What is Watts per Kilogram and Why Does it Matter?
Watts per kilogram (W/kg) is a critical metric in cycling that measures a rider’s power output relative to their body weight. This power-to-weight ratio is essential for cyclists, as it directly affects their performance, efficiency, and overall competitiveness. A higher W/kg value indicates a rider’s ability to generate more power while minimizing their body weight, resulting in improved acceleration, climbing, and endurance.
In the world of professional cycling, W/kg is a key factor in determining a rider’s potential for success. Top cyclists typically possess a high W/kg value, which enables them to maintain a high pace over extended periods. For example, a rider with a W/kg value of 5.5 can sustain a power output of 275 watts for an hour, while a rider with a W/kg value of 4.5 can only maintain 225 watts. This difference in power output can significantly impact a rider’s performance in competitions.
For recreational and amateur cyclists, understanding W/kg is equally important. By monitoring and improving their power-to-weight ratio, riders can optimize their training, set realistic goals, and track their progress. A good W/kg value can also help riders to identify areas for improvement, such as increasing their power output or reducing their body weight.
While there is no one-size-fits-all answer to the question of what is a good watts per kg, general guidelines suggest that a W/kg value of 3.5 or higher is considered good for recreational cyclists. However, this value can vary depending on factors such as the rider’s fitness level, bike setup, and terrain. As cyclists strive to improve their performance, understanding and optimizing their W/kg value is crucial for achieving success in the sport.
How to Calculate Your Watts per Kilogram
Calculating watts per kilogram (W/kg) is a straightforward process that requires two key pieces of data: power output in watts and body weight in kilograms. To calculate W/kg, follow these steps:
1. Determine your power output in watts. This can be measured using a power meter on your bike or estimated using online calculators or cycling apps. A power meter provides the most accurate measurement, but estimates can be used as a rough guide.
2. Record your body weight in kilograms. This can be done using a bathroom scale or a smart scale that provides weight measurements in kilograms.
3. Use the following formula to calculate W/kg: W/kg = Power Output (watts) / Body Weight (kilograms)
For example, if your power output is 250 watts and your body weight is 70 kilograms, your W/kg would be:
W/kg = 250 watts / 70 kilograms = 3.57 W/kg
It’s essential to note that W/kg is a dynamic value that can fluctuate depending on various factors, such as fitness level, training, and nutrition. Regularly tracking your W/kg can help you monitor your progress and adjust your training accordingly.
When calculating W/kg, consider the following:
– Use a reliable power meter or estimation method to ensure accurate power output data.
– Weigh yourself regularly to account for any changes in body weight.
– Consider your body composition, as a higher percentage of muscle mass can impact your W/kg.
– Keep in mind that W/kg is just one metric to evaluate your cycling performance. Other factors, such as endurance, technique, and strategy, also play a crucial role in determining your overall competitiveness.
By understanding how to calculate W/kg, you can gain valuable insights into your cycling performance and make data-driven decisions to improve your training and racing. Remember to regularly track your W/kg and adjust your training accordingly to optimize your power-to-weight ratio.
Factors Affecting Watts per Kilogram: Understanding the Variables
Watts per kilogram (W/kg) is a complex metric that is influenced by a multitude of factors. Understanding these variables is crucial to optimizing your power-to-weight ratio and improving your cycling performance. The following factors contribute to a rider’s overall W/kg:
Body Composition: A rider’s body composition plays a significant role in determining their W/kg. A higher percentage of muscle mass relative to body weight can improve power output, while excess body fat can negatively impact W/kg. Cyclists with a leaner body composition tend to have a higher W/kg.
Muscle Power: Muscle power is the ability to generate force quickly. Cyclists with high muscle power can produce more watts per kilogram, making them more efficient and competitive. Training programs that focus on building muscle power, such as sprint intervals and strength training, can help improve W/kg.
Cardiovascular Endurance: Cardiovascular endurance is the ability to sustain a high intensity effort over a prolonged period. Cyclists with high cardiovascular endurance can maintain a higher power output for longer periods, resulting in a higher W/kg. Endurance training, such as long steady-state rides and interval training, can help improve cardiovascular endurance.
Bike Setup: A rider’s bike setup can significantly impact their W/kg. A lighter bike with optimized gearing and aerodynamics can improve power output and reduce energy expenditure. Cyclists can optimize their bike setup by using lightweight components, adjusting their gearing, and improving their aerodynamic position.
Training and Experience: A rider’s training and experience level can also impact their W/kg. Cyclists who have a strong training background and extensive racing experience tend to have a higher W/kg. This is due to their ability to optimize their training programs, develop efficient pedaling techniques, and adapt to different racing conditions.
Genetics and Physiology: Genetic and physiological factors, such as muscle fiber type and aerobic capacity, can also influence a rider’s W/kg. While these factors are largely outside of a rider’s control, understanding their impact can help cyclists develop targeted training programs to optimize their W/kg.
By understanding the factors that affect W/kg, cyclists can develop targeted training programs and make informed decisions about their equipment and nutrition. This knowledge can help riders optimize their power-to-weight ratio and improve their overall cycling performance.
When considering what is a good watts per kg, it’s essential to take into account these variables and how they impact an individual’s W/kg. By understanding the complex interplay between these factors, cyclists can set realistic goals and develop effective strategies to improve their W/kg and enhance their cycling performance.
What is a Good Watts per Kilogram for Cyclists?
When it comes to watts per kilogram (W/kg), there is no one-size-fits-all answer to what constitutes a good value. W/kg benchmarks vary depending on the type of cyclist, their level of experience, and the specific discipline or event. Here are some general guidelines for W/kg values for different types of cyclists:
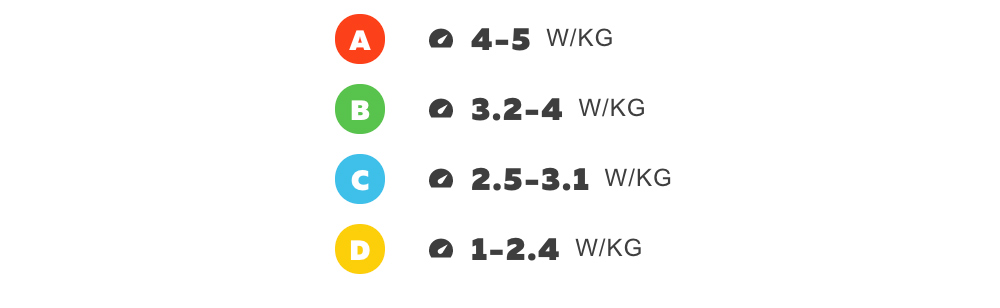
Recreational Cyclists: For casual riders who enjoy cycling for fitness and recreation, a W/kg value of 2.5-3.5 is considered average. This range indicates a moderate level of fitness and a decent power-to-weight ratio.
Amateur Cyclists: For amateur riders who participate in local racing events or gran fondos, a W/kg value of 3.5-4.5 is considered good. This range indicates a higher level of fitness and a more efficient power-to-weight ratio.
Professional Cyclists: For professional riders who compete at the highest level, a W/kg value of 5.5-6.5 is considered excellent. This range indicates an extremely high level of fitness and a highly efficient power-to-weight ratio.
It’s essential to note that these benchmarks are general guidelines and may vary depending on the specific discipline or event. For example, a professional sprinter may have a lower W/kg value than a professional climber, but still be highly competitive in their respective discipline.
When evaluating W/kg values, it’s also important to consider the limitations and potential biases of these benchmarks. For example:
– W/kg values can be influenced by factors such as body composition, muscle power, and cardiovascular endurance.
– Different power meters and testing protocols can produce varying results.
– W/kg values may not accurately reflect a rider’s overall cycling ability or competitiveness.
Despite these limitations, W/kg values can provide a useful benchmark for cyclists to evaluate their progress and set realistic goals. By understanding what is a good watts per kg for their specific level and discipline, cyclists can develop targeted training programs and make informed decisions about their equipment and nutrition.
Ultimately, the key to improving W/kg is to focus on developing a well-rounded training program that addresses all aspects of cycling performance, including power output, endurance, and efficiency. By doing so, cyclists can unlock their full potential and achieve their goals, regardless of their W/kg value.
Real-World Examples: Watts per Kilogram in Professional Cycling
Professional cycling is a highly competitive sport where every advantage counts. Watts per kilogram (W/kg) is a critical metric that can make or break a rider’s performance. Let’s take a look at some real-world examples of W/kg values in professional cycling:
Tour de France Winners: The winners of the Tour de France typically have W/kg values ranging from 5.5 to 6.5. For example, Chris Froome, a four-time Tour de France winner, has a reported W/kg value of 5.8. This is an extremely high value, indicating a very high level of fitness and a highly efficient power-to-weight ratio.
Professional Sprinters: Professional sprinters, on the other hand, tend to have lower W/kg values due to their focus on short, intense efforts. For example, Mark Cavendish, a renowned sprinter, has a reported W/kg value of 4.8. This is still a very high value, but lower than that of a Tour de France winner.
Climbing Specialists: Climbing specialists, such as Nairo Quintana and Alberto Contador, tend to have higher W/kg values due to their focus on long, intense efforts in the mountains. For example, Quintana has a reported W/kg value of 6.1, while Contador has a reported W/kg value of 6.0.
These examples illustrate the importance of W/kg in professional cycling. A high W/kg value can be a major advantage in competitions, especially in events that require sustained efforts over long periods. However, it’s also important to note that W/kg is just one metric, and other factors such as tactics, teamwork, and mental toughness also play a critical role in determining success in professional cycling.
When analyzing W/kg values in professional cycling, it’s also important to consider the following factors:
– The type of event or competition: Different events require different types of fitness and W/kg values. For example, a time trial requires a high W/kg value, while a criterium requires a high anaerobic capacity.
– The rider’s specific role: Different riders have different roles within a team, and their W/kg values may reflect this. For example, a domestique may have a lower W/kg value than a team leader.
– The rider’s training and preparation: W/kg values can fluctuate depending on a rider’s training and preparation. For example, a rider who has been training specifically for a event may have a higher W/kg value than a rider who has been training for a different type of event.
By understanding the W/kg values of professional cyclists, we can gain insights into the physical demands of the sport and the importance of optimizing power-to-weight ratio. Whether you’re a professional cyclist or a recreational rider, understanding W/kg can help you improve your performance and achieve your goals.
Improving Your Watts per Kilogram: Training Strategies and Tips
Improving your watts per kilogram (W/kg) requires a well-structured training program that addresses all aspects of cycling performance. Here are some actionable advice and training strategies to help you improve your W/kg:
Interval Training: Interval training is a highly effective way to improve your W/kg. This involves alternating between high-intensity efforts and active recovery periods. For example, you can do 4-6 x 8-minute intervals at maximum effort, followed by 8-10 minutes of active recovery.
Strength Training: Strength training is essential for building muscular power and endurance. Focus on exercises that target your legs, core, and upper body, such as squats, lunges, deadlifts, and bench press. Aim to do 2-3 strength training sessions per week.
Nutrition Planning: Proper nutrition is critical for optimizing your W/kg. Focus on consuming a balanced diet that includes plenty of protein, complex carbohydrates, and healthy fats. Aim to eat 5-6 meals per day, spaced out every 2-3 hours.
Progressive Overload: Progressive overload involves gradually increasing the intensity of your workouts over time. This can be achieved by increasing the weight, resistance, or duration of your workouts. Aim to increase the intensity of your workouts by 2-5% each week.
Consistency and Patience: Consistency and patience are key when it comes to improving your W/kg. Aim to train regularly, ideally 4-5 times per week, and be patient with your progress. It can take several months to see significant improvements in your W/kg.
Additionally, consider the following tips to optimize your training:
– Periodization: Periodize your training into specific blocks, focusing on different aspects of cycling performance, such as endurance, intensity, and recovery.
– Recovery: Prioritize recovery techniques, such as foam rolling, stretching, and self-myofascial release, to help your body adapt to the demands of training.
– Technology and Data Analysis: Use technology, such as power meters and heart rate monitors, to track your progress and optimize your training. Analyze your data to identify areas for improvement and adjust your training accordingly.
By incorporating these training strategies and tips into your program, you can improve your W/kg and take your cycling performance to the next level. Remember to stay consistent, patient, and focused, and you’ll be on your way to achieving your cycling goals.
When it comes to what is a good watts per kg, it’s essential to remember that this value is highly individualized and depends on various factors, including your fitness level, training experience, and cycling discipline. By focusing on improving your W/kg through structured training and nutrition planning, you can optimize your power-to-weight ratio and achieve your cycling goals.
Watts per Kilogram and Bike Setup: Optimizing Your Equipment
When it comes to optimizing your watts per kilogram (W/kg), your bike setup plays a crucial role. A well-optimized bike setup can help you achieve a higher W/kg, while a poorly optimized setup can hinder your performance. Here are some key factors to consider when optimizing your bike setup:
Bike Weight: A lighter bike can significantly improve your W/kg. Look for ways to reduce your bike’s weight, such as using lighter components, removing unnecessary accessories, and optimizing your bike’s geometry.
Gearing: Proper gearing is essential for optimizing your W/kg. Make sure your gearing is suitable for your riding style and terrain. A well-geared bike can help you maintain a high cadence and generate more power.
Aerodynamics: Aerodynamics play a significant role in cycling performance. Optimize your bike’s aerodynamics by using aerodynamic wheels, frames, and components. Additionally, consider your riding position and make adjustments to reduce air resistance.
Component Selection: The components you choose can significantly impact your W/kg. Look for lightweight, high-performance components that are designed to optimize power output and efficiency.
When optimizing your bike setup, consider the following tips:
– Consult a Professional: Consult with a professional bike fitter or mechanic to ensure your bike is properly optimized for your riding style and goals.
– Experiment and Test: Experiment with different bike setups and test their impact on your W/kg. Use data and analytics to inform your decisions and optimize your setup.
– Consider Your Riding Style: Consider your riding style and goals when optimizing your bike setup. For example, if you’re a sprinter, you may prioritize aerodynamics and gearing over bike weight.
By optimizing your bike setup, you can improve your W/kg and take your cycling performance to the next level. Remember to consider your riding style, goals, and terrain when making adjustments to your bike setup.
When it comes to what is a good watts per kg, a well-optimized bike setup can make a significant difference. By prioritizing bike weight, gearing, aerodynamics, and component selection, you can achieve a higher W/kg and improve your overall cycling performance.
Conclusion: Unlocking Your Cycling Potential with Watts per Kilogram
In conclusion, understanding and improving watts per kilogram (W/kg) is crucial for cyclists who want to unlock their full potential and achieve their goals. By grasping the concept of W/kg and its significance in cycling, riders can optimize their training, nutrition, and bike setup to improve their power-to-weight ratio.
Throughout this article, we have discussed the various factors that influence W/kg, including body composition, muscle power, cardiovascular endurance, and bike setup. We have also provided actionable advice and training strategies for improving W/kg, including interval training, strength training, and nutrition planning.
Additionally, we have examined the relationship between W/kg and bike setup, highlighting the importance of optimizing bike weight, gearing, and aerodynamics to improve power output and efficiency.
By applying the concepts and strategies discussed in this article, cyclists can improve their W/kg and take their cycling performance to the next level. Whether you’re a recreational, amateur, or professional rider, understanding and improving W/kg is essential for achieving your goals and unlocking your full potential.
Remember, what is a good watts per kg is highly individualized and depends on various factors, including your fitness level, training experience, and cycling discipline. By focusing on improving your W/kg through structured training and nutrition planning, you can optimize your power-to-weight ratio and achieve your cycling goals.
In the end, the key to unlocking your cycling potential is to understand and improve your W/kg. By doing so, you can optimize your performance, efficiency, and overall competitiveness, and achieve your goals in the world of cycling.