How to Get the Most Out of Your Bike Ride
Cycling is a low-impact, high-reward form of exercise that offers numerous benefits for cardiovascular health, muscle strength, and mental well-being. As a popular recreational activity and competitive sport, cycling is an excellent way to improve overall fitness and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. But what makes cycling so effective? The answer lies in the muscles used during cycling. Understanding which muscles are engaged during cycling can help optimize your workout and achieve your fitness goals. When you pedal a bike, you’re not just moving your legs – you’re engaging a complex system of muscles that work together to propel the bike forward. By targeting these muscles, you can improve your cycling performance, increase your endurance, and enhance your overall fitness. So, what muscles does biking exercise? Let’s take a closer look at the benefits of cycling and how understanding the muscles used can help you get the most out of your bike ride.
The Primary Muscle Groups Used in Cycling
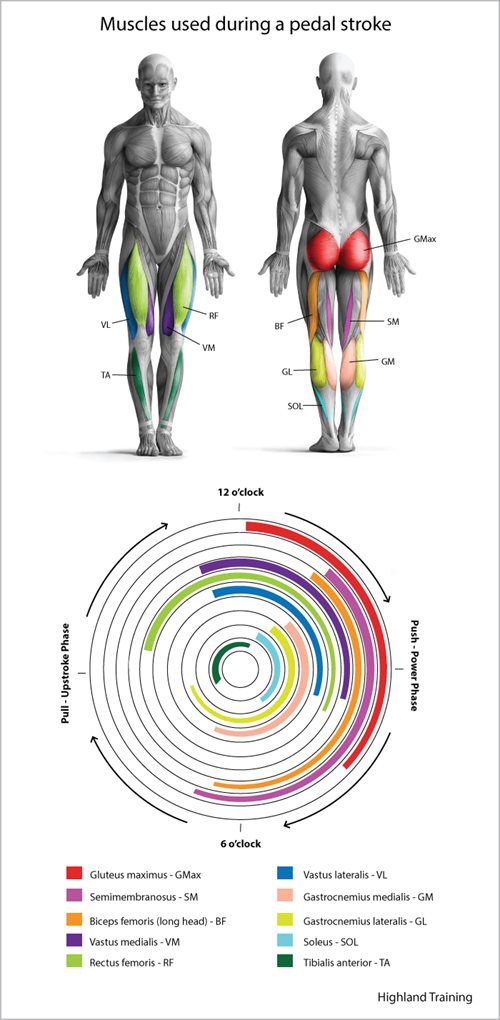
When it comes to cycling, the primary muscle groups used are the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and calf muscles. These muscles work together to propel the bike forward, with the quadriceps and hamstrings being the primary movers. The quadriceps, located on the front of the thigh, are responsible for extending the knee and straightening the leg. The hamstrings, located on the back of the thigh, are responsible for flexing the knee and bending the leg. The glutes, located in the buttocks, help to extend the hip and propel the bike forward. The calf muscles, located in the lower leg, help to flex the foot and push the pedal down. Understanding how these muscles work together can help you optimize your cycling workout and improve your overall performance.
The Role of Secondary Muscle Groups in Cycling
While the primary muscle groups used in cycling, such as the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and calf muscles, are responsible for propelling the bike forward, secondary muscle groups also play a crucial role in maintaining good posture and stability. The core muscles, including the abdominals and lower back muscles, help to stabilize the body and maintain good posture while cycling. The arm muscles, including the biceps and triceps, help to control the handlebars and maintain balance. The back muscles, including the latissimus dorsi and trapezius, help to maintain good posture and stability. These secondary muscle groups work together to help you maintain control and balance while cycling, and are essential for efficient and effective pedaling. Understanding the role of these secondary muscle groups can help you optimize your cycling workout and improve your overall performance.
How Different Types of Cycling Engage Different Muscles
Different types of cycling, such as road cycling, mountain biking, and stationary cycling, engage different muscle groups in unique ways. Road cycling, for example, tends to engage the quadriceps and hamstrings more than other types of cycling, due to the repetitive motion of pedaling on flat terrain. Mountain biking, on the other hand, engages the glutes and calf muscles more, due to the need to navigate rough terrain and maintain balance. Stationary cycling, such as spinning or using a stationary bike, tends to engage the core muscles and arms more, due to the need to maintain stability and control on a fixed bike. Understanding how different types of cycling engage different muscle groups can help you vary your workout and prevent plateaus. By incorporating different types of cycling into your routine, you can target different muscle groups and improve your overall fitness. Additionally, knowing what muscles does biking exercise can help you tailor your workout to your specific goals and needs.
The Benefits of Strengthening Your Cycling Muscles
Strengthening your cycling muscles can have a significant impact on your performance and overall fitness. By targeting the specific muscle groups used in cycling, you can improve your power output, increase your endurance, and reduce your risk of injury. Understanding what muscles does biking exercise can help you tailor your strength training program to your specific needs and goals. For example, strengthening your quadriceps and hamstrings can help you generate more power and speed on the bike, while strengthening your core muscles can help you maintain good posture and stability. Additionally, strengthening your glutes and calf muscles can help you improve your pedaling efficiency and reduce your risk of knee pain and other injuries. By incorporating strength training into your cycling routine, you can take your fitness to the next level and achieve your goals.
How to Incorporate Strength Training into Your Cycling Routine
Incorporating strength training into your cycling routine can be done in a variety of ways. One effective method is to focus on exercises that target the specific muscle groups used in cycling, such as the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and calf muscles. Squats, lunges, and deadlifts are all effective exercises for strengthening the legs and glutes, while leg press and leg curls can target the quadriceps and hamstrings. Additionally, exercises like planks and Russian twists can help strengthen the core muscles, which are essential for maintaining good posture and stability on the bike. When scheduling strength training sessions, it’s best to aim for 2-3 times per week, with at least one day of rest in between. This will allow your muscles to recover and rebuild, making them stronger and more efficient for your next cycling workout. By incorporating strength training into your cycling routine, you can improve your performance, increase your endurance, and reduce your risk of injury.
Common Injuries Associated with Cycling and How to Prevent Them
Cycling is a low-impact activity, but it can still cause injuries, especially if proper precautions are not taken. Two common injuries associated with cycling are knee pain and lower back strain. Knee pain can occur due to overuse or poor pedaling technique, while lower back strain can occur due to poor posture or inadequate core strength. However, these injuries can be prevented by strengthening the muscles used in cycling, including the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and calf muscles. Incorporating exercises such as squats, lunges, and deadlifts into your strength training routine can help strengthen these muscles and reduce the risk of injury. Additionally, incorporating proper warm-up and cool-down routines into your cycling routine can also help prevent injuries. A warm-up routine can include light cardio and dynamic stretching, while a cool-down routine can include static stretching and foam rolling. By taking these precautions, you can reduce the risk of injury and enjoy a safe and effective cycling workout.
Maximizing Your Cycling Workout: Tips and Tricks
To maximize your cycling workout, it’s essential to optimize your bike fit, use proper pedaling technique, and incorporate interval training into your routine. A proper bike fit can help you maintain good posture and reduce the risk of injury, while proper pedaling technique can help you generate more power and efficiency. Interval training can help you improve your cardiovascular fitness and increase your endurance. Additionally, incorporating hill sprints and other high-intensity interval training (HIIT) workouts can help you improve your power output and speed. By incorporating these tips and tricks into your cycling routine, you can take your fitness to the next level and achieve your goals. Remember to always listen to your body and adjust your workout routine accordingly. With consistent practice and dedication, you can unlock the full potential of cycling and achieve a stronger, healthier, and happier you.