The Science Behind Fat Burning and Heart Rate Zones
Cycling is a popular form of exercise that can help individuals achieve their fitness goals, including weight loss and improved cardiovascular health. One effective method for maximizing fat burning during cycling is through heart rate zone training. This approach involves monitoring and adjusting exercise intensity to promote fat oxidation, the process by which the body breaks down fat molecules for energy.
During exercise, the body uses a combination of carbohydrates and fats for energy. The relative contribution of these energy sources depends on several factors, including exercise intensity and duration. At lower intensities, the body primarily uses fat as a fuel source, while at higher intensities, it relies more on carbohydrates. Heart rate zone training takes advantage of this relationship by targeting specific heart rate zones that promote fat burning.
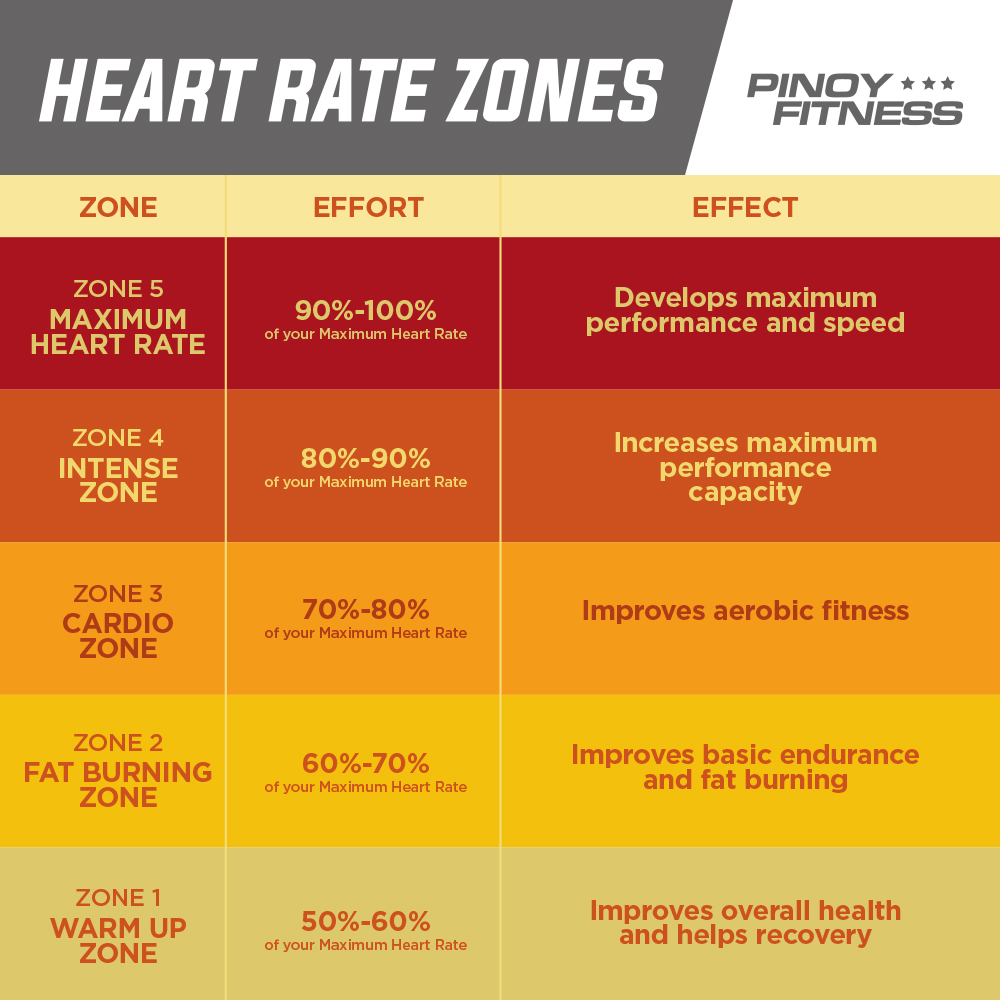
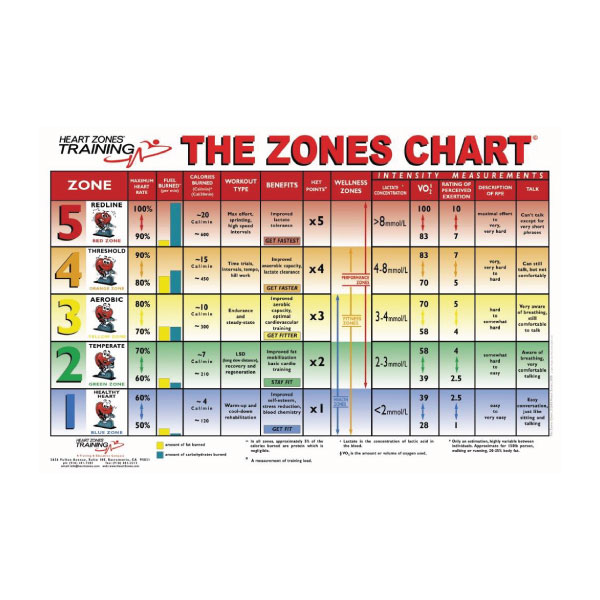
There are five general heart rate zones, each corresponding to a specific intensity level. The fat burning zone typically falls within zones 1 and 2, which correspond to 50-70% of an individual’s maximum heart rate (MHR). Exercising within these zones allows the body to efficiently use fat as a fuel source, promoting weight loss and overall fitness.
It is essential to accurately measure heart rate zones for optimal fat burning. Several tools, such as heart rate monitors and fitness trackers, can help individuals determine their MHR and corresponding heart rate zones. These devices provide real-time feedback on exercise intensity, allowing individuals to adjust their efforts accordingly and stay within their desired heart rate zone.
How to Measure Your Heart Rate Zone for Optimal Fat Burning
To effectively incorporate heart rate zone training into your cycling workouts, it is crucial to accurately measure your heart rate zones. This section outlines the steps and tools necessary for determining your heart rate zones for optimal fat burning.
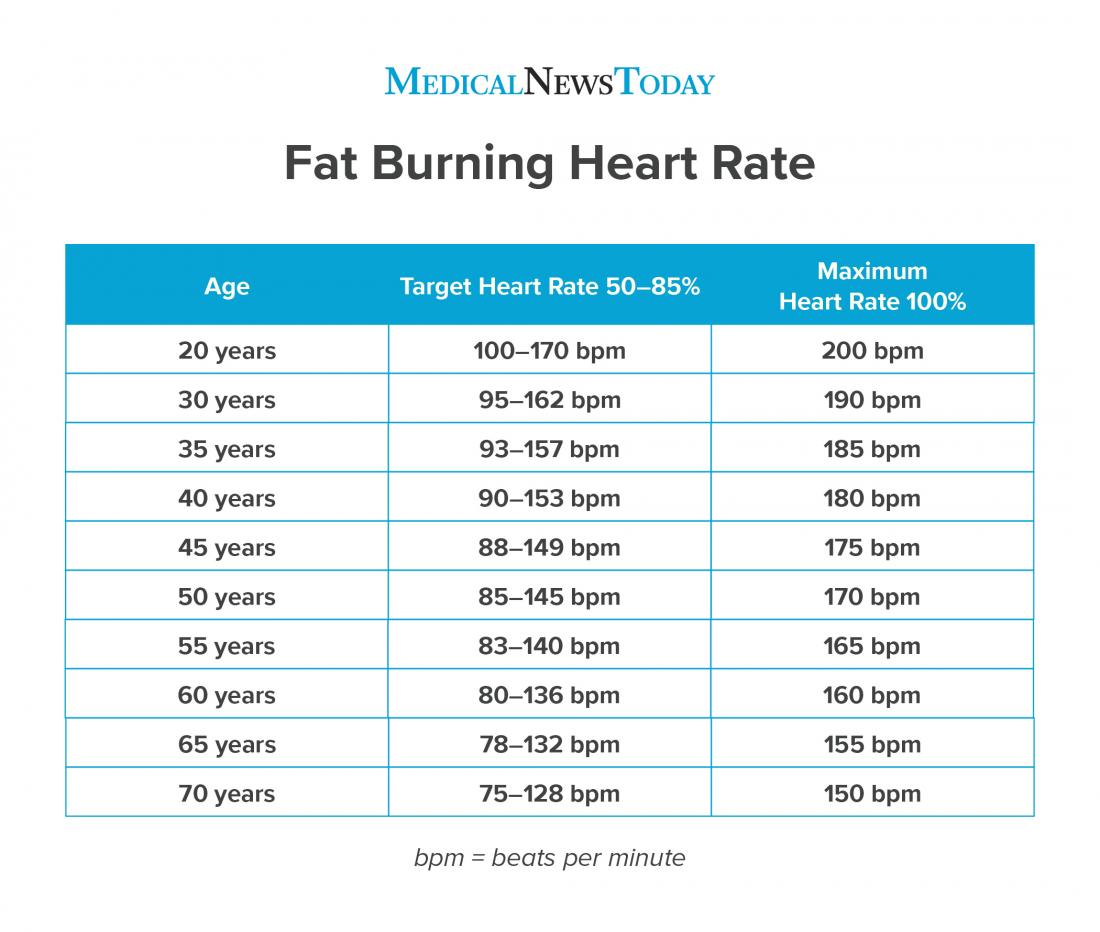
The most common method for measuring heart rate zones involves calculating your maximum heart rate (MHR). The MHR is the highest number of times your heart can beat per minute during intense exercise. While there are several formulas for estimating MHR, the most widely used is the age-based formula: 220 minus your age.
Once you have calculated your MHR, you can determine your heart rate zones using percentages of your MHR. For example, zone 1 (the fat burning zone) typically falls between 50-60% of your MHR, while zone 2 ranges from 60-70% of your MHR. It is essential to note that these ranges may vary slightly depending on the source, so it is essential to consult a reliable fitness resource for accurate information.
Several tools can help you measure your heart rate zones during cycling workouts. Heart rate monitors, either worn as a chest strap or integrated into a smartwatch or fitness tracker, provide real-time feedback on your heart rate. These devices can help ensure that you stay within your desired heart rate zone during your workouts.
Additionally, many cycling apps and indoor cycling bikes offer heart rate zone tracking features. These tools can help you monitor your heart rate throughout your workout and provide valuable insights into your exercise intensity and fat burning potential.
Regardless of the tools you use, it is essential to prioritize accuracy in measuring your heart rate zones. Inaccurate heart rate data can lead to suboptimal workout intensities and hinder your progress towards your fitness goals. By investing in reliable heart rate measurement tools and regularly calibrating them for accuracy, you can ensure that your heart rate zone training is both safe and effective for fat burning.
Incorporating Heart Rate Zone Training into Your Cycling Workouts
Once you have determined your heart rate zones, you can begin incorporating heart rate zone training into your cycling workouts. This section offers practical tips and strategies for effectively integrating this training method into your fitness routine.
First, consider the duration and intensity of your workouts. To maximize fat burning, aim to spend the majority of your workout time in zones 1 and 2 (50-70% of your MHR). These zones correspond to lower-intensity exercise, which allows the body to efficiently use fat as a fuel source. However, it is essential to incorporate higher-intensity intervals to improve overall fitness and promote muscle development. These intervals can be performed in zones 3-5 (70-90% of your MHR) and should be included in your workouts for a well-rounded fitness program.
Next, determine the frequency of your workouts. To see progress in your fat burning goals, aim to cycle at least three times per week. However, be careful not to overtrain, as this can lead to injury and burnout. Ensure that you are allowing adequate recovery time between workouts, particularly if you are incorporating high-intensity intervals or strength training exercises.
Consider incorporating a variety of cycling workouts into your routine to keep your workouts interesting and challenging. For example, try steady-state rides, interval training, hill climbs, and endurance rides. Each type of workout offers unique benefits and can help you achieve your fat burning goals.
Lastly, be consistent with your heart rate zone training. Consistency is key to seeing progress and achieving your fitness goals. By regularly monitoring your heart rate and adjusting your workout intensity accordingly, you can ensure that you are effectively training in your desired heart rate zones and making progress towards your fat burning goals.
Designing a Personalized Cycling Program for Fat Burning
To effectively incorporate heart rate zone training into your cycling workouts, it is essential to create a personalized program that considers your individual fitness level, goals, and preferences. This section offers practical tips and strategies for designing a cycling program that focuses on fat burning through heart rate zone training.
First, assess your current fitness level. Consider factors such as your cardiovascular health, muscular strength, and endurance. This information will help you determine an appropriate starting point for your cycling program and ensure that you are training at a safe and effective intensity.
Next, establish specific and measurable goals for your cycling program. Do you want to lose weight, improve your cardiovascular health, or increase your muscular endurance? Once you have identified your goals, you can design a program that focuses on fat burning through heart rate zone training. For example, if your goal is to lose weight, aim to spend the majority of your workout time in zones 1 and 2 (50-70% of your MHR) to promote fat oxidation.
Consider your personal preferences when designing your cycling program. Do you prefer indoor or outdoor cycling? Do you enjoy steady-state rides or high-intensity interval training? By incorporating activities that you find enjoyable and engaging, you are more likely to maintain motivation and consistency in your workouts.
Lastly, regularly review and adjust your cycling program based on your progress. Use tools such as a heart rate monitor or cycling app to track your heart rate zones, workout duration, and intensity. Based on this data, make adjustments to your program as needed to ensure that you are effectively training in your desired heart rate zones and making progress towards your fat burning goals.
Monitoring Progress and Adjusting Your Cycling Program
To effectively incorporate heart rate zone training into your cycling workouts, it is essential to regularly monitor your progress and adjust your program as needed. This section offers practical tips and strategies for tracking your heart rate zones, workout duration, and intensity, as well as strategies for making adjustments based on your progress.
First, invest in a reliable heart rate monitor or fitness tracker. These tools can provide real-time feedback on your heart rate zones, allowing you to ensure that you are training at the appropriate intensity for fat burning. Additionally, many heart rate monitors and fitness trackers offer features such as GPS tracking, calorie burn estimates, and workout history, which can help you track your progress over time.
Next, consider tracking your workout duration and intensity. Aim to cycle for at least 30 minutes per session, with a focus on spending the majority of your workout time in zones 1 and 2 (50-70% of your MHR) for optimal fat burning. However, it is essential to incorporate higher-intensity intervals to improve overall fitness and promote muscle development. These intervals can be performed in zones 3-5 (70-90% of your MHR) and should be included in your workouts for a well-rounded fitness program.
Regularly review your progress and make adjustments to your cycling program as needed. If you find that you are consistently training in higher heart rate zones, consider adjusting your program to focus more on lower-intensity, longer-duration workouts. Conversely, if you find that you are not challenging yourself enough, consider incorporating higher-intensity intervals or strength training exercises into your workouts.
Lastly, be patient and consistent with your heart rate zone training. Progress may be gradual, but by regularly monitoring your progress and making adjustments as needed, you can ensure that you are effectively training in your desired heart rate zones and making progress towards your fat burning goals.
Combining Cycling with Other Forms of Exercise for Maximum Fat Burning
While cycling is an effective method for enhancing fat oxidation and promoting weight loss, incorporating other forms of exercise into your fitness routine can further maximize your fat burning potential. This section offers practical tips and strategies for combining cycling with other forms of exercise, such as strength training and high-intensity interval training (HIIT), for maximum fat burning.
First, consider incorporating strength training exercises into your fitness routine. Strength training can help build lean muscle mass, which can increase your resting metabolic rate and promote fat burning. Additionally, strength training exercises can help improve overall fitness, balance, and stability, which can enhance your cycling performance.
Next, consider incorporating high-intensity interval training (HIIT) into your fitness routine. HIIT involves short bursts of high-intensity exercise followed by periods of rest or low-intensity exercise. This training method can help improve cardiovascular fitness, increase metabolism, and promote fat burning. Additionally, HIIT workouts can be performed in a variety of ways, making them a versatile and engaging addition to your fitness routine.
When combining cycling with other forms of exercise, it is essential to consider factors such as workout duration, intensity, and frequency. Aim to cycle for at least 30 minutes per session, with a focus on spending the majority of your workout time in zones 1 and 2 (50-70% of your MHR) for optimal fat burning. However, it is essential to incorporate higher-intensity intervals to improve overall fitness and promote muscle development. These intervals can be performed in zones 3-5 (70-90% of your MHR) and should be included in your workouts for a well-rounded fitness program.
Lastly, regularly review and adjust your fitness program based on your progress. Use tools such as a heart rate monitor or fitness tracker to track your heart rate zones, workout duration, and intensity. Based on this data, make adjustments to your program as needed to ensure that you are effectively training in your desired heart rate zones and making progress towards your fat burning goals.
Maintaining Motivation and Consistency in Your Cycling Workouts
Maintaining motivation and consistency in your cycling workouts is essential for achieving your fat burning goals. This section offers practical tips and strategies for staying engaged and committed to your cycling program, even when faced with challenges or setbacks.
First, set realistic and achievable goals for your cycling workouts. Consider factors such as your current fitness level, available time, and desired outcomes. By setting specific and attainable goals, you can help ensure that your workouts are both challenging and rewarding, which can enhance motivation and consistency.
Next, track your progress and celebrate your achievements. Use tools such as a heart rate monitor or fitness tracker to monitor your heart rate zones, workout duration, and intensity. Regularly review this data to track your progress and identify areas for improvement. Celebrate your achievements, no matter how small, to help maintain motivation and consistency in your workouts.
Consider incorporating variety and novelty into your cycling workouts. Try new routes, terrain, or training methods to keep your workouts interesting and engaging. Additionally, consider incorporating other forms of exercise, such as strength training or high-intensity interval training (HIIT), to help challenge your body and promote overall fitness.
Lastly, find ways to make your workouts enjoyable and engaging. Listen to music, podcasts, or audiobooks during your workouts. Consider cycling with a friend or group to help build a sense of community and accountability. By finding ways to enjoy your workouts, you can help maintain motivation and consistency in your cycling program.
Overcoming Common Challenges in Heart Rate Zone Training for Fat Burning
Heart rate zone training for fat burning can be an effective method for enhancing fitness and promoting weight loss. However, like any training method, it can come with its own set of challenges. This section offers practical solutions and strategies for overcoming common challenges in heart rate zone training for fat burning, such as hitting plateaus or experiencing burnout.
First, consider incorporating variety and novelty into your cycling workouts. Try new routes, terrain, or training methods to help challenge your body and promote continued progress. Additionally, consider incorporating other forms of exercise, such as strength training or high-intensity interval training (HIIT), to help promote overall fitness and prevent boredom or burnout.
Next, regularly review and adjust your cycling program based on your progress. Use tools such as a heart rate monitor or fitness tracker to track your heart rate zones, workout duration, and intensity. Based on this data, make adjustments to your program as needed to ensure that you are effectively training in your desired heart rate zones and making progress towards your fat burning goals.
Consider incorporating active recovery days or cross-training activities into your fitness routine. Active recovery days involve light-intensity exercise, such as walking or stretching, which can help promote recovery and prevent burnout. Cross-training activities, such as swimming or yoga, can help promote overall fitness and prevent overuse injuries associated with cycling.
Lastly, prioritize rest and recovery. Ensure that you are getting adequate sleep and allowing your body time to recover between workouts. Listen to your body and take rest days as needed. By prioritizing rest and recovery, you can help prevent burnout and promote continued progress in your heart rate zone training for fat burning.