What Affects Your Cycling Speed?
When it comes to cycling, speed is a crucial aspect that can make all the difference in your performance. Whether you’re a professional cyclist or a recreational rider, understanding what affects your cycling speed is essential to improve your overall riding experience. Several factors come into play when determining your cycling speed, including fitness level, bike type, terrain, and weather conditions.
Fitness level, for instance, plays a significant role in determining your cycling speed. A rider with a high level of cardiovascular fitness will generally be able to maintain a faster speed than someone who is less fit. Bike type is another crucial factor, as different types of bikes are designed for specific terrains and riding styles. For example, a road bike is designed for speed and efficiency on paved roads, while a mountain bike is designed for navigating rough terrain.
Terrain also has a significant impact on cycling speed. Riding on flat, smooth roads will generally allow for faster speeds than riding on hilly or mountainous terrain. Weather conditions, such as wind, rain, and temperature, can also affect your cycling speed. For example, riding into a strong headwind can significantly slow down your speed, while riding on a cool, sunny day can help you maintain a faster pace.
Understanding these factors is crucial to improving your cycling speed. By recognizing how each factor affects your speed, you can make adjustments to your training, bike, and riding style to optimize your performance. In the next section, we’ll explore how to measure your cycling speed and calculate your average speed.
How to Measure Your Cycling Speed
Measuring your cycling speed is crucial to understanding your performance and tracking your progress. There are several methods to measure cycling speed, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. In this section, we’ll explore the different methods of measuring cycling speed and provide tips on how to accurately measure speed and calculate average speed.
One of the most common methods of measuring cycling speed is using a GPS device. GPS devices can provide accurate speed readings, as well as other valuable data such as distance, time, and elevation gain. Many GPS devices also allow you to download your ride data to a computer or mobile device, making it easy to track your progress over time.
Another method of measuring cycling speed is using a cycle computer. Cycle computers are devices that attach to your bike and provide real-time speed and distance data. They are often more affordable than GPS devices and can provide accurate speed readings. However, they may not provide as much data as a GPS device.
A stopwatch is another simple and affordable method of measuring cycling speed. By timing yourself over a set distance, you can calculate your average speed. This method is less accurate than using a GPS device or cycle computer, but can still provide a general idea of your cycling speed.
When measuring your cycling speed, it’s essential to ensure accuracy. Here are some tips to help you get accurate speed readings:
- Use a consistent method of measurement to ensure accurate comparisons.
- Calibrate your GPS device or cycle computer regularly to ensure accuracy.
- Take into account external factors such as wind, terrain, and weather conditions that can affect your speed.
By accurately measuring your cycling speed, you can track your progress, set realistic goals, and improve your overall performance. In the next section, we’ll explore the average cycling speeds for different types of riders and provide statistics and data to support the information.
The Average Cycling Speed: What to Expect
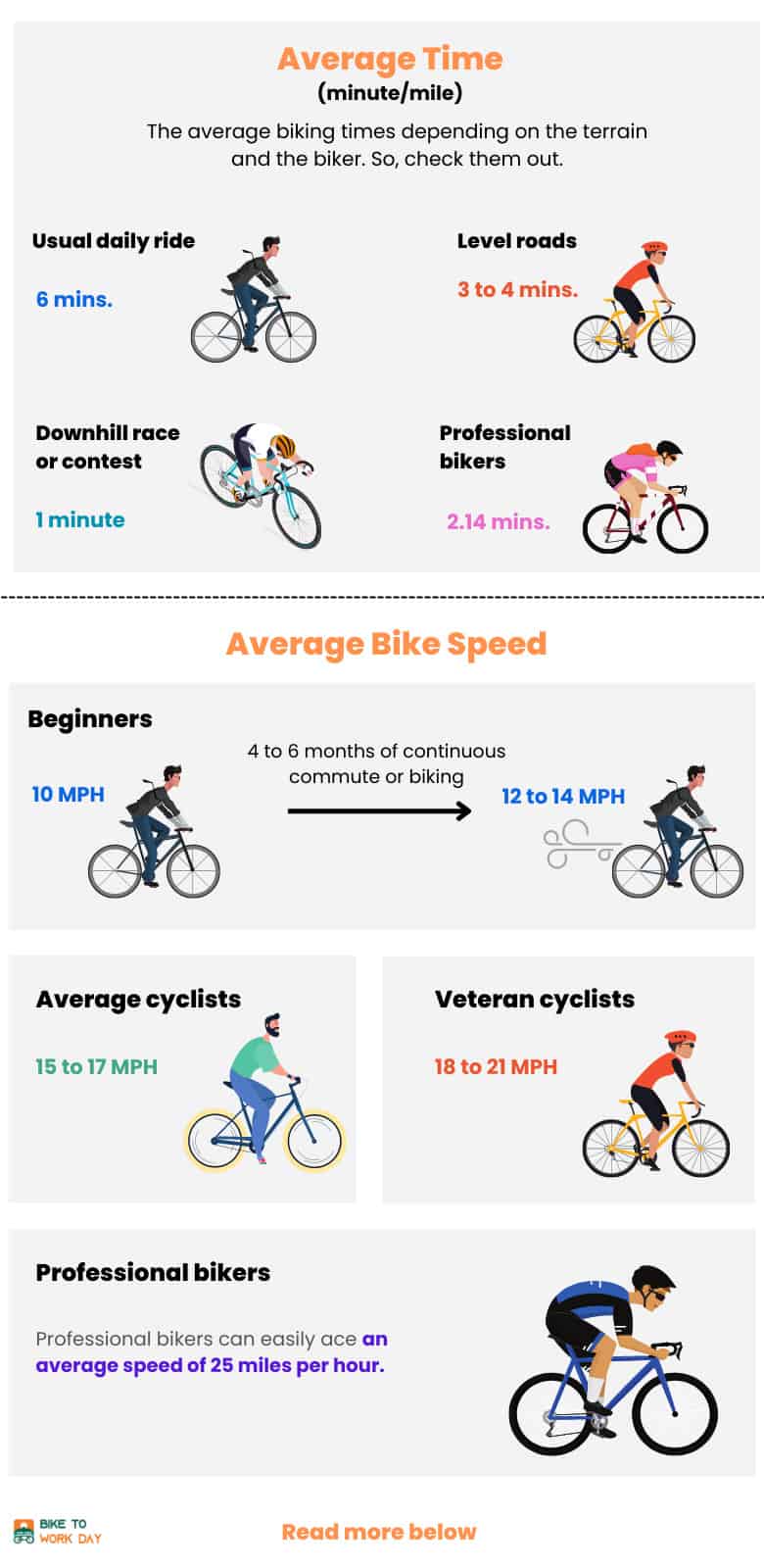
When it comes to cycling, understanding what constitutes an average cycling speed is essential to setting realistic goals and tracking progress. Average cycling speeds vary greatly depending on the type of rider, with beginners, recreational riders, and professional cyclists all having different expectations.
For beginners, an average cycling speed of 10-15 miles per hour (mph) is a reasonable expectation. This speed is achievable with minimal training and is a great starting point for those new to cycling. As riders gain experience and fitness, their average speed can increase to 15-20 mph.
Recreational riders, who cycle regularly but not competitively, typically have an average speed of 15-25 mph. This speed range is suitable for riders who enjoy cycling as a hobby and want to maintain a moderate level of fitness.
Professional cyclists, on the other hand, have average speeds that far exceed those of recreational riders. Elite cyclists can maintain speeds of 25-35 mph or more over long distances, making them some of the fittest athletes in the world.
According to data from the National Bicycle Dealers Association, the average cycling speed for adult cyclists in the United States is around 17.3 mph. This speed is based on data from over 10,000 cyclists and provides a benchmark for riders to compare their own performance.
It’s essential to remember that average cycling speeds can vary greatly depending on factors such as terrain, weather conditions, and bike type. Understanding what constitutes an average cycling speed for your specific type of riding is crucial to setting realistic goals and tracking progress.
Factors That Influence Average Cycling Speed
While understanding what constitutes an average cycling speed is essential, it’s equally important to delve deeper into the factors that affect it. Several factors can influence average cycling speed, including age, fitness level, and bike type.
Age is a significant factor in determining average cycling speed. As riders age, their physical abilities decline, leading to a decrease in speed. According to a study published in the Journal of Aging and Physical Activity, cyclists over the age of 50 experience a significant decline in speed, with average speeds decreasing by up to 2 mph per decade.
Fitness level is another critical factor in determining average cycling speed. Riders with a higher level of fitness tend to have faster average speeds due to their increased cardiovascular endurance and muscular strength. A study published in the Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research found that cyclists who engaged in regular high-intensity interval training had significant improvements in their average speed.
Bike type is also a crucial factor in determining average cycling speed. Road bikes, designed for speed and efficiency, typically allow riders to achieve faster average speeds than mountain bikes or hybrid bikes. This is due to the aerodynamic design and lightweight materials used in road bikes, which reduce air resistance and increase pedaling efficiency.
Other factors, such as terrain and weather conditions, can also impact average cycling speed. Riders who frequently cycle in hilly or mountainous terrain may have slower average speeds due to the increased energy expenditure required to navigate these terrains. Similarly, riders who cycle in windy or rainy conditions may experience slower average speeds due to the increased air resistance and reduced visibility.
Understanding the factors that influence average cycling speed is essential to setting realistic goals and tracking progress. By recognizing the impact of age, fitness level, bike type, and other factors, riders can develop targeted training plans to improve their speed and overall cycling performance.
Improving Your Cycling Speed: Tips and Tricks
Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced cyclist, improving your cycling speed can be a challenging but rewarding goal. With the right training and techniques, you can increase your speed and take your cycling to the next level.
One of the most effective ways to improve your cycling speed is through interval training. This involves alternating between periods of high-intensity cycling and active recovery. For example, you could cycle at maximum effort for 2 minutes, followed by 2 minutes of easy cycling. This type of training helps to improve your anaerobic endurance, allowing you to sustain high speeds for longer periods.
Hill sprints are another effective way to improve your cycling speed. Find a steep hill and cycle up it at maximum effort. This type of training helps to improve your explosive power and acceleration, allowing you to quickly gain speed.
Proper bike maintenance is also essential for improving your cycling speed. A well-maintained bike is more efficient and allows you to cycle faster with less effort. Make sure to regularly clean and lubricate your chain, check your tire pressure, and adjust your brakes and gears.
Many successful cyclists have improved their speed through dedication and hard work. For example, professional cyclist Chris Froome increased his speed by incorporating high-intensity interval training into his regimen. Similarly, amateur cyclist Sarah Hammer improved her speed by focusing on hill sprints and proper bike maintenance.
In addition to these tips and tricks, it’s essential to set realistic goals and track your progress. Use a cycle computer or GPS device to track your speed and distance, and set achievable targets for improvement. With consistent training and dedication, you can improve your cycling speed and take your riding to the next level.
Cycling Speed for Different Types of Riding
When it comes to cycling speed, different types of riding require varying levels of speed and endurance. Understanding the average cycling speeds for different types of riding can help riders set realistic goals and improve their performance.
Road cycling, for example, typically involves high speeds over long distances. Average cycling speeds for road cyclists can range from 15-25 mph (24-40 km/h), with professional riders reaching speeds of up to 30 mph (48 km/h) or more. In contrast, mountain biking often involves slower speeds due to the technical nature of the terrain. Average cycling speeds for mountain bikers can range from 5-15 mph (8-24 km/h), with more experienced riders able to maintain higher speeds.
Commuting, on the other hand, often involves slower speeds due to traffic and urban terrain. Average cycling speeds for commuters can range from 10-15 mph (16-24 km/h), with some riders able to maintain higher speeds depending on the route and traffic conditions.
Other types of riding, such as track cycling and time trialing, require high speeds over short distances. Average cycling speeds for track cyclists can range from 25-35 mph (40-56 km/h), with professional riders reaching speeds of up to 40 mph (64 km/h) or more.
Understanding the average cycling speeds for different types of riding can help riders tailor their training and set realistic goals. By recognizing the unique demands of each type of riding, riders can improve their performance and achieve their goals.
Setting Realistic Cycling Speed Goals
Setting realistic cycling speed goals is crucial for improving performance and staying motivated. To set achievable targets, it’s essential to assess your current fitness level and understand what is average cycling speed for your type of riding.
Start by tracking your current cycling speed using a GPS device, cycle computer, or stopwatch. This will give you a baseline to work from and help you identify areas for improvement. Next, set specific, measurable, and achievable goals for yourself, such as increasing your average speed by 1-2 mph (1.6-3.2 km/h) over a certain distance.
Creating a training plan is also essential for improving cycling speed. This should include a mix of interval training, hill sprints, and endurance rides to help you build speed and endurance. For example, you could aim to do three interval sessions per week, with one longer endurance ride on the weekends.
It’s also important to consider your current fitness level and riding experience when setting goals. If you’re a beginner, it may be more realistic to aim for smaller increases in speed, such as 0.5-1 mph (0.8-1.6 km/h) per month. As you gain more experience and fitness, you can set more ambitious goals.
Additionally, consider breaking down your goals into smaller, manageable chunks. For example, if you want to increase your average speed by 2 mph (3.2 km/h) over a 10-mile (16 km) distance, you could aim to increase your speed by 0.5 mph (0.8 km/h) every two weeks.
By setting realistic cycling speed goals and creating a training plan, you can improve your performance and stay motivated. Remember to focus on your own progress and improvement, rather than comparing yourself to others.
Conclusion: Embracing Your Cycling Speed
In conclusion, understanding cycling speed is crucial for improving performance and achieving your goals. By recognizing the various factors that influence cycling speed, measuring your speed accurately, and setting realistic goals, you can take your riding to the next level.
Remember, what is average cycling speed for one rider may not be the same for another. It’s essential to focus on your own progress and improvement, rather than comparing yourself to others. By doing so, you’ll be able to celebrate your achievements and stay motivated to continue improving.
Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced cyclist, understanding cycling speed can help you optimize your training, improve your performance, and enhance your overall riding experience. So, take the time to assess your current fitness level, set achievable goals, and create a training plan that works for you.
By embracing your cycling speed and focusing on your own progress, you’ll be able to pedal to perfection and achieve your goals. So, get out there and start riding – and remember to always keep an eye on your speed!