding the Formula: Calculating Your Power-to-Weight Ratio
Calculating your power-to-weight ratio is a straightforward process that requires some basic math and an understanding of the formula. The power-to-weight ratio is typically expressed in watts per kilogram (W/kg) and is calculated by dividing your maximum power output (in watts) by your body weight (in kilograms).
The formula to calculate power-to-weight ratio is:
Power-to-Weight Ratio (W/kg) = Maximum Power Output (W) ÷ Body Weight (kg)
For example, if you can produce a maximum power output of 250 watts during a cycling sprint, and you weigh 70 kilograms, your power-to-weight ratio would be:
Power-to-Weight Ratio (W/kg) = 250 W ÷ 70 kg = 3.57 W/kg
This means that for every kilogram of body weight, you can produce 3.57 watts of power. A higher power-to-weight ratio indicates a greater ability to generate power relative to your body weight, which can be a significant advantage in sports and fitness activities.
It’s essential to note that power-to-weight ratio can vary depending on the specific activity or sport. For instance, a good power-to-weight ratio for a cyclist may be different from that of a weightlifter. Understanding how to calculate your power-to-weight ratio and what constitutes a good ratio for your specific sport or activity is crucial for optimizing your performance.
How to Improve Your Power-to-Weight Ratio for Enhanced Performance
Improving your power-to-weight ratio requires a well-structured approach that focuses on increasing strength, reducing body fat, and optimizing training methods. By implementing these strategies, athletes and fitness enthusiasts can enhance their overall performance and efficiency.
One of the most effective ways to improve power-to-weight ratio is to increase strength through resistance training. This can be achieved by incorporating exercises that target multiple muscle groups, such as squats, deadlifts, and bench press. As muscle mass increases, so does the ability to generate power, leading to a higher power-to-weight ratio.
Reducing body fat is another crucial aspect of improving power-to-weight ratio. Excess body fat can hinder athletic performance by decreasing power output and increasing energy expenditure. By adopting a healthy diet and engaging in regular cardiovascular exercise, individuals can reduce their body fat percentage and improve their power-to-weight ratio.
Optimizing training methods is also essential for improving power-to-weight ratio. This can be achieved by incorporating high-intensity interval training (HIIT) and plyometric exercises into your workout routine. These types of exercises are designed to improve power output and explosiveness, leading to a higher power-to-weight ratio.
It’s essential to note that improving power-to-weight ratio takes time and consistent effort. Athletes and fitness enthusiasts should be patient and focus on making gradual improvements over time. Aiming to increase strength, reduce body fat, and optimize training methods will ultimately lead to a higher power-to-weight ratio and enhanced athletic performance.
So, what is a good power to weight ratio? A good power-to-weight ratio varies depending on the specific sport or activity. However, a general guideline is to aim for a power-to-weight ratio of at least 2-3 W/kg for general fitness and 4-5 W/kg for competitive athletes. By focusing on improving power-to-weight ratio, individuals can unlock their full potential and achieve peak performance.
The Impact of Body Composition on Power-to-Weight Ratio
Body composition plays a crucial role in determining an individual’s power-to-weight ratio. The ratio of muscle mass, body fat, and lean body mass can significantly impact overall performance and efficiency. Understanding the effects of body composition on power-to-weight ratio is essential for athletes and fitness enthusiasts seeking to optimize their performance.
Muscle mass is a critical component of body composition that affects power-to-weight ratio. As muscle mass increases, so does the ability to generate power. This is because muscle fibers are responsible for producing force and speed. Therefore, individuals with a higher percentage of muscle mass tend to have a higher power-to-weight ratio.
Body fat, on the other hand, can hinder athletic performance by decreasing power output and increasing energy expenditure. Excess body fat can also reduce muscle mass, leading to a lower power-to-weight ratio. Maintaining a healthy body fat percentage is essential for optimizing power-to-weight ratio.
Lean body mass, which includes muscle mass, bone density, and water content, also plays a significant role in determining power-to-weight ratio. A higher lean body mass typically indicates a higher power-to-weight ratio, as it reflects an individual’s ability to generate power relative to their body weight.
For example, a cyclist with a high percentage of muscle mass and low body fat percentage will typically have a higher power-to-weight ratio than a cyclist with a lower percentage of muscle mass and higher body fat percentage. This is because the former cyclist will be able to generate more power relative to their body weight, resulting in improved performance and efficiency.
Understanding the impact of body composition on power-to-weight ratio is essential for developing effective training and nutrition strategies. By focusing on increasing muscle mass, reducing body fat, and optimizing lean body mass, individuals can improve their power-to-weight ratio and unlock their full potential.
Real-World Examples: Power-to-Weight Ratios in Professional Sports
Professional athletes in various sports have optimized their power-to-weight ratios to achieve success and dominance in their respective fields. Analyzing their power-to-weight ratios provides valuable insights into the importance of this metric in achieving peak performance.
In cycling, professional riders like Chris Froome and Geraint Thomas have power-to-weight ratios of around 6-7 W/kg, allowing them to maintain high speeds over long distances. This is achieved through a combination of high power output and low body weight, making them highly efficient on the bike.
In running, elite athletes like Eliud Kipchoge and Paula Radcliffe have power-to-weight ratios of around 5-6 W/kg, enabling them to maintain fast paces over long distances. Their high power output and low body weight allow them to generate speed and endurance, making them successful in their respective events.
In weightlifting, athletes like Lu Xiaojun and Naim Suleymanoglu have power-to-weight ratios of around 8-10 W/kg, allowing them to lift heavy weights with ease. Their high power output and low body weight enable them to generate explosive force, making them successful in their respective weight classes.
These examples demonstrate the importance of power-to-weight ratio in achieving success in various sports. By optimizing their power-to-weight ratios, professional athletes can gain a competitive edge and achieve peak performance. For athletes and fitness enthusiasts, understanding the power-to-weight ratio can help them set realistic goals and develop effective training strategies to improve their performance.
So, what is a good power to weight ratio? While it varies depending on the sport and individual, a good power-to-weight ratio is one that is optimized for peak performance. By understanding the power-to-weight ratios of professional athletes, individuals can set realistic goals and develop effective training strategies to improve their performance.
Setting Realistic Goals: What’s a Good Power-to-Weight Ratio for You?
Setting realistic goals for improving power-to-weight ratio is crucial for achieving success and maintaining motivation. A good power-to-weight ratio varies depending on individual factors such as fitness level, age, and sport-specific requirements. Understanding these factors is essential for setting achievable goals and developing effective training strategies.
For beginners, a good power-to-weight ratio may be around 2-3 W/kg, which is a realistic starting point for those new to exercise or sports. As fitness levels improve, individuals can aim to increase their power-to-weight ratio to 4-5 W/kg, which is a more advanced level of performance.
For athletes, a good power-to-weight ratio may be higher, depending on the specific demands of their sport. For example, professional cyclists may aim for a power-to-weight ratio of 6-7 W/kg, while elite runners may target 5-6 W/kg. Weightlifters, on the other hand, may aim for a power-to-weight ratio of 8-10 W/kg, depending on their weight class and lifting style.
What is a good power to weight ratio for you? It’s essential to consider your individual factors, such as fitness level, age, and sport-specific requirements, when setting goals for improving power-to-weight ratio. By understanding these factors and setting realistic goals, individuals can develop effective training strategies and achieve success in their respective sports or fitness activities.
Remember, improving power-to-weight ratio takes time, patience, and consistent effort. Setting realistic goals and developing a well-structured training plan can help individuals achieve their desired power-to-weight ratio and unlock their full potential.
Common Misconceptions About Power-to-Weight Ratio Debunked
Despite its importance in fitness and sports, power-to-weight ratio is often misunderstood or misrepresented. Several common misconceptions surround this concept, which can lead to ineffective training strategies and poor performance.
One common myth is that power-to-weight ratio is only relevant for elite athletes. However, this metric is essential for anyone looking to improve their performance, regardless of fitness level. Whether you’re a recreational runner or a professional cyclist, understanding and optimizing your power-to-weight ratio can help you achieve your goals.
Another misconception is that power-to-weight ratio is solely dependent on muscle mass. While muscle mass does play a role, it’s not the only factor. Body fat, lean body mass, and overall body composition also significantly impact power-to-weight ratio. A well-balanced body composition, combined with effective training, is essential for achieving a good power-to-weight ratio.
Some individuals believe that power-to-weight ratio is only relevant for endurance sports, such as cycling and running. However, this metric is also crucial for strength-based sports, such as weightlifting and gymnastics. In fact, power-to-weight ratio can be a key differentiator between athletes in these sports, as it allows them to generate explosive force and power.
Finally, some people think that improving power-to-weight ratio requires a significant amount of time and effort. While it’s true that optimizing power-to-weight ratio takes time and dedication, it’s not an insurmountable task. By setting realistic goals, developing a well-structured training plan, and incorporating effective strategies, individuals can improve their power-to-weight ratio and achieve their desired performance levels.
By debunking these common misconceptions, individuals can gain a better understanding of power-to-weight ratio and its importance in fitness and sports. By recognizing the value of this metric, individuals can develop effective training strategies and achieve their desired performance levels, regardless of their fitness goals or sport of choice.
Conclusion: Optimizing Your Power-to-Weight Ratio for Long-Term Success
In conclusion, power-to-weight ratio is a critical metric for athletes and fitness enthusiasts seeking to optimize their performance. By understanding the significance of power-to-weight ratio, calculating it accurately, and implementing effective strategies to improve it, individuals can unlock their full potential and achieve long-term success.
Achieving a good power-to-weight ratio requires a balanced approach that incorporates strength training, body composition optimization, and tailored training methods. It’s essential to set realistic goals, taking into account individual factors such as fitness level, age, and sport-specific requirements. By doing so, individuals can create a personalized roadmap for improving their power-to-weight ratio and achieving their desired performance levels.
Remember, what is a good power-to-weight ratio for one individual may not be the same for another. It’s crucial to focus on individual progress and celebrate small victories along the way. With patience, consistent effort, and a deep understanding of power-to-weight ratio, athletes and fitness enthusiasts can overcome plateaus, push their limits, and achieve remarkable results.
By applying the principles outlined in this article, individuals can unlock their full potential, dominate their respective sports, and enjoy a lifetime of peak performance. So, take the first step today, and start optimizing your power-to-weight ratio for long-term success.